Архив офтальмологии Украины Том 11, №1, 2023
Вернуться к номеру
Вміст аргінази-1 у хворих на проліферативну діабетичну ретинопатію з різною тривалістю цукрового діабету залежно від генотипу CYP2E1
Авторы: Ганюк В.М.
Національний університет охорони здоров’я України імені П.Л. Шупика, м. Київ, Україна
Рубрики: Офтальмология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
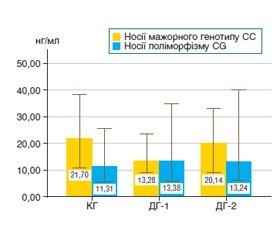
Актуальність. Аргіназа-1 — фермент, що експресується в ендотелії і може сприяти накопиченню оксидантів і виникненню судинної дисфункції. Ген CYP2E1 (rs2070676) кодує фермент, який бере участь у метаболізмі ліків, інактивації N-нітрозамінів, поліциклічних вуглеводів та інших низькомолекулярних сполук. Мета: вивчити вміст аргінази-1 у сироватці крові хворих на проліферативну діабетичну ретинопатію (ПДР) з різною тривалістю цукрового діабету 2-го типу (ЦД2) залежно від генотипу CYP2E1 як можливого чинника розвитку ендотеліальної дисфункції. Матеріали та методи. До обстеження були залучені 106 пацієнтів офтальмологічної клініки з встановленим діагнозом ПДР із тривалістю ЦД2 до і понад 20 років (групи ДГ-1 і ДГ-2 відповідно). Контрольну групу (КГ) становили 43 добровольці без діабету, порівнянні за віком і статтю з пацієнтами груп ДГ-1 і ДГ-2. Поліморфізм гена визначали за допомогою полімеразної ланцюгової реакції RealTime на ампліфікаторі Gene Amp® PCR System 7500. Вміст аргінази-1 визначали в сироватці крові методом ELISA (набір Human Arginase, Hycult Biotech). Порівнювали дані за критерієм Крускала — Уолліса в статистичній програмі SPSS 23. Результати. У групі ДГ-1 вміст аргінази-1 становив 12,66 ± 11,81 нг/мл, у групі ДГ-2 — 17,57 ± 12,97 нг/мл, що вірогідно не відрізнялося від значень КГ — 14,80 ± 14,31 нг/мл. У групі помірної ПДР вміст протеїну був в 1,7 раза вище, ніж у КГ, і становив 24,02 ± 13,16 нг/мл. У групі тяжкої ПДР — 10,70 ± 7,24 нг/мл, спостерігали зменшення у 2,4 раза порівняно з групою з помірною ПДР (р < 0,05). У пацієнтів із прогресуючою ПДР вміст аргінази-1 становив 13,24 ± 11,93 нг/мл. У носіїв мажорного генотипу (СС) гена CYP2E1 різниця була менш значною, і вміст аргінази-1 при поглибленні стадії ПДР із помірної до тяжкої зменшувався в 2 рази. У носіїв поліморфного варіанта гена вміст аргінази-1 у КГ був більше ніж в 2,6 раза (р < 0,05), при поглибленні стадії ПДР із помірної до тяжкої зменшувався в 3,5 раза (р < 0,05) і на стадії прогресуючої ПДР був вище в 1,8 раза (р < 0,05) порівняно з тяжкою ПДР. Висновки. На стадії помірної ПДР відбувається критичний вплив надекспресії аргінази, що є шкідливим для ендотеліальних клітин. Носії поліморфного варіанта CYP2E1, зокрема алелі G, були однаково поширені в популяції (14–17 %), але мали підвищену схильність до експресії аргінази-1 при розвитку ПДР. Це дані підтверджують уявлення про вплив оксидативно-нітрозативного стресу як базового механізму в патогенезі ендотеліальної дисфункції і виникненні мікросудинних аномалій.
Background. Arginase-1 is an enzyme that is expressed in the endothelium and can contribute to the accumulation of oxidants and the occurrence of vascular dysfunction. The CYP2E1 gene (rs2070676) encodes an enzyme involved in drug metabolism, inactivation of N-nitrosamines, polycyclic carbohydrates, and other low-molecular-weight compounds. The purpose of the work is to study the content of arginase-1 in the blood serum of patients with proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR) with different duration of type 2 diabetes depending on the CYP2E1 genotype as a possible factor for the development of endothelial dysfunction. Materials and methods. One hundred and six patients of the ophthalmology clinic with a diagnosis of PDR and type 2 diabetes duration of up to and over 20 years (groups G-1 and G-2) were involved in the study. The control group (CG) consisted of 43 volunteers without diabetes who were comparable in terms of age and gender to the patients from groups G-1 and G-2. Gene polymorphism was determined using real-time polymerase chain reaction on the GeneAmp® PCR System 7500 amplifier. The content of arginase-1 in the blood serum was evaluated by the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (Human Arginase kit, Hycult Biotech). Data were compared using the Kruskal-Wallis test in the SPSS 23 statistical program. Results. In the G-1 group, the level of arginase-1 was 12.66 ± 11.81 ng/ml, in the G-2 group, 17.57 ± 12.97 ng/ml, which was not significantly different from the CG values of 14.80 ± 14.31 ng/ml. In the group with moderate PDR, the protein content was 1.7 times higher than in the CG and was 24.02 ± 13.16 ng/ml. In the group of severe PDR, protein level was 10.70 ± 7.24 ng/ml, a 2.4-fold decrease was observed compared to the group with moderate PDR (p < 0.05). In patients with progressing PDR, the content was 13.24 ± 11.93 ng/ml. In carriers of the major (CC) genotype of the CYP2E1 gene, the difference was less significant, and the content of arginase-1 at the stage of PDR progression from moderate to severe decreased by 2 times. Among carriers of the polymorphic variant of the gene, the content of arginase-1 in the CG was more than 2.6 times higher (p < 0.05), at the stage of aggravation from moderate PDR to severe, it decreased by 3.5 times (p < 0.05) and at the advanced PDR stage, it was 1.8 times higher (p < 0.05) in comparison with severe PDR. Conclusions. At the stage of moderate PDR, there is a critical effect of arginase overexpression, which is harmful to endothelial cells. Carriers of the CYP2E1 polymorphic variant, in particular the G allele, were equally common in the population (14–17 %) but had an increased tendency to express arginase-1 in PDR development. These data confirm the idea about the effect of oxidative-nitrosative stress as a basic mechanism in the pathogenesis of endothelial dysfunction and the occurrence of microvascular abnormalities.
діабетична ретинопатія; цукровий діабет 2-го типу; генотип; аргіназа-1
diabetic retinopathy; type 2 diabetes; genotype; arginase-1
Для ознакомления с полным содержанием статьи необходимо оформить подписку на журнал.
- Visaria J., Iver N.N., Raval A., Kong S., Hobbs T., Bou–chard J., Kern D.M., Willey V. Incidence and prevalence of microvascular and macrovascular diseases and all-cause mortality in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A 10-year study in a US commercially insured and Medicare Advantage population. Clin. Ther. 2019. 41. 1522-1536. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2019.05.012.
- Wang S., Fang F., Jin W.B., Wang X., Zheng D.W. Assessment of serum arginase 1, as a type 2 diabetes mellitus diagnosis biomarker in patients. Exp. Ther. Med. 2014. 8. 585-590. doi: 10.3892/etm.2014.1768.
- Romero M.I., Platt D.H., Tawfik H.E., Labazi M., Remessy A.B., Bartoli M., Caldwell R., Caldwell R.W. Diabetes-induced coronary vascular dysfunction involves increased arginase activity. Circ. Res. 2008. 102. 95-102. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.107.155028.
- Buraczynska M., Zakrocka I. Arginase Gene Polymorphism Increases Risk of Diabetic Retinopathy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2021 Nov 19. 10(22). 5407. doi: 10.3390/jcm10225407. PMID: 34830689; PMCID: PMC8620112.
- Elms S.C., Togue H.A., Rajas M., Xu Z., Caldwell R.W., Caldwell R.B. The role of arginase 1 in diabetes-induced retinal vascular dysfunction in mouse and rat models of diabetes. Diabetologia. 2013. 56. 654-662. doi: 10.1007/s00125-012-2789-5.
- Narayanan S.P., Rojas M., Suwanpradid J., Toque H.A., Caldwell W., Caldwell R.B. Arginase in retinopathy. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2013. 36. 260-280. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2013.06.002.
- Zhang L., Tang J., Wang Y., Wang X., Wang F. Association of CYP7A1 and CYP2E1 Polymorphisms with Type 2 Diabetes in the Chinese Han Populations. Pharmgenomics Pers. Med. 2022. 15. 843-855.
- Arinç E., Arslan S., Bozcaarmutlu A., Adali O. Effects of diabetes on rabbit kidney and lung CYP2E1 and CYP2B4 expression and drug metabolism and potentiation of carcinogenic activity of N-nitrosodimethylamine in kidney and lung. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2007 Jan. 45(1). 107-18. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2006.07.026. Epub 2006 Aug 30. PMID: 17034923.
- Wang Z., Hall S.D., Maya J.F. et al. Diabetes mellitus increases the in vivo activity of cytochrome P450 2E1 in humans. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2003. 55(1). 77-85. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2125.2003.01731.x https://doi.org/10.2147/PGPM.S367806.
- Ming X.F., Rajapakse A.G., Yepuri G. et al. Arginase II promotes macrophage inflammatory responses through mitochondrial reactive oxygen species, contributing to insulin resistance and atherogenesis. Journal of the American Heart Association. 2012. 1(4). doi: 10.1161/JAHA.112.000992.
- Adebayo A.A., Oboh G., Ademosun A.O. Effect of dietary inclusion of almond fruit on sexual behavior, arginase activity, pro-inflammatory, and oxidative stress markers in diabetic male rats. Journal of Food Biochemistr. 2021. 45(3). doi: 10.1111/jfbc.13269.
- Ren Y., Li Z., Li W., Fan X., Han F., Huang Y., Yu Y., Qian L., Xiong Y. Arginase: Biological and Therapeutic Implications in Diabetes Mellitus and Its Complications. Oxid Med. Cell. Longev. 2022 Oct 26. 2022. 2419412. doi: 10.1155/2022/2419412. PMID: 36338341; PMCID: PMC9629921.
- Zhou Z., Mahdi A., Tratsiakovich Y. et al. Erythrocytes from patients with type 2 diabetes induce endothelial dysfunction via arginase I. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 2018. 72(7). 769-780. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2018.05.052.