Архив офтальмологии Украины Том 12, №2, 2024
Вернуться к номеру
Системний профіль прозапальних і протизапальних цитокінів та його зміни у пацієнтів з катарактою після оперативного лікування
Авторы: Гребень Н.К., Скрипниченко І.Д., Тихончук Н.А., Царик В.В.
Національний медичний університет імені О.О. Богомольця, м. Київ, Україна
Рубрики: Офтальмология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
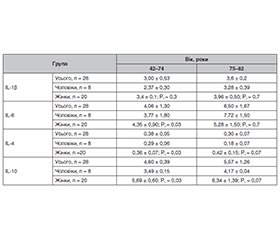
Актуальність. Унаслідок значної поширеності та захворюваності катаракта є актуальною медико-соціальною проблемою. Останніми роками у патогенезі очних захворювань значна увага приділяється імунному запаленню, зокрема імунній регуляції дистрофічних процесів. Імунологічні порушення відіграють важливу роль у розвитку очних захворювань, пов’язаних із віком (катаракта, дистрофії рогівки, глаукома, вікова макулярна дегенерація). Вплив прозапальних і протизапальних цитокінів на розвиток вікової катаракти залишається до кінця не вивченим, як і роль цих цитокінів у прогнозуванні перебігу післяопераційного періоду після екстракції вікової катаракти, що й зумовлює актуальність проведеного дослідження. Мета: оцінити стан цитокінового профілю у пацієнтів із віковою катарактою шляхом визначення вмісту прозапальних (IL-1β, IL-6) і протизапальних (IL-4, IL-10) інтерлейкінів у сироватці крові до та після хірургічного лікування катаракти. Матеріали та методи. Проведено вивчення рівня прозапальних (IL-1β, IL-6) і протизапальних цитокінів (IL-4, IL-10) до та після хірургічного лікування у 28 пацієнтів із віковою катарактою (56 очей) віком від 42 до 82 років, з них чоловіків 8, жінок 20. Середній вік пацієнтів становив 71,79 ± 1,9 року. Вміст цитокінів у сироватці крові визначали методом твердофазного імуноферментного аналізу (ІФА) за допомогою тест-систем «ВЕКТОР-БЕСТ Україна». Результати. Перевищення референсних значень рівнів IL-1β і IL-6 у сироватці крові у пацієнтів із віковою катарактою до хірургічного лікування не відзначалося. Аналіз вмісту прозапального інтерлейкіну IL-6 у сироватці крові цих пацієнтів залежно від статі виявив вірогідне збільшення його рівня в 1,3 раза у чоловіків і вірогідне зниження його рівня в 1,1 раза у жінок порівняно з його середнім показником (р < 0,06 і р < 0,01 відповідно). Рівень протизапальних інтерлейкінів IL-4 та IL-10 у сироватці крові обстежуваних пацієнтів був у межах референсних значень. Під час вивчення вмісту прозапальних та протизапальних інтерлейкінів у сироватці крові залежно від статі та віку у пацієнтів із віковою катарактою віком від 75 років відзначалося статистично значуще підвищення вмісту IL-6 і IL-10. У цій віковій групі рівень IL-6 був у 1,4 раза вищим у чоловіків порівняно з жінками, а рівень IL-10 був у 1,8 раза вищим у жінок порівняно з чоловіками. У пацієнтів з віковою катарактою після хірургічного лікування рівні прозапальних інтерлейкінів IL-1β, IL-6 та протизапальних інтерлейкінів IL-4, IL-10 у сироватці крові були вищими порівняно з їх рівнями до операції. Найвищими рівні інтерлейкінів IL-1β, IL-6 були у сироватці крові пацієнтів з післяопераційним набряком рогівки. Рівень інтерлейкіну IL-6 у сироватці крові пацієнтів з післяопераційним набряком рогівки був вищим за рівень інтерлейкіну IL-1β. Рівні інтерлейкінів IL-4, IL-10 були вищими у пацієнтів з післяопераційним набряком рогівки, рівень інтерлейкіну IL-10 у цих пацієнтів превалював над рівнем інтерлейкіну IL-4. Висновки. У пацієнтів із віковою катарактою рівень прозапальних і протизапальних цитокінів у сироватці крові відповідає референсним значенням і не має вірогідних відмінностей із контрольною групою пацієнтів. Однак визначення цитокінового профілю у пацієнтів із віковою катарактою виявило порушення системного імунологічного статусу залежно від віку та статі. Згідно з нашими результатами, у пацієнтів з віковою катарактою старших за 75 років відзначалося вірогідне підвищення в сироватці крові рівня прозапального цитокіну IL-6 і протизапального цитокіну IL-10. У цій віковій групі рівень IL-6 був вищим у чоловіків, а рівень IL-10 був вищим у жінок. Також нами відзначено відсутність вірогідних відмінностей у вмісті IL-1β, що може свідчити про більш специфічне значення рівнів IL-6 для розвитку катаракти. У пацієнтів з віковою катарактою після хірургічного лікування рівні прозапальних IL-1β, IL-6 та протизапальних IL-4, IL-10 у сироватці крові були вищими порівняно з їх рівнями до операції. Найвищими рівні інтерлейкінів IL-1β, IL-6 були у сироватці крові пацієнтів з післяопераційним набряком рогівки, а також відмічалося зниження рівня інтерлейкінів IL-4, IL-10 при набряку рогівки. Рівень інтерлейкіну IL-6 у сироватці крові пацієнтів з післяопераційним набряком рогівки був вищим за рівень інтерлейкіну IL-1β, а рівень інтерлейкіну IL-10 превалював над рівнем інтерлейкіну IL-4.
Background. Due to its high prevalence and morbidity, cataract is an urgent medical and social problem. In recent years, immune inflammation, in particular the immune regulation of dystrophic processes, has been of great importance in the pathogenesis of eye diseases. Immunological disorders play a crucial role in the development of age-related eye diseases (cataract, corneal dystrophy, glaucoma, age-related macular degeneration). The effect of pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines on the development of age-related cataract remains understudied, as well at their role in predicting the course of the postoperative period after extraction of age-related cataract has not been fully studied, which determines the relevance of the study. The objective: to assess the state of cytokine profile in patients with age-related cataract by determining the content of pro-inflammatory (IL-1β, IL-6) and anti-inflammatory (IL-4, IL-10) interleukins in blood serum before and after surgical treatment of cataract. Materials and methods. The level of pro-inflammatory (IL-1β, IL-6) and anti-inflammatory cytokines (IL-4, IL-10) was studied before and after surgical treatment in 28 patients with age-related cataract (56 eyes), 8 men and 20 women aged 42 to 82 years. The average age of the patients was 71.79 ± 1.90 years. Serum content of cytokines was determined by the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using test systems Vector-Best-Ukraine. Results. There was no excess of IL-1β and IL-6 reference values in the blood serum of patients with age-related cataract prior to surgical treatment. Analysis of the pro-inflammatory IL-6 in these patients depending on sex revealed a significant increase in its level by 1.3 times in men and a significant decrease by 1.1 times in women compared to its average content (p < 0.06 and p < 0.01, respectively). The level of anti-inflammatory IL-4 and IL-10 in the blood serum of the examined patients was within the reference values. When studying the content of pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory interleukins in serum depending on sex and age in patients with age-related cataract aged 75 years and older, there was a statistically significant increase in IL-6 and IL-10. In this age group, the level of IL-6 was 1.4 times higher in men compared to women, and IL-10 was 1.8 times higher in women than in men. In patients with age-related cataract after surgical treatment, serum content of pro-inflammatory IL-1β, IL-6 and anti-inflammatory IL-4, IL-10 was higher than levels before surgery. The highest levels of IL-1β, IL-6 were in patients with postoperative corneal edema. Serum content of IL-6 in patients with postoperative corneal edema was higher compared to that of IL-1β. Levels of IL-4, IL-10 were higher in patients with postoperative corneal edema, IL-10 in these patients prevailed over IL-4. Conclusions. In patients with age-related cataract, the content of pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines in the blood serum corresponds to reference values and has no significant differences from the control group. However, determination of the cytokine profile in people with age-related cataract revealed a violation of the systemic immunological status depending on age and gender. According to our results, patients with age-related cataract over 75 years of age had a significant increase in the level of pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-6 and anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 in blood serum. In this age group, IL-6 was higher in men and IL-10 was higher in women. We also noted the absence of significant differences in the content of IL-1β, which may indicate a more specific value of IL-6 levels for the development of cataract. In patients with age-related cataract after surgical treatment, serum levels of pro-inflammatory IL-1β, IL-6 and anti-inflammatory IL-4, IL-10 were higher than preoperative ones. The highest levels of IL-1β, IL-6 were in the blood serum of patients with postoperative corneal edema, and a decrease in the level of IL-4, IL-10 was also noted in cases of corneal edema. Serum content of IL-6 in patients with postoperative corneal edema was higher than that of IL-1β, and IL-10 prevailed over IL-4 levels.
катаракта; цитокіни; прозапальні інтерлейкіни; протизапальні інтерлейкіни; факоемульсифікація з імплантацією інтраокулярної лінзи; післяопераційні ускладнення
cataract; cytokines; pro-inflammatory interleukins; anti-inflammatory interleukins; phacoemulsification with intraocular lens implantation; postoperative complications
Для ознакомления с полным содержанием статьи необходимо оформить подписку на журнал.
- Xia S., Zhang X., Zheng S. et al. An update on inflammaging: mechanisms, prevention, and treatment. J Immunol Res. 2016;8:8426874. DOI: 10.1155/2016/8426874.
- Ferrucci L., Fabbri E. Inflammageing: chronic inflammation in ageing, cardiovascular disease, and frailty. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2018;15(9):505-22. DOI: 10.1038/S41569-018-0064-2.
- Brüünsgaard H., Pedersen B.K. Agerelatedinflammatory cytokines and disease. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2003;23(1):15-39. DOI: 10.1016/S0889-8561(02)00056-5.
- Rea I.M., Gibson D.S., McGilligan V. et al. Age and age-related diseases: role of inflammation triggers and cytokines. Front Immunol. 2018;9(9):586. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00586.
- Mikó A., Pótó L., Márai P. et al. Genderdifference in the effects of interleukin-6 on grip strength — a systematic reviewand meta-analysis. BMC Geriatr. 2018;18(1):107. DOI: 10.1186/s12877-018-0798-z.
- Werner S., Grose R. Regulation of wound healing by growth factors and cytokines. Physiol. Rev. 2003;83 (3):835-870.
- Wang L., Zhang Z., Koch D.D., Jia Y., Cao W., Zhang S. Anterior chamber interleukin 1beta, interleukin 6 and prostaglandin E2 in patients undergoing femtosecond laser-assisted cataract surgery. Brit J Ophthalmol. 2016;100(4):579-582.
- Zhou Z., He S., Cheng X. An experimental study of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and interleukin-1 (IL-1) in aqueous humor after intraocular lens implantation. Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi. 1996;32(4):301-303.
- Shigemitsu T., Ishiguro K., Shimizu Y., Horiguchi M., Kasahara M., Arakaki S. Immunocytochemical features of lens after cataract tissue-signalling molecules (growth factors, cytokines, other signalling molecules), cytoskeleton proteins, cellular and extracellular matrix proteins. International Ophthalmology. 1999;23(3):137-144.
- Klein B.E., Klein R., Lee K.E., Knudtson M.D., Tsai M.Y. Markers of inflammation, vascular endothelial dysfunction, and age-related cataract. Am. J Ophthalmol. 2006;141(1):116-122.
- Kany S., Vollrath J.T., Relja B. Cytokines in inflammatory disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(23):6008. DOI: 10.3390/ijms20236008.
- Narazaki M., Kishimoto T. The Two-Faced Cytokine IL-6 in host defense and diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(11):3528. DOI: 10.3390/ijms19113528.
- Robert P.L. Wisse, Jonas J.W. Kuiper, et al. Cytokine Expression in Keratoconus and its Corneal Microenvironment: A Systematic Review, The Ocular Surface. 2015;13(4):272-283. https://doi.org/–10.1016/j.jtos.2015.04.006.