Журнал «Здоровье ребенка» Том 16, №5, 2021
Вернуться к номеру
Регуляція вмісту мікроРНК. Частина 2. Деградація мікроРНК
Авторы: Абатуров О.Є., Бабич В.Л.
Дніпровський державний медичний університет, м. Дніпро, Україна
Рубрики: Педиатрия/Неонатология
Разделы: Справочник специалиста
Версия для печати
У науковому огляді наведено процес регуляції вмісту мікроРНК — деградація мікроРНК. Для написання статті здійснювався пошук інформації з використанням баз даних Scopus, Web of Science, MedLine, PubMed, Google Scholar, EMBASE, Global Health, The Cochrane Library, CyberLeninka. У статті надана характеристика найважливішого процесу метаболізму РНК — деградації 3'→5' РНК. Деградація мікроРНК притаманна організмам всіх царств життя і бере участь у регуляції представництва РНК, усуненні дисфункціональних або неправильно сконструйованих молекул РНК і процесингу попередників РНК. Наведені екзорибонуклеази, що впливають на стабільність зрілих форм мікроРНК. Підкреслено, що екзорибонуклеази XRN деградують різноманітні РНК-субстрати під час загального розпаду РНК і беруть участь у таких спеціалізованих процесах, як нонсенс-опосередкована деградація, сайленсинг генів, матурація рРНК і термінація транскрипції. Наведено, що екзорибонуклеаза XRN2 відіграє вирішальну роль у термінації транскрипції під час вірусної інфекції, а саме проявляє цитоплазматичну противірусну активність щодо вірусу гепатиту С. Розглянута роль РНК-деградуючої екзосоми в деградації мікроРНК. РНК-деградуюча екзосома є убіквітарним комплексом і 3'-5'-ендо- та екзорибонуклеаз еукаріотів, що взаємодіє з декількома кофакторами процесингу та здійснює деградацію практично всіх класів цитоплазматичних РНК. У статті відображено функцію еволюційно-консервативної фосфоролітичної 3'-5'-екзорибонуклеази — полінуклеотидфосфорилази. Показана роль екзорибонуклеази 1, яка є еволюційно консервативною 3'-5'-екзорибонуклеазою родини DEDDh, що бере участь у кінцевому процесингу 5.8S рРНК, реплікаційно-залежних гістонових мРНК, міРНК і мікроРНК. Зазначено, що екзорибонуклеаза Eri1 регулює глобальний гомеостаз мікроРНК у лімфоцитах і бере участь у розвитку NK-клітин і противірусній відповіді. Таким чином, одним із механізмів регуляції вмісту мікроРНК є найважливіший процес метаболізму РНК, притаманний організмам всіх царств життя, а саме деградація мікроРНК.
The scientific review presents the process of regulation of microRNA content — microRNA degradation. To write the article, information was searched using databases Scopus, Web of Science, MedLine, PubMed, Google Scholar, EMBASE, Global Health, The Cochrane Library, CyberLeninka. The article presents the characteristics of the most important process of RNA metabolism — degradation of 3'→5' RNA. Degradation of microRNA is inherent in organisms of all kingdoms of life and is involved in the regulation of RNA representation, elimination of dysfunctional or incorrectly constructed RNA molecules and processing of RNA precursors. Exoribonucleases that affect the stability of mature forms of miRNA are presented. It is emphasized that XRN exoribonucleases degrade various RNA substrates during total RNA degradation and are involved in specific processes such as nonsense-mediated degradation, gene silencing, rRNA maturation, and transcription termination. It is shown that exoribonuclease XRN2 plays a crucial role in the termination of transcription during viral infection, namely it has cytoplasmic antiviral activity against hepatitis C virus. The role of RNA-degrading exosome in microRNA degradation is presented. RNA-degrading exosome is a ubiquitous complex and 3'-5'-endo- and exoribonucleases of eukaryotes, which interacts with several processing cofactors and degrades almost all classes of cytoplasmic RNA. The article reflects the function of evolutionarily conserved phosphorolytic 3'-5'-exoribonuclease — polynucleotide phosphorylase. The role of exoribonuclease 1, which is an evolutionarily conserved 3'-5'-exoribonuclease of the DEDDh family, is involved in the final processing of 5.8S rRNA, replication-dependent histone mRNA, siRNA, and miRNA. Eri1 exoribonuclease has been shown to regulate global microRNA homeostasis in lymphocytes and to participate in NK cell development and antiviral response. Thus, one of the mechanisms of regulation of miRNA content is the most important process of RNA metabolism, which is inherent in organisms of all kingdoms of life, namely the degradation of miRNAs.
мікроРНК; деградація мікроРНК; екзорибонуклеази; РНК-деградуюча екзосома; полінуклеотидфосфорилаза; огляд
microRNA; microRNA degradation; exoribonucleases; RNA-degrading exosome; polynucleotide phosphorylase; review
Вступ
5'-3'-екзорибонуклеази XRN
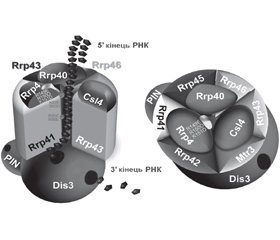
3'-5'-екзорибонуклеази
Висновки
- Bail S., Swerdel M., Liu H. et al Differential regulation of microRNA stability. RNA. 2010 May. 16(5). 1032-9. doi: 10.1261/rna.1851510.
- Black J.J., Johnson A.W. Genetics animates structure: leveraging genetic interactions to study the dynamics of ribosome biogenesis. Current Genetics. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-021-01187-y
- Cai Y., Yu X., Hu S., Yu J. A brief review on the mechanisms of miRNA regulation. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2009 Dec. 7(4). 147-54. doi: 10.1016/S1672-0229(08)60044-3.
- Chang J.H., Xiang S., Tong L. 5'-3' exoribonucleases. In: Nicholson A.W., editor. Ribonucleases. Springer; Heidelberg, 2011. Vol. 26. Р. 167-192.
- Chatterjee S., Grosshans H. Active turnover modulates mature microRNA activity in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 2009 Sep 24. 461(7263). 546-9. doi: 10.1038/nature08349.
- Cheng Y., Patel D.J. Crystallographic structure of the nuclease domain of 3'hExo, a DEDDh family member, bound to rAMP. J. Mol. Biol. 2004 Oct 15. 343(2). 305-12. Doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2004.08.055.
- Das S.K., Sokhi U.K., Bhutia S.K. et al Human polynucleotide phosphorylase selectively and preferentially degrades microRNA-221 in human melanoma cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci U S A. 2010 Jun 29. 107(26). 11948-53. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0914143107.
- Delan-Forino C., Schneider C., Tollervey D. Transcriptome-wide analysis of alternative routes for RNA substrates into the exosome complex. PLoS Genet. 2017 Mar 29. 13(3). e1006699. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006699.
- Drazkowska K., Tomecki R., Stodus K. et al The RNA exosome complex central channel controls both exonuclease and endonuclease Dis3 activities in vivo and in vitro/ K. Drazkowska. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Apr 1. 41(6). 3845-58. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt060.
- Evguenieva-Hackenberg E., Hou L., Glaeser S., Klug G. Structure and function of the archaeal exosome. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2014 Sep-Oct. 5(5). 623-35. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1234.
- Evguenieva-Hackenberg E. The archaeal exosome. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2011. 702. 29-38. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4419-7841-7_3.
- Frazier M.N., Pillon M.C., Kocaman S. et al. Structural overview of macromolecular machines involved in ribosome biogenesis. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2020. 67. 51-60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbi.2020.09.003.
- Frederick M., Heinemann I. Regulation of RNA stability at the 3′ end. Biological Chemistry. 2021. 402(4). 425-431. https://doi.org/10.1515/hsz-2020-0325.
- Grosshans H., Chatterjee S. MicroRNAses and the regulated degradation of mature animal miRNAs. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2010. 700. 140-55. PMID: 21627036.
- Hui Jiang, Lige Bai, Lina Ji et al. Degradation of MicroRNA miR-466d-3p by Japanese Encephalitis Virus NS3 Facilitates Viral Replication and Interleukin-1β Expression. Journal of Virology. 2020 Jul. 94 (15). e00294-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00294-20.
- Januszyk K., Lima C.D. The eukaryotic RNA exosome. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2014 Feb. 24. 132-40. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2014.01.011.
- Kilchert C. RNA Exosomes and Their Cofactors. The Eukaryotic RNA Exosome. Methods in Molecular Biology. 2020. 2062. 215-235. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-9822-7_11
- Koyano K., Bahn J.H., Xiao X. Extracellular microRNA 3’ end modification across diverse body fluids. Epigenetics. 2020. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2020.1834922.
- Łabno A., Tomecki R., Dziembowski A. Cytoplasmic RNA decay pathways — Enzymes and mechanisms. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Dec. 1863(12). 3125-3147. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2016.09.023.
- Lau B., Cheng J., Flemming D. et al. Structure of the maturing 90S pre-ribosome in association with the RNA exosome. Mol. Cell. 2021;81:293-303.e4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2020.11.009.
- Liu X., Haniff H.S., Childs-Disney J.L., Shuster A., Aikawa H., Adibekian A., Disney M.D. Targeted Degradation of the Oncogenic MicroRNA 17-92 Cluster by Structure-Targeting Ligands. Journal of the American Chemical Society. 2020. 142(15). 6970-6982. doi: 10.1021/jacs.9b13159.
- Machlin E.S., Sarnow P., Sagan S.M. Masking the 5' terminal nucleotides of the hepatitis C virus genome by an unconventional microRNA-target RNA complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci U S A. 2011 Feb 22. 108(8). 3193-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1012464108.
- Miki T.S., Großhans H. The multifunctional RNase XRN2. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2013 Aug. 41(4). 825-30. doi: 10.1042/BST20130001.
- Morton D.J., Kuiper E.G., Jones S.K. et al The RNA exosome and RNA exosome-linked disease. RNA. 2018 Feb. 24(2). 127-142. doi: 10.1261/rna.064626.117.
- Nagarajan V.K., Jones C.I., Newbury S.F., Green P.J. XRN 5'→3' exoribonucleases: structure, mechanisms and functions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2013 Jun-Jul. 1829(6–7). 590-603. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2013.03.005.
- Nejad C., Pillman K.A., Siddle K.J. et al. miR-222 isoforms are differentially regulated by type-I interferon. RNA. 2018 Mar. 24(3). 332-341. doi: 10.1261/rna.064550.117.
- Porrua O., Libri D. RNA quality control in the nucleus: the Angels’ share of RNA. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2013 Jun-Jul. 1829(6–7). 604-11. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2013.02.012.
- Proudfoot N.J. Ending the message: poly(A) signals then and now. Genes. Dev. 2011 Sep 1. 25(17). 1770-82. doi: 10.1101/gad.17268411.
- Sarkar D., Fisher P.B. Polynucleotide phosphorylase: an evolutionary conserved gene with an expanding repertoire of functions. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006 Oct. 112(1). 243-63. PMID: 16733069.
- Sedano C.D., Sarnow P. Hepatitis C virus subverts liver-specific miR-122 to protect the viral genome from exoribonuclease Xrn2. Cell. Host. Microbe. 2014 Aug 13. 16(2). 257-264. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2014.07.006.
- Sedano C.D., Sarnow P. Interaction of host cell microRNAs with the HCV RNA genome during infection of liver cells. Semin. Liver. Dis. 2015 Feb. 35(1). 75-80. doi: 10.1055/s-0034-1397351.
- Sikorska N., Zuber H., Gobert A. RNA degradation by the plant RNA exosome involves both phosphorolytic and hydrolytic activities. Nat. Commun. 2017 Dec 18. 8(1). 2162. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-02066-2.
- Sokhi U.K., Bacolod M.D., Dasgupta S. et al Identification of genes potentially regulated by human polynucleotide phosphorylase (hPNPase old-35) using melanoma as a model. PLoS One. 2013 Oct 15. 8(10). e76284. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076284.
- Thomas M.F., Abdul-Wajid S., Panduro M. et al Eri1 regulates microRNA homeostasis and mouse lymphocyte development and antiviral function. Blood. 2012 Jul 5. 120(1). 130-42. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-11-394072.
- Thomas M.F., L’Etoile N.D., Ansel K.M. Eri1: a conserved enzyme at the crossroads of multiple RNA-processing pathways. Trends. Genet. 2014 Jul. 30(7). 298-307. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2014.05.003.
- Towler B.P., Jones C.I., Viegas S.C. et al The 3'-5' exoribonuclease Dis3 regulates the expression of specific microRNAs in Drosophila wing imaginal discs. RNA Biol. 2015. 12(7). 728-41. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2015.1040978.
- Zangari J., Ilie M., Rouaud F. et al Rapid decay of engulfed extracellular miRNA by XRN1 exonuclease promotes transient epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nucleic. Acids. Res. 2017 Apr 20. 45(7). 4131-4141. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw1284.
- Zhao S., Liu M.F. Mechanisms of microRNA-mediated gene regulation. Sci. China Life Sci. 2009 Dec. 52(12). 1111-6. doi: 10.1007/s11427-009-0152-y.

/85.jpg)
/86.jpg)
/87.jpg)
/88.jpg)