Журнал «Здоровье ребенка» 3 (54) 2014
Вернуться к номеру
Clinical case. Visceral leishmaniasis
Авторы: Bogadelnikov I.V., Lagunova N.V., Lukyanets L.V., Syurina N.A., Kryuger E.A. - Crimea State Medical University named after S.I. Georgievsky, Department of Pediatrics with the Course of Child''s Infectious Diseases, Simferopol, Ukraine
Рубрики: Педиатрия/Неонатология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
Child Marina T., 9 months., admitted to the Republican hospital with a diagnosis: iron deficiency anemia, severe thrombocytopenia, congenital heart disease?, viral myocarditis?
Complaints on admission: fever up to 38 º C, stuffy nose, fatigue, lethargy, absence of appetite, paleness of skin, increased abdomen, changes in blood tests and urine tests.
Anamnesis of disease. Acutely ill, when the body temperature rose to 39,1 º C, appeared weakness, lethargy. During 7 days there are in the city hospital, the condition has not improved, progressed anemia, fever kept, increasing weakness and lethargy. Transferred for further treatment in the Republican Hospital.
Anamnesis of life. Child of II pregnancy, childbirth II term, without stimulation, Apgar score - 7-8 points, cried at once, attached to the chest in the delivery room, weight - 3500 grams, height - 55 cm, BCG - on the third day, was discharged on the third day. Neonatal period without features. Breastfed up to the present time. Postponed diseases -ARVI in 8 months. Blood and blood products are not transfused..
Data of objective examination: the child's condition severity, due to the severity of anemic and intoxication syndrome, thrombocytopenia.
Clear consciousness, meningeal signs are absent, flaccid, capricious.
Psychomotor development corresponds to age. Correct physique satisfactory supply. The bregmatic fontanel - closed.
Skin - pale, jaundiced, hemorrhagic petechial elements on the face, thighs, in the groin area. Subcutaneous fat layer is developed uniformly. Peripheral lymph nodes were not enlarged, small, unremarkable. Osteomuscular system - without pathology.
Shape of the chest - regular, breathing through the nose difficult, mucous discharge from the nose. Fauces moderately hyperemic.
Percussion - over the light dullness right.
Auscultation - breathing hardmoist single small bubbling rale right.
From the heart - tachycardia up to 140 beats per 1 min., muffled heart sounds, systolic murmur at the apex, at the point of Botkin.
Abdomen increased in volume, soft, painful on palpation, rumbling along the intestine. The liver protruded 3.5 cm beyond the costal margin, the spleen - + 4.0 cm
Urination free enough. Stool - 1-2 times a day, yellow with mucus.
Clinical diagnosis: acute right-segmental pneumonia with cardiorespiratory syndrome, intrauterine infection? Anemia III degree of mixed origin.
The results of laboratory examinations:
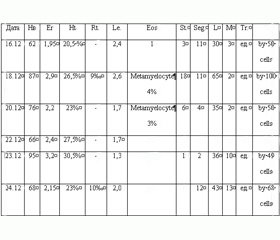
Table 1. The data general analysis of blood
ESR - 3 mm / hr up to 6 mm / hr.
Clotting time - 13 minutes 45 seconds. - 14 minutes 30 seconds.; the duration of bleeding - 0 minutes 30 seconds. from 18.12.
Common urine analysis and coprological study - without features.
Blood cultures for sterility - microflora is not detected.
Blood for HIV - negative.
Coagulogram of 18.12. - the prothrombin index - 69.3; recalcification time - 108.6; fibrinogen A - 1,776; ethanol test - slightly positive.
ALT - 1.6 mmol/ L, AST - 3.06 mmol/L from 18.12.; alkaline phosphatase - 7339 mmmol/l
Bilirubin - 12.8 mmol/l; thymol test - 20.7 units. - from 18.12.2003
Total bilirubin 79.2 mmol/l; direct - 37.4 mmol/l; indirect - 41.8 mmol/l from 23.12.2003
Serum iron - 15.5 mmol/l
Blood on the thick drop - the malaria parasite - is not found.
Serum Potassium - 4.7 mmol/l, sodium - 149 mmol/l, calcium - 2.5 mmol/l.
Urea - 4.2 mmol/l, creatinine - 0.07 mg/l.
Sips-puncture from 17.12.
Blasts -5.5; Metamyelocytes-20; Promyelocytes-1, 5, Young-25; Stab-13; Seg.-4; Eos.-3; Lym.-10; Ph-10; Оx-8.
Punctate moderately rich in cellular elements. 18% are germ cells red. Marked irritation granulocyte germ.
Instrumental examination:
1. Ultrasonography of the abdomen from 17.12. 2003.
Liver - + 30 mm, increased, smooth contours clear, parenchyma grained density normal, vascular drawing saved,
Gall bladder – 45x14 mm thick wall, the bile ducts are not dilated.
Pancreas – 19x10x13 mm (№ - 9,0 ± 3,0 x 7,0 ± 2,0 x 7,0 ± 3,0 mm), the insufficiently distinct contours, smooth, echo texture uniform, echo density unevenly increased.
Spleen - + 85 mm, increased contour clear, echo density is not changed; splenic vienna - not expanded, diameter - 6 mm. Lymph nodes were not enlarged.
2. Computer tomogram of the abdominal organs of 24.12.2003.
Conclusion: The bilateral pleural effusion. Hepatomegaly and splenomegaly. Effusion in the lodge of the spleen. Reduction in the density of the liver (swelling? Hepatosis? Hepatitis?)
Since admitted to the hospital and to death condition of the child remained severe due to the intoxication syndrome. Fever wore periodical exposure character did not decrease under the action of antibiotic treatment. Decreased appetite, expressed lethargy, weakness. Expressed hepato-splenic syndrome and cytopenia (anemia, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, neutropenia), elevated blood transaminase, bilirubin, increased blood clotting time of more than 20 min., in prescribe hemostatic therapy.
The child was examined:
1) Otolaryngology - acute rhinitis.
2) Cardiology - the child has no signs of myocarditis. Given the presence of anemia III degree, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia can think about during the septic process, possibly pneumonia with cardiorespiratory syndrome, intrauterine infection?
3) Hematologist - aggravation is possible intrauterine infection, during sepsis, sided pneumonia, blood disease can not be excluded.
4) oculist - optic disc pale, clear boundaries, veins normal caliber, moderately narrowed artery.
5) Neurologist - the bregmatic fontanel closed. No focal signs. Psychomotor development by age. Conclusion - at the time of inspection of organic disease of the CNS is not revealed.
Treatment: prescribe antibacterial wide spectrum of action therapy, hormone therapy, transfusion of immunoglobulin daily transfusion of FFP, haemostatic therapy, symptomatic therapy.
Epidemiology anamnesis: the child 2 months ago came with his parents from Georgia, where, according to the mother, was subjected to the bites of mosquitoes. First heard the diagnosis "leishmaniasis." Recommended for diagnostic purposes Sips-puncture.
In the bone marrow punctate - determined depletion of cellular elements. In a smear detected cells resembling Leishmania.
However, the condition does not improve, maintain pancytopenia, liver and spleen size increased progressively and the baby was transferred to the intensive care unit, the 24.12.03.
In 18 hours, 35 minutes there was a stop breathing and blood circulation; reanimation measures for 45 minutes without success, and in 19 hours 25 minutes pronounced biological death.
Conclusion: leishmaniasis, acute form, visceral form, severe course.
Complication: multiorgan failure, pancytopenia, intracranial hemorrhage, cerebral edema, polyserositis.
Pathological diagnosis: ICD B 55.0
I. Visceral leishmaniasis (23.12.03. - in bone marrow punctate - Leishmania).
II. Cerebral edema. Pulmonary edema. Hepatosplenomegaly. Hepatic steatosis. Hemorrhagic syndrome: bleeding from the injection sites, focal hemorrhages in the spleen, mesenteric lymph nodes, myocardium. Venous congestion and parenchymatous degeneration of internal organs. Accident transformation thymus IV degree.
Conclusion. As you know, diagnosis is based on the life anamnesis and anamnesis of history of the disease, as well as epidemiological anamnesis. Also discusses the general and local manifestations of the disease are taken into account the diverse and numerous results of laboratory and instrumental investigations.
Undoubtedly, the most important in the diagnosis - clinic. But, the common symptoms of the disease, especially infectious, are nonspecific: fever, lethargy, weakness, weakness, absence of interest to others, bad appetite, pale skin, etc. and do not contain (with a few exceptions: typhoid fever, tuberculosis, tetanus and others) are no specific manifestations.
Local clinical manifestations of the disease can be erased, inconclusive, but sometimes they are specific (pathognomonic: measles, scarlet fever, diphtheria, meningococcal disease). But, unfortunately, they are observed in some diseases. Other clinical manifestations of the disease, most often observed in severe forms, such as hepatomegaly, splenomegaly, generalized lymphadenopathy, hypersensitivity, etc., are also found in children with a wide range of diseases.
Trying to establish a connection of a symptom with a possible pathogen (bacterial, viral or mixed etiology), it usually takes time.
Prescription of syndromic treatment is carried out (preservation of vital functions) that occurs on a background of desintoxication therapy. Such treatment assignment is supported, usually an antibiotic or broad-spectrum antibiotics, immunoglobulins, hormones, protease inhibitors, etc.
However, many infectious diseases require treatment (diphtheria, HIV / AIDS, botulism, leishmaniasis, tetanus, herpes infections, etc.).
In this clinical case was poorly assembled epidemiological anamnesis (fact families with a child moving from Georgia, where he had been bitten by mosquitoes (as we know, Georgia is included in the endemic regions leishmaniasis and mosquitoes are carriers of the infection).
The child's death occurred on the day of diagnosis.
And the last. It should be remembered that leishmaniasis refers to AIDS opportunistic infections (indicator, marker). Its development, directly or indirectly, may indicate not only on existing immunodeficiency, but also a manifestation of changes in current epidemiological processes in nature.
1. Супотницкий М.В. Эволюционная патология. К вопросу о месте ВИЧ-инфекции и ВИЧ/СПИД-пандемии среди других инфекционных, эпидемических и пандемических процессов: монография / М.: М.В.Супотницкий – М.: Вузовская книга, 2009. – 400 с.

/157/45.jpg)