Журнал «Травма» Том 26, №4, 2025
Вернуться к номеру
Порівняльний аналіз результатів застосування операції Сайма та транстибіальної ампутації у пацієнтів із вогнепальними ушкодженнями нижньої кінцівки
Авторы: Лябах А.П., Турчин О.А., Пятковський В.М., Харчик В.С., Євлантьєва Т.А.
ДУ «Інститут травматології та ортопедії НАМН України», м. Київ, Україна
Рубрики: Травматология и ортопедия
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
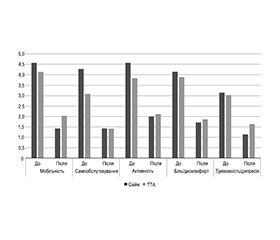
Актуальність. Операція Сайма у пацієнтів з вогнепальними пораненнями стопи має низку переваг, однак її виконують дуже рідко. Мета: провести порівняльний аналіз функціональної спроможності та якості життя у пацієнтів із вогнепальною травмою нижньої кінцівки після операції Сайма та транстибіальної ампутації (ТТА). Матеріали та методи. 46 пацієнтів віком 20–63 роки із вогнепальними ушкодженнями нижньої кінцівки та їх наслідками, яким виконали операцію Сайма (І група, 10 пацієнтів) та транстибіальну ампутацію (ІІ група, 36 пацієнтів). Тяжкість ушкодження кінцівки визначали за Hannover Fracture Score 98, функціональний результат оцінювали за Short Musculoskeletal Function Assessment (SMFA), якість життя — за EQoL-5D-5L. Результати. Не було суттєвих відмінностей у значеннях середніх, що характеризували вік, тяжкість ушкодження кінцівки та кількість операцій до госпіталізації. Результати лікування були оцінені у всіх пацієнтів у строки від 1 до 10 років. Пацієнти, яким виконали операцію Сайма, мали вірогідно кращі показники середніх за застосованими системами оцінки порівняно із пацієнтами, які перенесли ТТА. Середнє значення нормованого індексу неспроможності (SMFA) у пацієнтів І групи становило 0,13 проти 0,22 у пацієнтів ІІ групи (p = 0,006; двовибірковий t-тест). Якість життя поранених, що входили до І групи, за EQoL-5D-5L (VAS) була кращою, ніж у пацієнтів ІІ групи (83,6 та 75,4 відповідно, p = 0,04; двовибірковий t-тест), за рахунок сегментів «мобільність», «активність», «тривожність/депресія» (відповідно p = 0,02; 0,04; 0,01; двовибірковий t-тест). Висновки. Операція Сайма забезпечує кращий функціональний результат лікування за SMFA та кращу якість життя за EQoL-5D-5L, ніж ТТА. Це обумовлює можливість більш широкого застосування операції Сайма у пацієнтів із вогнепальною травмою нижньої кінцівки у показаних випадках.
Background. Syme’s operation in patients with gunshot injuries of the foot has a number of advantages, but it is performed very rarely. The aim was to conduct a comparative analysis of functional capacity and quality of life in patients with gunshot injuries of the lower limb after Syme’s operation and transtibial amputation (TTA). Materials and methods. Forty-six patients aged 20–63 years with gunshot injuries of the lower limb and their consequences who underwent Syme’s operation (group I, 10 patients) and TTA (group II, 36 patients). The severity of limb injury was determined by the Hannover Fracture Scale-98, functional outcome was assessed by the Short Musculoskeletal Function Assessment (SMFA), and quality of life was assessed by the EQoL-5D-5L. Results. There were no significant differences in the mean values characterizing age, severity of limb injury and number of surgeries prior to hospitalization. Outcomes were assessed in all patients in terms from 1 to 10 years. Patients who underwent Syme’s operation had significantly better mean scores on the applied scoring systems compared to patients who underwent TTA. The mean value of standardized disability index (SMFA) in patients of group I was 0.13 vs 0.22 in patients of group II (p = 0.006; two-sample t-test). The quality of life of the injured in group I, according to EQoL-5D-5L (VAS), was better than that in patients of group II (83.6 and 75.4 respectively, p = 0.04; two-sample t-test) due to the mobility, activity, anxiety/depression segments (p = 0.02; 0.04; 0.01, respectively; two-sample t-test). Conclusions. Syme’s operation provides a better functional outcome according to SMFA and a better quality of life according to EQoL-5D-5L than TTA. This makes it possible to use Syme’s operation more widely in patients with gunshot injuries of the lower limb in indicated cases.
вогнепальна травма; нижня кінцівка; операція Сайма; транстибіальна ампутація; якість життя
gunshot injury; lower limb; Syme’s operation; transtibial amputation; quality of life