Журнал «Здоровье ребенка» Том 19, №2, 2024
Вернуться к номеру
Роль фенотипових факторів у прогнозі ефективності хіміопрофілактики у дітей
Авторы: Бодня К.І., Зосімов А.М., Рогожин А.В., Асоян І.М., Кондратюк В.В.
Харківський національний медичний університет, м. Харків, Україна
Рубрики: Педиатрия/Неонатология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
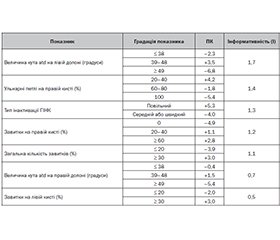
Актуальність. Мета — вивчити прогностичну значущість деяких фенотипових факторів щодо ефективності хіміопрофілактики туберкульозу у дітей на сучасному етапі. Матеріали та методи. Для вивчення ролі фенотипових факторів у прогнозі ефективності хіміопрофілактики туберкульозу проведено аналіз показників дерматогліфіки, статі та фенотипу інактивації гідразиду ізонікотинової кислоти (ГІНК) у 76 дітей з віражем туберкулінових реакцій, яким проводився 3-місячний курс хіміопрофілактики ізоніазидом. Дерматогліфіка пальців рук і долонь визначалася за стандартною методикою [5]. Як критерій ефективності хіміопрофілактики використовувалася динаміка чутливості шкіри до туберкуліну ППД-Л за пробою Манту з 2 ТО. Згідно з ефективністю хіміопрофілактики обстежуваних розподілили на дві групи: першу становили діти (52 особи), у яких розміри папули після закінчення курсу зменшилися на 4 мм і більше (ефективна хіміопрофілактика), а другу — 24 дитини, у яких чутливість шкіри до туберкуліну наростала чи залишалася на тому самому рівні або знизилась за величиною папули на 3 мм і менше (неефективна хіміопрофілактика). Результати. Проведений статистичний аналіз встановив суттєву різницю між групами (р < 0,05) щодо 7 показників. Визначення їх прогностичної інформативності дозволило скласти рейтинг прогностичної значущості фенотипових ознак, а саме: величина кута atd на лівій долоні (J = 1,7), число ульнарних петель на правій кисті (J = 1,4), тип інактивації ГІНК (J = 1,3), кількість завитків на правій кисті (J = 1,2), загальна кількість завитків (J = 1,1), величина кута аtd на правій долоні (J = 0,7), число завитків на лівій кисті (J = 0,5). Проведений кореляційний аналіз між показниками дерматогліфіки і типом інактивації ГІНК показав, що між ними існують вірогідні зв’язки (р < 0,05), але їх кількість суттєво відрізняється в групах. У групі з неефективною хіміопрофілактикою кількість кореляцій (n = 13) більше ніж у 6 разів перевищила таку альтернативної групи (n = 2), що свідчить про значні структурні фенотипові відмінності в групах. Висновки. Між типом інактивації ГІНК і показникими дерматогліфіки виявлені суттєві кореляції, але у дітей з неефективною хіміопрофілактикою таких зв’язків у 6 разів більше, ніж в альтернативній групі. Це свідчить про те, що більш виражена інтеграція дерматогліфічних генів і здатність нейтралізувати ГІНК є в цілому сприятливим моментом, але негативним щодо ефективності профілактики туберкульозу.
Background. The purpose was to study the prognostic role of some phenotypic factors in the effectiveness of tuberculosis chemoprophylaxis in children at present stage. Materials and methods. To study the role of phenotypic factors in predicting the effectiveness of tuberculosis chemoprophylaxis, an analysis was performed of dermatoglyphic indicators, gender, and the inactivation phenotype of isonicotinic acid hydrazide (IAH) in 76 children with tuberculin skin test conversion who underwent a 3-month course of preventive therapy with isoniazid. Dermatoglyphics of fingers and palms was determined according to the standard method [5]. The dynamics of skin sensitivity to tuberculin PPD-L according to the Mantoux test with 2 tuberculin units was used as a criterion for the effectiveness of chemoprophylaxis. According to the latter, the examinees were divided into two groups: the first one consisted of 52 children in whom the size of a wheal decreased by 4 mm or more after the end of a course (effective chemoprevention); the second one included 24 patients in whom skin sensitivity to tuberculin increased or remained at the previous level or decreased by a wheal size for 3 mm or less (ineffective chemoprevention). Results. The conducted statistical analysis revealed a significant difference in 7 indicators between the groups (p < 0.05). Determination of their prognostic informativeness made it possible to rank the prognostic significance of phenotypic signs, namely: the size of the atd angle on the left palm (J = 1.7), the number of ulnar loops on the right hand (J = 1.4), the type of IAH inactivation (J = 1.3), the number of whorls on the right hand (J = 1.2), the total number of whorls (J = 1.1), the atd angle on the right palm (J = 0.7), the number of whorls on the left hand (J = 0.5). The correlation analysis between the dermatoglyphic indicators and the type of IAH inactivation showed that there are reliable connections between them (p < 0.05), but their number differs significantly in groups. In patients with ineffective chemoprophylaxis, the number of correlations (n = 13) exceeded that of the alternative group (n = 2) by more than 6 times, which indicates significant structural phenotypic differences. Conclusions. There were significant correlations between the type of IAH inactivation and dermatoglyphic indicators, but the number of such connections was 6 times higher in children with ineffective chemoprophylaxis than in the alternative group. This indicates that a more pronounced integration of dermatoglyphic genes and the ability to neutralize IAH is a favorable moment in general, but negative in relation to the effectiveness of tuberculosis prevention.
ефективність профілактики туберкульозу ізоніазидом; діти; фенотипові ознаки; прогноз
effectiveness of tuberculosis prevention with isoniazid; children; phenotypic signs; prognosis