Архив офтальмологии Украины Том 10, №1, 2022
Вернуться к номеру
Оцінка клінічної ефективності ендоскопічної ендоназальної дакріоцисториностомії та особливості післяопераційного періоду у хворих на хронічний дакріоцистит та цукровий діабет 2-го типу
Авторы: Бездітко П.А. (1), Безега Н.М. (2)
(1) — Харківський національний медичний університет, м. Харків, Україна
(2) — Полтавський державний медичний університет, м. Полтава, Україна
Рубрики: Офтальмология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
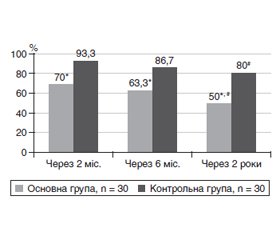
Мета роботи: оцінити ефективність ендоскопічної ендоназальної дакріоцисториностомії (ЕЕД) та визначити особливості післяопераційного періоду у хворих на хронічний дакріоцистит залежно від наявності цукрового діабету 2-го типу (ЦД2). Матеріали та методи. У дослідження включили 30 хворих на хронічний дакріоцистит та ЦД2 (основна група) та 30 хворих на хронічний дакріоцистит без ЦД (контрольна група), яким була проведена ЕЕД за стандартною методикою. Компенсований ЦД2 (НbА1с < 7,1 %) був виявлений у 6 хворих основної групи, субкомпенсований (НbА1с 7,1–7,5 %) — у 7 хворих, декомпенсований (НbА1с > 7,5 %) — у 17 хворих. Вік хворих основної групи в середньому становив 66,5 ± 9,5 року, контрольної групи — 66,3 ± 11,1 року. Результати операції оцінювали через 2 місяці, 6 місяців та через 2 роки. ЕЕД вважали ефективним методом лікування за відновлення вільного пасивного сльозовідведення при промиванні слізних шляхів, зникнення сльозотечі у хворого та відсутності повторного інфікування слізного мішка. Крім стандартних, методи офтальмологічного дослідження включали слізно-носову, сльозовсмоктуючу пробу та пробу рефлюксу, промивання сльозовідвідних шляхів, зондування слізних канальців, комп’ютерну томографію, ендоскопічне дослідження порожнини носа. Результати. Ефективність ЕЕД через 2 місяці після операції у хворих основної групи (70,0 ± 8,4 % хворих) була у 1,3 раза, через 6 місяців (63,3 ± 8,8 % хворих) — у 1,4 раза, а у віддалений період, через 2 роки (50,0 ± 9,1 % хворих), — у 1,6 раза нижчою, ніж у хворих контрольної групи (р < 0,05). Аналізуючи наявність основних симптомів хронічного дакріоциститу в динаміці спостереження, відзначили, що після проведення ЕЕД найчастішим симптомом була сльозотеча, проте частота її у хворих основної групи через 2 місяці (30, ± 8,4 % хворих) була у 4,5 раза, через 6 місяців (36,7 ± 8,8 % хворих) — у 2,8 раза, через 2 роки (50,0 ± 9,1 % хворих) — у 2,5 раза вищою, ніж у хворих контрольної групи (р < 0,05). Висновки. У хворих на ЦД2 клінічна ефективність ЕЕД при хронічному дакріоциститі нижча, ніж у хворих без ЦД, а післяопераційний період має свої особливості.
Background. The study was aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of endoscopic endonasal dacryocystorhinostomy (EED) and to determine the postoperative features in patients with chronic dacryocystitis depending on the presence of type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM2). Materials and methods. The study included 30 DM2 patients with chronic dacryocystitis (basic group) and 30 nondiabetic patients with chronic dacryocystitis (control group), who underwent EED by the standard methods. Compensated DM2 (HbA1c < 7.1 %) was found in 6 patients of the basic group, subcompensated (HbA1c 7.1–7.5 %) — in 7 patients, decompensated (HbA1c > 7.5 %) — in 17 patients. The average age of patients in the basic group was 66.5 ± 9.5 years, in the control group — 66.3 ± 11.1 years. The results of the operation were evaluated after 2, 6 months, and 2 years. EED was considered as an effective method of treatment in case of the restoration of free passive lacrimation during lavage of the lacrimal ducts, the disappearance of tearing in the patient and the absence of re-infection of the lacrimal sac. In addition to standard, ophthalmic examination methods included nasolacrimal duct probe, lacrimal absorption, and reflux test, lacrimal duct lavage, lacrimal duct probing, computed tomography, and endoscopic examination of the nasal cavity. Results. The efficiency of EED 2 months after surgery in patients of the basic group (70.0 ± 8.4 % of patients) was 1.3 times lower, after 6 months (63.3 ± 8.8 % of patients) — 1.4 times lower, and in recovery period for 2 years (50.0 ± 9.1 % of patients) — 1.6 times lower than in patients of the control group (p < 0.05). The analysis of the presence of the main symptoms of chronic dacryocystitis in the dynamics of observation demonstrated that after EED the most common symptom was tearing, but its frequency in patients of the basic group was higher by 4.5 times after 2 months (30.0 ± 8.4 % of patients), by 2.8 times — after 6 months (36.7 ± 8.8 % of patients), and 2.5 times — after 2 years (50.0 ± 9.1 % of patients) compared to patients of the control group (p < 0.05). Conclusions. In DM2 patients, the clinical effectiveness of EED in chronic dacryocystitis is lower than in nondiabetic patients, and the postoperative period has its own characteristics.
цукровий діабет 2-го типу; хронічний дакріоцистит; ефективність ендоскопічної ендоназальної дакріоцисториностомії; особливості післяопераційного періоду; сльозотеча
type 2 diabetes mellitus; chronic dacryocystitis; effectiveness of endoscopic endonasal dicryocystorhinostomy; postoperative features; lacrimation
Вступ
Матеріали та методи
Результати та обговорення
/6.jpg)
Висновки
- Rabina G., Golan S., Neudorfer M., Leibovitch I. External Dacryocystorhinostomy: Characteristics and Surgical Outcomes in Patients with and without Previous Dacryocystitis. J. Ophthalmol. 2013. 2013. 287524. doi: 10.1155/2013/287524.
- Sung J.Y., Lee Y.H., Kim K.N., Kang T.S., Lee S.B. Surgical outcomes of endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy: analysis of age effect. Sci Rep. 2019 Dec 27. 9(1). 19861. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-56491-y.
- Keren S., Abergel A., Manor A., Rosenblatt A., Koenigstein D., Leibovitch I., Ben Cnaan R. Endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy: reasons for failure. Eye (Lond). 2020 May. 34(5). 948-53. doi: 10.1038/s41433-019-0612-y.
- Белдовская Н.Ю., Карпищенко С.А., Куликова О.А., Баранская С.В. К вопросу о неудачных исходах лазерной эндоназальной дакриоцисториностомии. Офтальмологические ведомости. 2016. 9(2). 14-8. doi: 10.17816/OV9214-18.
- Kraiem A., Abdessalem R., Christov T., Ben Romdhane B., Kamoun M. La dacryocysto-rhinostomie chez le diabétique [Dacryocystorhinostomy in diabetics]. Tunis Med. 1986 Oct. 64(10). 873-6. (French).
- Goel R., Garg S., Nagpal S., Kumar S., Kamal S. Naso-cutaneous fistula following transcanalicular laser dacrocystorhinostomy. Saudi J. Ophthalmol. 2014 Jan. 28(1). 69-71. doi: 10.1016/j.sjopt.2013.11.006.
- Школьник С.Ф. Хирургическое лечение хронического дакриоцистита на основе применения радиоволновой энергии [диссертация]. Чебоксары: Чебоксарский филиал Федеративного государственного учреждения «Межотраслевой научно-технический комплекс «Микрохирургия глаза» им. акад. С.Н. Федорова Федерального агентства по высокотехнологической медицинской помощи», 2009. 138 с.
- Smirnov G. Outcome of Endonasal Endoscopic Dacryocystorhinostomy in Adults. Publications of the University of Eastern Finland. Dissertations in Health Sciences. 2010. 83 p.
- Allen K., Berlin A.J. Dacryocystorhinostomy failure: association with nasolacrimal silicone intubation. Ophthalmic Surg. 1989 Jul. 20(7). 486-9.
- Ben Simon G.J., Joseph J., Lee S., Schwarcz R.M., McCann J.D., Goldberg R.A. External versus endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy for acquired nasolacrimal duct obstruction in a tertiary referral center. Ophthalmology. 2005 Aug. 112(8). 1463-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2005.03.015.
- Yigit O., Samancioglu M., Taskin U., Ceylan S., Eltutar K., Yener M. External and endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy in chronic dacryocystitis: comparison of results. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2007 Aug. 264(8). 879-85. doi: 10.1007/s00405-007-0286-0.
- Leong S.C., Karkos P.D., Burgess P., Halliwell M., Hampal S. A comparison of outcomes between nonlaser endoscopic endonasal and external dacryocystorhinostomy: single-center experience and a review of British trends. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2010 Jan-Feb. 31(1). 32-7. doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2008.09.012.
- Tsai S., Clemente-Casares X., Revelo X.S., Winer S., Winer D.A. Are obesity-related insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes autoimmune diseases? Diabetes. 2015 Jun. 64(6). 1886-97. doi: 10.2337/db14-1488.
- Velloso L.A., Eizirik D.L., Cnop M. Type 2 diabetes mellitus — an autoimmune disease? Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2013 Dec. 9(12). 750-5. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2013.131.
- Zhong J., Gong Q., Mima A. Inflammatory Regulation in Diabetes and Metabolic Dysfunction. J. Diabetes Res. 2017. 2017. 5165268. doi: 10.1155/2017/5165268.

/7.jpg)