Журнал «Травма» Том 26, №4, 2025
Вернуться к номеру
Чи потрібно використовувати цемент у пацієнтів похилого віку? Ефективність безцементної ніжки з гідроксиапатитовим покриттям у первинному ендопротезуванні кульшового суглоба в літніх осіб
Авторы: Yasser Reda Mohamed, Mohammed Kanal Asal, Ahmed Mohamed Mohasseb, Waleed Elsayd Elshabrawy, Amr Mohamed Nagy, Ayman Fathy Mounir
Faculty of Medicine, Ain Shams University, Cairo, Egypt
Рубрики: Травматология и ортопедия
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
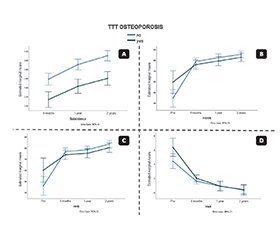
Актуальність. Синдром імплантації кісткового цементу залишається серйозним ускладненням у пацієнтів похилого віку, які перенесли тотальне ендопротезування кульшового суглоба з цементною фіксацією. Безцементні ніжки з гідроксиапатитовим (ГА) покриттям були запропоновані як життєздатна альтернатива, що може поліпшити остеоінтеграцію та знизити частоту синдрому імплантації кісткового цементу. Мета: оцінити ефективність та стабільність безцементних ніжок з ГА-покриттям у літніх осіб при первинному ендопротезуванні кульшового суглоба. Матеріали та методи. Було проведено проспективне когортне дослідження за участю 34 пацієнтів віком ≥ 65 років, яким у період з листопада 2021 року по лютий 2022 року виконано безцементне ендопротезування кульшового суглоба. Із них 30 осіб завершили спостереження та були включені у фінальний аналіз. Рентгенологічне осідання стегнової ніжки оцінювали за методом Engh і Massin через 6 місяців, 1 та 2 роки. Функціональні результати визначали за наступними шкалами: Harris Hip Score (HHS), Hip Disability and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score (HOOS) і візуальною аналоговою шкалою (VAS). У підгруповому аналізі досліджували зв’язок між антиостеопоротичною терапією та курінням. Результати. Середнє осідання ніжки збільшувалося з часом і становило 1,92 ± 0,34 мм через 2 роки (p < 0,001). Функціональні результати суттєво поліпшилися в усіх часових точках: показники HHS збільшилися з 54,7 до 87,3 (p < 0,001), HOOS — з 48,1 до 85,9 (p < 0,001), а VAS — знизилися з 7,2 до 2,1 (p < 0,001). У пацієнтів, які отримували антиостеопоротичну терапію, спостерігалося вірогідно менше осідання ніжки (p < 0,001), тоді як у курців — більше на всіх етапах (p = 0,007). Висновки. Безцементні стегнові ніжки з ГА-покриттям є надійним варіантом в осіб похилого віку, демонструючи низьке осідання імплантата, сприятливе функціональне відновлення та мінімальні ускладнення. Антиостеопоротична терапія може поліпшити стабільність імплантата, тоді як куріння становить значний ризик для цілісності фіксації.
Background. Bone cement implantation syndrome remains a serious complication in elderly patients undergoing cemented total hip arthroplasty. Cementless femoral stems with hydroxyapatite (HA) coating have been proposed as a viable alternative, offering potential improvements in osteointegration and reduction in bone cement implantation syndrome incidence. This study aimed to evaluate the efficacy and stability of HA-coated cementless femoral stems in elderly patients undergoing primary hip arthroplasty. Materials and methods. A prospective case series was conducted on 34 patients aged ≥ 65 years who underwent cementless hip arthroplasty between November 2021 and February 2022. Of these, 30 completed follow-up and were included in the final analysis. Radiographic stem subsidence was measured using Engh and Massin’s method at 6 months, 1, and 2 years. Functional outcomes were assessed via the Harris Hip Score (HHS), Hip Disability and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score (HOOS), and Visual Analog Scale (VAS). Subgroup analyses explored associations with anti-osteoporotic therapy and smoking status. Results. Mean stem subsidence progressively increased over time, reaching 1.92 ± 0.34 mm at 2 years (p < 0.001). Functional outcomes significantly improved across all time points: HHS increased from 54.7 to 87.3 (p < 0.001), HOOS from 48.1 to 85.9 (p < 0.001), and VAS decreased from 7.2 to 2.1 (p < 0.001). Patients receiving anti-osteoporotic therapy had significantly lower subsidence (p < 0.001), while smokers demonstrated higher subsidence at all intervals (p = 0.007). Conclusions. HA-coated cementless femoral stems are a reliable option in elderly patients, demonstrating low subsidence, favorable functional recovery, and minimal complications. Anti-osteoporotic therapy may enhance implant stability, while smoking poses a significant risk to fixation integrity.
ендопротезування кульшового суглоба; безцементна ніжка; гідроксиапатитове покриття; осідання; літні пацієнти
hip arthroplasty; cementless femoral stem; hydroxyapatite coating; subsidence; elderly patients