Международный эндокринологический журнал Том 17, №2, 2021
Вернуться к номеру
Комплаєнс до лікування левотироксином хворих на гіпотиреоз під час пандемічної ери SARS-CoV-2
Авторы: Satilmis Bilgin, Burcin Meryem Atak Tel, Tuba Taslamacioglu Duman, Ozge Kurtkulagi, Gizem Bakir Kahveci, Tugrul Sagdic, Gulali Aktas
Abant Izzet Baysal University Hospital, Department of Internal Medicine, Bolu, Turkey
Рубрики: Эндокринология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
Актуальність. Гіпотиреоз потребує замісної терапії левотироксином (L-T4), щоб підтримувати в пацієнтів стан еутиреозу. Кількість госпіталізацій з приводу хронічних захворювань зменшилась протягом ери COVID-19. Мета дослідження — встановити частоту госпіталізацій пацієнтів з гіпотиреозом під час пандемії COVID-19 порівняно з аналогічним періодом часу в 2019 році. Матеріали та методи. Дослідження було проведене серед пацієнтів, які звернулись у відділення внутрішньої медицини університетської лікарні Abant Izzet Baysal та отримували замісну терапію L-T4 внаслідок гіпотиреозу. 108 пацієнтів з гіпотиреозом були включені в дослідження, підписавши інформаційну згоду. Пацієнти були розділені на дві групи відповідно до прихильності до лікування: хворі, які відповідали вимогам лікування, і хворі, які не дотримувались режиму лікування. Результати. Рівень тиреотропного гормона (ТТГ) перед включенням у дослідження у групі осіб, які відповідали вимогам лікування, був вірогідно нижчим, ніж у групі хворих, які не дотримувались режиму лікування (p < 0,001). При цьому рівень вільного тироксину (вТ4) серед пацієнтів першої групи був вірогідно вищим, ніж в осіб другої групи (p = 0,04). Медіана нерегулярного прийому левотироксину становила 35 (10–90) днів у групі осіб, які не відповідали вимогам лікування, і 0 (0–0) днів у групі осіб, які відповідали вимогам лікування (p < 0,001). Кількість днів, коли левотироксин використовувався нерегулярно, вірогідно позитивно корелювала з останнім значенням ТТГ (r = 0,564, p < 0,001) та негативно — з останнім значенням вT4 (r = –0,492, p < 0,001). Середній об’єм еритроцитів (MCV) у хворих першої та другої груп становив 85 (69,1–97,5) та 89 (66–96,6) фл відповідно (p = 0,03). Ретроспективний характер та порівняно невелика кількість досліджуваних були двома основними обмеженнями проведеного дослідження. Висновки. Дотримання режиму лікування є дуже важливим для досягнення стану еутиреозу в пацієнтів з гіпотиреозом під час пандемії COVID-19. Підвищений рівень MCV може передбачати невідповідність лікування у хворих на гіпотиреоз.
Background. Hypothyroidism requires treatment with levothyroxine (L-T4) to keep patients euthyroid. The rate of hospital admissions for chronic conditions decreased during COVID-19 era. We aimed to observe whether hospital admissions of the patients with hypothyroidism decreased during COVID-19 compared to the same time period in 2019. We also aimed to find out the rate of treatment compliance in subjects with hypothyroidism during pandemic era. Materials and methods. This cross-sectional study was performed on patients who applied to Internal Medicine Department of Abant Izzet Baysal University Hospital, and who received L-T4 replacement therapy due to hypothyroidism. 108 hypothyroidism patients were included in the study with their consent forms. The patients were divided into 2 groups according to the treatment compliance; either as compliant or incompliant patients. Results. The last TSH level of compliant group was significantly lower than incompliant group (p < 0.001). The last fT4 level of the compliant group was significantly higher than that of the incompliant group (p = 0.04). The median of the LT-4 treatment used irregularly was 35 (10–90) days in incompliant group and was 0 (0–0) days in compliant group (p < 0.001). The number of irregularly L-T4 used days was significantly positively correlated with last TSH value (r = 0.564, p < 0.001), and negatively correlated with last FT4 value (r = –0.492, p < 0.001). Mean corpuscular volume (MCV) of the compliant and incompliant groups were 85 (69.1–97.5) fL and 89 (66–96.6) fL, respectively (p = 0.03). Retrospective nature and relatively small study population are two main limitations of our study. Conclusions. Compliance to treatment is very important to achieve euthyroid hormone levels in patients with hypothyroidism during COVID-19 pandemic. Elevated MCV levels could predict incompliance to treatment in hypothyroidism.
гіпотиреоз; левотироксин; комплаєнс; тиреотропний гормон
hypothyroidism; levothyroxine; compliance; thyroid stimulation hormone
Introduction
Methods
Study population
Laboratory analyses
Statistical analyses
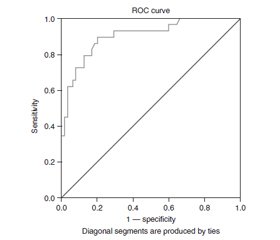
Results
Discussion
- McDermott M.T. Hypothyroidism. Ann. Intern. Med. 2020. 173(1). ITC1-ITC16. doi: 10.7326/AITC202007070.
- Garber J.R., Cobin R.H., Gharib H., Hennessey J.V., Klein I., Mechanick J.I., Pessah-Pollack R. et al.; American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American Thyroid Association Taskforce on Hypothyroidism in Adults. Clinical practice guidelines for hypothyroidism in adults: cosponsored by the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and the American Thyroid Association. Endocr. Pract. 2012. 18(6). 988-1028. doi: 10.4158/EP12280.GL.
- Cooper D.S., Biondi B. Subclinical thyroid disease. Lancet. 2012. 379. 1142-1154. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(11)60276-6.
- Leng O., Razvi S. Hypothyroidism in the older population. Thyroid Res. 2019. 12. 2. doi: 10.1186/s13044-019-0063-3.
- Ingoe L., Phipps N., Armstrong G., Rajagopal A., Kamali F., Razvi S. Prevalence of treated hypothyroidism in the community: analysis from general practices in north-East England with implications for the United Kingdom. Clin. Endocrinol. 2017. 87. 860-864. doi: 10.1111/cen.13440.
- Brown S.J., Bremner A.P., Hadlow N.C., Feddema P., Leedman P.J., O’Leary P.C. et al. The log TSH-free T4 relationship in a community-based cohort is nonlinear and is influenced by age, smo–king and thyroid peroxidase antibody status. Clin. Endocrinol. 2016. 85. 789-796. doi: 10.1111/cen.13107.
- Razvi S., Bhana S., Mrabeti S. Challenges in Interpre–ting Thyroid Stimulating Hormone Results in the Diagnosis of Thyroid Dysfunction. J. Thyroid. Res. 2019. 2019. 4106816. doi: 10.1155/2019/4106816.
- Fitzgerald S.P., Bean N.G. Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) autoregulation reduces variation in the TSH response to thyroid hormones. Temperature (Austin). 2018. 5(4). 380-389. doi: 10.1080/23328940.2018.1513110.
- Hennessey J.V., Espaillat R. Current evidence for the treatment of hypothyroidism with levothyroxine/levotriiodothyronine combination therapy versus levothyroxine monotherapy. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2018. 72(2). e13062. doi: 10.1111/ijcp.13062.
- Jonklaas J., Bianco A.C., Bauer A.J., Burman K.D., Cappola A.R., Celi F.S., Cooper D.S. et al.; American Thyroid Asso–ciation Task Force on Thyroid Hormone Replacement. Guidelines for the treatment of hypothyroidism: prepared by the american thyroid association task force on thyroid hormone replacement. Thyroid. 2014. 24(12). 1670-751. doi: 10.1089/thy.2014.0028.
- Taylor P.N., Razvi S., Pearce S.H., Dayan C.M. Clinical review: A review of the clinical consequences of variation in thyroid function within the reference range. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013. 98(9). 3562-71. doi: 10.1210/jc.2013-1315.
- Biondi B. The normal TSH reference range: what has changed in the last decade? J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013. 98. 3584-3587. doi: 10.1210/jc.2013-2760.
- Cerqueira C., Knudsen N., Ovesen L., Laurberg P., Perrild H., Rasmussen L.B., Jørgensen T. Doubling in the use of thyroid hormone replacement therapy in Denmark: association to iodization of salt? Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2011. 26(8). 629-35. doi: 10.1007/s10654-011-9590-5.
- Hoermann R., Midgley J.E. TSH Measurement and Its Implications for Personalised Clinical Decision-Making. J. Thyroid Res. 2012. 2012. 438037. doi: 10.1155/2012/438037.
- Chen Y., Tai H.Y. Levothyroxine in the treatment of overt or subclinical hypothyroidism: a systematic review and meta-ana–lysis. Endocr. J. 2020. 67(7). 719-732. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.EJ19-0583.
- De Filippo O., D’Ascenzo F., Angelini F. et al. Reduced Rate of Hospital Admissions for ACS during Covid-19 Outbreak in Nor–thern Italy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020. 383. 88-89. doi: 10.1056/–NEJMc2009166.
- Mafham M.M., Spata E., Goldacre R. et al. COVID-19 pandemic and admission rates for and management of acute coronary syndromes in England. Lancet. 2020. 396. 381-389. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(20)31356-8.
- Zhang Y., Wen J., Alamgir M., Xie J., Jing H., Fang M., Wang J. et al. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on inpatient dermatology: a multicentre study from Hubei, China. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2021. 35(3). e179-e181. doi: 10.1111/jdv.17041.
- Silva A.B., Freschi G., Carrera R.V., Astolfi R.H., Berti F.F., Gattas N., Meller A. COVID-19 pandemic impact on clinical outcomes of patients with obstructive pyelonephritis. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2020 Nov 21. 1-7. doi: 10.1007/s11255-020-02708-3.
- Nef H.M., Elsässer A., Möllmann H., Abdel-Hadi M., Bauer T., Brück M., Eggebrecht H. et al.; CoVCAD — Study Group. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on cardiovascular mortality and catherization activity during the lockdown in central Germany: an observational study. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2021. 110(2). 292-301. doi: 10.1007/s00392-020-01780-0.
- Stöhr E., Aksoy A., Campbell M., Al Zaidi M., Öztürk C., Vorloeper J. et al. Hospital admissions during Covid-19 lock-down in Germany: Differences in discretionary and unavoidable cardiovascular events. PLoS ONE. 2020. 15(11). e0242653. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0242653
- Karia M., Gupta V., Zahra W. et al. The effect of COVID-19 on the trauma burden, theatre efficiency and training opportunities in a district general hospital: planning for a future outbreak. Bone & Joint Open. 2020. 1. 494-499. doi: 10.1302/2633-1462.18.bjo-2020-0074.r1.
- Fahy S., Moore J., Kelly M. et al. Analysing the variation in volume and nature of trauma presentations during COVID-19 lockdown in Ireland. Bone & Joint Open. 2020. 1. 261-266. doi: 10.1302/2046-3758.16.bjo-2020-0040.r1.
- Grech V., Borg D., Agius S., Scherb H. Sharp decline in acute and elective hospital attendances and admissions due to COVID-19 in Malta (Q1 2020) — A population-based study. Early Hum. Dev. 2020. 105250. doi: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2020.105250.
- Atik F., Aktas G., Kocak M.Z., Erkus E., Savli H. Analysis of the Factors Related to the Blood Pressure Control in Hypertension. J. Coll. Physicians Surg. Pak. 2018. 28(6). 423-426. doi: 10.29271/jcpsp.2018.06.423.
- Erdogan M., Kösenli A., Ganidagli S., Kulaksizoglu M. Characteristics of anemia in subclinical and overt hypothyroid patients. Endocr. J. 2012. 59(3). 213-20. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.ej11-0096.

/15.jpg)