Журнал «Здоровье ребенка» Том 18, №4, 2023
Вернуться к номеру
Роль мікроРНК у розвитку холангіопатій. Частина 1
Авторы: Абатуров О.Є., Бабич В.Л.
Дніпровський державний медичний університет, м. Дніпро, Україна
Рубрики: Педиатрия/Неонатология
Разделы: Справочник специалиста
Версия для печати
У науковому огляді висвітлено роль мікроРНК у розвитку холангіопатій. У цій статті розглянуто роль мікроРНК при первинному склерозуючому холангіті та первинному біліарному холангіті. Для написання статті здійснювався пошук інформації з використанням баз даних Scopus, Web of Science, MedLine, PubMed, Google Scholar, Embase, Global Health, The Cochrane Library. Автори показують, що при захворюваннях гепатобіліарної системи, а саме холангіопатіях, мікроРНК впливають на регулювання проліферації гепатоцитів, холангіоцитів і клітинний цикл, процеси запалення, фіброз, хеморезистентність і виживання клітин. Дослідниками визначено, що у хворих із первинним склерозуючим холангітом спостерігаються вірогідно підвищені рівні miR-26a, miR-30b, miR-126, miR-122, miR-194, miR-1281 у сироватці крові і miR- 412, miR-640, miR-1537 і miR-3189 у жовчі відносно здорових людей. Відомо, що кількість диференціально експресованих мікроРНК у хворих з первинним біліарним холангітом сягає 97, з них найбільш діагностично значимою є miR-139-5p. Науковці відзначають, що підвищена експресія miR-139-5p у гепатоцитах корелює з підвищеною продукцією TNF-α і репресією транскрипції гена c-FOS. Висвітлено, що дослідники запропонували альтернативну гіпотезу мікроРНК-опосередкованої індукції запальної реакції жовчних проток при первинному біліарному холангіті. Подана гіпотеза, що в основі функціонування мережі мікроРНК-мРНК при первинному біліарному холангіті лежить активність генерації miR-106b-5p, miR-20a-5p, і miR-93-5p, які виконують у ній ключові регуляторні функції. Отже, дані сучасних досліджень свідчать, що холангіопатії супроводжуються зміною спектра продукції різних мікроРНК, які регулюють активацію запалення, регенерацію, проліферацію, апоптоз гепатоцитів, холангіоцитів. Зниження або підвищення рівня експресії деяких мікроРНК є критичним у патологічних процесах при первинному склерозуючому холангіті та первинному біліарному холангіті, однак мікроРНК можуть бути не тільки маркерами, але й мішенню цих процесів.
The role of miRNA in the development of cholangiopathies is given in the scientific review. This article discusses the role of miRNA in primary sclerosing cholangitis and primary biliary cholangitis. To write the article, information was searched using Scopus, Web of Science, MedLine, PubMed, Google Scholar, Embase, Global Health, The Cochrane Library databases. The authors state that in hepatobiliary diseases, namely cholangiopathies, micro-RNAs affect the regulation of hepatocyte, cholangiocyte proliferation, cell cycle, inflammatory processes, fibrosis, chemoresistance and cell survival. Researchers have determined that patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis have significantly increased levels of miR-26a, miR-30b, miR-126, miR-122, miR-194, miR-1281 in blood serum and miR-412, miR-640, miR-1537 and miR-3189 in the bile of relatively healthy individuals. It is known that the number of differentially expressed miRNAs in patients with primary biliary cholangitis reaches 97, of which the most diagnostically significant is miR-139-5p. Scientists note that increased miR-139-5p expression in hepatocytes correlates with increased production of TNF-α and repression of c-FOS gene transcription. It is stated that the researchers proposed an alternative hypothesis of miRNA-mediated induction of the inflammatory reaction of the bile ducts in primary biliary cholangitis. The hypothesis is presented that the activity of the generation of miR-106b-5p, miR-20a-5p, and miR-93-5p, which perform key regulatory functions in it, is the basis of the functioning of the miRNA-mRNA network in primary biliary cholangitis. Thus, the data of modern research indicate that cholangiopathies are accompanied by a change in the spectrum of production of various micro-RNAs that regulate the activation of inflammation, regeneration, proliferation, apoptosis of hepatocytes and cholangiocytes. A decrease or increase in the level of some micro-RNA expression is critical in the pathological processes that occur in primary sclerosing cholangitis and primary biliary cholangitis, but micro-RNAs can be not only markers, but also targets of these processes.
мікроРНК; холангіопатії; холангіоцити; первинний склерозуючий холангіт; первинний біліарний холангіт; огляд
microRNA; miRNA; miR; cholangiopathy; cholangiocytes; primary sclerosing cholangitis; primary biliary cholangitis; review
Для ознакомления с полным содержанием статьи необходимо оформить подписку на журнал.
- Абатуров О.Є., Бабич В.Л. Роль мікро-РНК при захворюваннях біліарної системи. Здоров’я дитини. 2017. 7(12). 155-161. DOI: 10.22141/2224-0551.12.7.2017.116191.
- Абатуров О.Є., Бабич В.Л. Світ мікроРНК гепатобіліарної системи. Здоров’я дитини. 2021. 1(16). 122-131. DOI: 10.22141/2224-0551.16.1.2021.226462.
- Banales J.M., Prieto J., Medina J.F. Cholangiocyte anion exchange and biliary bicarbonate excretion. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006. 12. 3496-511. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i22.3496.
- Bernuzzi F., Marabita F., Lleo A. et al. Serum microRNAs as no–vel biomarkers for primary sclerosing cholangitis and cholangiocarcinoma. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2016 Jul. 185(1). 61-71. doi: 10.1111/cei.12776.
- de Liso F., Matinato C., Ronchi M., Maiavacca R. The diagnostic accuracy of biomarkers for diagnosis of primary biliary cholangitis (PBC) in anti-mitochondrial antibody (AMA)-negative PBC patients: a review of literature. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2017 Nov 27. 56(1). 25-31. doi: 10.1515/cclm-2017-0249.
- Dyson J.K., Beuers U., Jones D.E.J. Primary sclerosing cholangitis. Lancet. 2018 Feb 13. pii: S0140-6736(18)30300-3. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)30300-3.
- Erice O., Munoz-Garrido P., Vaquero J., Perugorria M.J., Fernandez-Barrena M.G., Saez E., Santos-Laso A., Arbelaiz A., Jimenez-Agüero R. MicroRNA-506 promotes primary biliary cholangitis-like features in cholangiocytes and immune activation. Hepatology. 2018. 67(4). 1420-40. doi: 10.1002/hep.29533.
- Esparza-Baquer A., Labiano I., Bujanda L., Perugorria M.J., Banales J.M. MicroRNAs in cholangiopathies: Potential diagnostic and therapeutic tools. Clinics and Research in Hepatology and Gastroentero–logy. 2016. 40(1). 15-27. doi: 10.1016/j.clinre.2015.10.001.
- Goldschmidt I., Thum T., Baumann U. Circulating miR-21 and miR-29a as Markers of Disease Severity and Etiology in Cholestatic Pediatric Liver Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2016 Mar. 5(3). 28. doi: 10.3390/jcm5030028.
- Isayama H., Tazuma S., Kokudo N. et al. Clinical guidelines for primary sclerosing cholangitis 2017. PSC guideline committee Members: Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (Japan) Research Project, The Intractable Hepatobiliary Disease Study Group. J. Gastroenterol. 2018 Jun 27. doi: 10.1007/s00535-018-1484-9.
- Katsumi T., Ninomiya M., Nishina T., Ueno Y. MiR-139-5p is associated with inflammatory regulation through c-FOS suppression, and contributes to the progression of primary biliary cholangitis. Laboratory Investigation. 2016. 96(11). DOI: 10.1038/labinvest.2016.95.
- Liang D.Y., Hou Y.Q., Luo L.J., Ao L. Altered expression of miR-92a correlates with Th17 cell frequency in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016 Jul. 38(1). 131-8. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2016.2610.
- Lindor K.D., Gershwin M.E., Poupon R. et al. Primary biliary cirrhosis. Hepatology. 2009 Jul. 50(1). 291-308. doi: 10.1002/hep.22906.
- Liu J., Xiao Y., Wu X.K., Jiang L.C., Yang S.R., Ding Z.M. et al. A circulating microRNA signature as noninvasive diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. BMC Genomics. 2018. 19. 188. doi: 10.1186/s12864-018-4575-3
- Marzioni M., Saccomanno S., Candelaresi C., Rychlicki C., Agostinelli L., Trozzi L., De Minicis S., Benedetti A. Clinical implications of novel aspects of biliary pathophysiology. Dig. Liver Dis. 2010. 42. 238-44. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2010.01.005.
- Munoz-Garrido P., de Barrena M.G.-F., Hijona E., Carracedo M., Marín J.J.G., Bujanda L., Banales J.M. MicroRNAs in biliary diseases. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012 Nov 21. 18(43). 6189-96. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i43.6189.
- Ninomiya M., Kondo Y., Funayama R. et al. Distinct microRNAs expression profile in primary biliary cirrhosis and evaluation of miR 505-3p and miR197-3p as novel biomarkers. PLoS One. 2013 Jun 12. 8(6). e66086. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0066086.
- O’Brien J., Hayder H., Zayed Y., Peng C. Overview of –MicroRNA biogenesis, mechanisms of actions, and circulation. Front. Endocrinol. 2018. 9. 402. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2018.00402.
- Padgett K.A., Lan R.Y., Leung P.C. et al. Primary biliary cirrhosis is associated with altered hepatic microRNA expression. J. Autoimmun. 2009 May-Jun. 32(3–4). 246-53. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2009.02.022.
- Panella M., Carotenuto P., Braconi C. MicroRNAs link inflammation and primary biliary cholangitis. Non-coding RNA Investig. 2018. 2. 29. doi: 10.21037/ncri.2018.05.02.
- Puik J.R., Meijer L.L., Le Large T.Y. еt al. Circulating biliary tract microRNA signature discriminates cholangiocarcinoma from pancreatic cancer [abstract]. In: Proceedings of the American Association for Cancer Research Annual Meeting. 2018. 2018 Apr 14–18. Chicago, IL. Philadelphia (PA): AACR; Cancer Res., 2018. 78 (13 Suppl.). Abstract nr 493. DOI: 10.1158/1538-7445.AM2018-493.
- Qin B., Huang F., Liang Y. et al. Analysis of altered microRNA expression profiles in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with primary biliary cirrhosis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013 Mar. 28(3). 543-50. doi: 10.1111/jgh.12040.
- Rodríguez-Ortigosa C.M., Banales J.M., Olivas I., Uriarte I., Marín J.J., Corrales F.J., Medina J.F., Prieto J. Biliary secretion of S-nitrosoglutathione is involved in the hypercholeresis induced by ursodeoxycholic acid in the normal rat. Hepatology. 2010. 52. 667-77. doi: 10.1002/hep.23709.
- Tan Y., Pan T., Ye Y. et al. Serum microRNAs as potential biomarkers of primary biliary cirrhosis. PLoS One. 2014 Oct 27. 9(10). e111424. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0111424.
- Tomiyama T., Yang G.X., Zhao M. et al. The modulation of co-stimulatory molecules by circulating exosomes in primary biliary cirrhosis. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2017 Mar. 14(3). 276-284. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2015.86.
- Voigtländer T., Gupta S.K., Thum S. et al. MicroRNAs in Serum and Bile of Patients with Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis and/or Cholangiocarcinoma. PLoS One. 2015 Oct 2. 10(10). e0139305. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0139305.
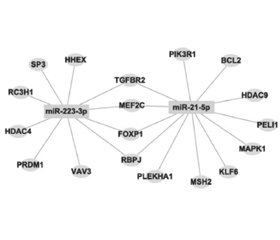
- Wang X., Wen X., Zhou J., Qi Y., Wu R., Wang Y. et al. MicroRNA-223 and microRNA-21 in peripheral blood B cells associated with progression of primary biliary cholangitis patients. PLoS One. 2017. 12(9). e0184292. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0184292.
- Wasik U., Kempinska-Podhorodecka A., Bogdanos D.P. et al. Enhanced expression of miR-21 and miR-150 is a feature of anti-mitochondrial antibody-negative primary biliary cholangitis. Mol. Med. 2020. 26(8). https://doi.org/10.1186/s10020-019-0130-1.