Журнал «Практическая онкология» Том 6, №2, 2023
Вернуться к номеру
Аналіз плазмового рівня міРНК-497 у крові хворих на рак молочної залози
Авторы: Гаращенко О.О.
Інститут експериментальної патології, онкології та радіобіології імені Р.Є. Кавецького НАН України,
м. Київ, Україна
Рубрики: Онкология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
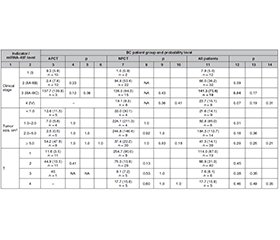
Актуальність. Рак молочної залози (РМЗ) є гетерогенним захворюванням з варіабельним клінічним перебігом, морфологічними й молекулярно-біологічними особливостями. Упродовж моніторингу клінічного перебігу патологічного процесу у хворих на РМЗ дослідники поставили завдання виявити можливий взаємозв’язок між клінічними проявами захворювання і рівнем експресії міРНК-497. Кореляція рівнів міРНК-497 з вираженістю клінічної симптоматики й біологічними субтипами пухлини може бути застосована для прогнозування клінічного перебігу хвороби, зокрема безрецидивної виживаності хворих на РМЗ. Матеріали та методи. Дослідили зв’язок рівня міРНК-497 у плазмі крові хворих на РМЗ з клініко-патологічними особливостями захворювання жінок двох груп: до 45 років і старше від 45 років. Результати. Встановлено вірогідно вищі рівні міРНК-497 у плазмі крові хворих у пременопаузальному віці порівняно з менопаузою, тоді як у здорових жінок відзначено протилежну тенденцію. Не виявлено залежності між рівнем міРНК-497 і розміром пухлин і стадією раку (Grade), але відзначено слабку позитивну кореляцію між рівнем міРНК-497 і стадією N0-N3, виражену тенденцію до зростання показника на стадії N3, яка в групі хворих після ад’ювантної поліхіміотерапії була вірогідною. Рівень міРНК-497 після першого й повторного курсу неоад’ювантної поліхіміотерапії не мав статистично значущої різниці. Не виявлено різниці показника між молекулярними субтипами РМЗ, а деяка різниця між хворими з HER2+ і тричі негативним раком не була переконливою з причини невеликої вибірки таких пацієнтів. Також не виявлено зв’язку між проаналізованим рівнем міРНК-497 і віддаленими результатами, а отримані позитивні найближчі результати потребують додаткових досліджень. Висновки. Аналіз рівня міРНК-497 може бути корисним при стадіюванні РМЗ. На думку авторів статті, доцільність продовження досліджень у цьому напрямі полягає перш за все в накопиченні масиву даних про рівні міРНК-497 в плазмі крові у хворих на РМЗ з метою виявлення взаємозв’язку експресії цього маркера з клінічним перебігом і прогнозом захворювання.
Background. Breast cancer is a heterogeneous disease with a variable clinical course, morphological and clinical features. When monitoring the clinical course of the pathological process, the researchers set the task of identifying a possible relationship between the clinical manifestations of the disease and the level of miRNA-497 expression. The correlation of miRNA-497 levels with the severity of clinical symptoms and biological subtypes of the tumor can be used to predict the clinical course of the disease, in particular, the relapse-free survival. Materials and methods. The relationship between the level of miRNA-497 in the blood plasma of patients with breast cancer and the clinical and pathological features of the disease in women of two groups (< 45 and ≥ 45 years) was studied. Results. It was found that miRNA-497 levels were significantly higher in the plasma of premenopausal compared to menopausal women, while the opposite is true for healthy women. We did not find a link between miRNA-497 and tumor size and clinical stage, though a weak positive correlation between miRNA-497 levels and the N0-N3 stage was noted, with a pronounced increase at the N3 stage, which was reliable in the group of patients after adjuvant polychemotherapy. MiRNA-497 levels after the first and second courses of non-adjuvant polychemotherapy did not differ statistically significantly. There was no correlation between miRNA-497 concentration and the molecular subtype of breast cancer, and the difference between patients with HER2+ and the triple-negative type was not convincing due to the small sample size. Also, no connection was found between the analyzed miRNA-497 levels and follow-up results, and positive initial results require additional research and analysis. Conclusions. Analysis of miRNA-497 levels can be useful in the study of the molecular type and stage of breast cancer. Prospects for further research are analyzing this indicator in a larger sample of breast cancer patients, obtaining remote results, and comparison with other types of miRNA
міРНК-497; рак молочної залози; плазма крові; хіміотерапія; результати лікування
miRNA-497; breast cancer; blood plasma; chemotherapy; treatment results