Журнал «Медицина неотложных состояний» Том 21, №6, 2025
Вернуться к номеру
Витривалість до навантаження та функціональне відновлення при переломах плато великогомілкової кістки, що лікували без хірургічного втручання
Авторы: Hussain J. Alkhatteib (1), Sarah Mazin Naeem (2)
(1) - University of Kufa, College of Medicine, Najaf, Iraq
(2) - Alsader Teaching Hospital, Najaf, Iraq
Рубрики: Медицина неотложных состояний
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
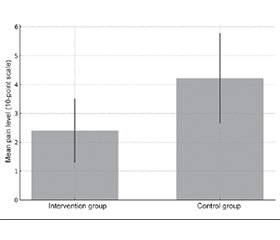
Актуальність. Одними з найскладніших у лікуванні переломів в ортопедії є переломи плато великогомілкової кістки, особливо коли їх потрібно лікувати консервативно. Це зумовлено тим, що такі травми спричиняють значні порушення, а стандартизованої програми навантаження не існує. Мета: продемонструвати вплив протоколів навантаження на час загоєння і зменшення частоти ускладнень, як-от повторні переломи й неправильне зрощення. Матеріали та методи. Це дослідження є проспективним клінічним випробуванням за участю 50 пацієнтів із переломами плато великогомілкової кістки, яких було розподілено на дві групи. В одній групі дотримувалися структурованої програми навантаження, в іншій — звичайного реабілітаційного лікування. Функціональну мобільність пацієнтів оцінювали за допомогою тесту «встань і йди», також фіксували інтенсивність больового синдрому. Результати. Через 84 дні пацієнти, які дотримувалися програми з навантаженням, продемонстрували кращий час виконання тесту «встань і йди» (7,60 проти 10,16 секунди; p < 0,0001) і більшу витривалість до навантаження (71,33 проти 54,14 кг; p < 0,0001), а також нижчий рівень болю (2,4 проти 4,2; p < 0,0001). Висновки. Пацієнти з переломами плато великогомілкової кістки, які дотримуються організованого протоколу навантаження, мають кращі результати відновлення. Це підкреслює необхідність розробки структурованої програми реабілітації, якої слід дотримуватися в майбутньому.
Background. One of the challenging fractures in orthopedic care are fractures of tibial plateau, especially when we need to treat them conservatively. This is because these fractures cause significant impairment and there is no standard weight-bearing program to be followed. The purpose of this study is to show the future effect of weight-bearing protocols on healing time and to reduce complications such as fracture recurrence and malunions. Materials and methods. Our study is a prospective clinical trial involving 50 participants with tibial plateau fractures divided into two groups. One group follows structured load-bearing program, and the other follows the conventional rehabilitation treatment. Patients’ functional mobility was assessed by timed up and go test, pain degree was recorded. Results. After 84 days, the patients followed the weight-bearing program evidenced a better timed up and go test time (7.60 vs. 10.16 seconds; p < 0.0001) and a better weight load endurance (71.33 vs. 54.14 kg; p < 0.0001), also a lower pain threshold (2.4 vs. 4.2; p < 0.0001). Conclusions. Patients with tibial plateau fractures who follow organized weight load protocol will have a better healing outcome and this reflects the need to diagram a structured rehabilitation program to be followed in the future.
переломи плато великогомілкової кістки; функціональне відновлення; реабілітація; протокол навантаження
tibial plateau fractures; functional recovery; rehabilitation; weight-bearing protocol
Для ознакомления с полным содержанием статьи необходимо оформить подписку на журнал.
- Birze A, Vtra R, Jakusonoka R. Functional outcome of patients following intra-articular tibial plateau fractures. Balt J Clin Med Res. 2024;45-52. doi: 10.25143/rsu-bjcmr.2024.01.045-052.
- Buvarp D, Rafsten L, Sunnerhagen K. Predicting longitudinal progression in functional mobility after stroke. Stroke. 2020;51:2179-2187.
- Callary SA, Jones CF, Kantar K, Du Toit H, Baker MP, et al. A new approach to surgical management of tibial plateau fractures. J Clin Med. 2020;9(3):626.
- Chen B, Ye Z, Wu J, Wang G, Yu T. The effect of early weight-bearing and later weight-bearing rehabilitation interventions on outcomes after ankle fracture surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. J Foot Ankle Res. 2024;17(2):e12011.
- Ganadhiepan G, Miramini S, Patel M, Mendis P, Zhang L. Optimal time-dependent levels of weight-bearing for bone fracture healing under Ilizarov circular fixators. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2021;121:104611.
- Giordano V, Pires RE, Faria LPG, Temtemples I, Macagno T, et al. Doctor, when should I start walking? Revisiting postoperative rehabilitation and weight-bearing protocols in operatively treated –acetabular fractures: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Med. 2024;13(12):3570.
- Gonzalez LJ, Hildebrandt K, Carlock K, Konda SR, Egol KA. Patient function continues to improve over the first five years following tibial plateau fracture managed by open reduction and internal fixation. Bone Joint J. 2020;102-B(5):632-637.
- Haag L, McCoy E, Patel S, Slaven J, Lopas L, Natoli R. Factors affecting patient reported outcomes following tibial plateau fracture. Proc IMPRS. 2024;6. doi: 10.18060/27935.
- Heiman E, Menken L, Tang A, Vialonga M, Jankowski J, et al. Early versus standard weight bearing following operative treatment of tibial plateau fractures: do we really have to wait so long? J Knee Surg. 2023;37:402-408.
- Henkelmann R, Palke L, Schneider S, Mller D, Karich B, et al. Impact of anti-gravity treadmill rehabilitation therapy on the clinical outcomes after fixation of lower limb fractures: a randomized clinical trial. Clin Rehabil. 2020;35:356-366.
- Hu H, Yang H. Impact of 3D printing technology-assis–ted rehabilitation cycles on prognostic motility in surgically treated tibial plateau fractures: a meta-analysis. Altern Ther Health Med. 2024:AT10445.
- Iliopoulos E, Galanis N. Physiotherapy after tibial plateau fracture fixation: a systematic review of the literature. SAGE Open Med. 2020;8:2050312120965316.
- Lee SJ, Choi Y, Choi S, Lee H. Early return to daily life through immediate weight-bearing after lateral malleolar fracture surgery. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(10):6052.
- Li H, Yu T, Zhu X, Wang H, Zhang Y. Locking compression plate + T-type steel plate for postoperative weight bearing and functional recovery in complex tibial plateau fractures. World J Clin Cases. 2022;10:502-510.
- Neidlein C, Watrinet J, Ptzold R, Berthold DP, Prall WC, et al. Patient-reported outcomes following tibial plateau fractures: mid- to short-term implications for knee function and activity level. J Clin Med. 2024;13(8):2327.
- Ngo W, Craddock G, Frangenberg A, Park A, Basu N. Tibial plateau fracture with use of tibia strut and bone filler in a 37-year-old male: a case report. Cureus. 2024;16(1):e52913.
- Ortiz-Pia M, Molina-Garcia P, Femia P, Ashe MC, Martn-
- Martn L, et al. Effects of tele-rehabilitation compared with home-based in-person rehabilitation for older adult’s function after hip fracture. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(10):5493.
- Palke L, Schneider S, Karich B, Mende M, Josten C, et al. Anti-gravity treadmill rehabilitation improves gait and muscle atrophy in patients with surgically treated ankle and tibial plateau fractures after one year: a randomised clinical trial. Clin Rehabil. 2021;36:87-98.
- Passias BJ, Korpi FP, Chu AK, Myers DM, Grenier G, et al. Safety of early weight bearing following fixation of bimalleolar ankle fractures. Cureus. 2020;12(4):e7557.
- Phansopkar P, Chitale N, Arora S. Efficacy of transcuta–neous electric nerve stimulation on gait training in subjects with tibial plateau fracture: a randomised control trial. J Med Pharm Allied Sci. 2022;11:4448-4450. doi: 10.55522/jmpas.v11i1.1359.
- Sato E, Treu E, Froerer D, Zhang C, O’Neill D, et al. Establishing the patient acceptable symptom state thresholds for patient-reported outcomes after operatively treated tibial plateau fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2023;38:121-128.
- Sharma D, Thahir A, Sharma V, Krkovic M. The Cambridge experience with tibial plateau fractures in older adults: a case series. Cureus. 2021;13(2):e13311.
- Spina S, Facciorusso S, D’ascanio M, Morone G, Baricich A, et al. Sensor based assessment of turning during instrumented Timed Up and Go test for quantifying mobility in chronic stroke patients. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2022;59:6-13.
- Takano E, Ozaki K, Satoh K, Kawamura K, Maltais M, Kondo I. Effects of a balance exercise assist robot on older patients with hip fracture: a preliminary study. J Med Biol Eng. 2020;40:783-789.
- Wang W, Zhu Y, Hu X. Staged protocol for the treatment of severe open tibial plateau fractures. Res Square. 2020. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-55354/v1.
- Yearson D, Melendez I, Anain F, Siniscalchi S, Drago J. Mobilization protocol and early postoperative weight-bearing in transyndesmal ankle fractures. J Foot Ankle. 2021;15(2):100-104.