Международный эндокринологический журнал Том 17, №3, 2021
Вернуться к номеру
R-енантіомер α-ліпоєвої кислоти. Можливості та перспективи клінічного використання
Авторы: Кравчун Н.О.(1, 3), Дунаєва І.П.(2), Кравчун П.П.(2)
(1) — Багатопрофільний медичний центр «Life Park», м. Харків, Україна
(2) — Харківський національний медичний університет, м. Харків, Україна
(3) — Державна установа «Інститут проблем ендокринної патології ім. В.Я. Данилевського
Національної академії медичних наук України», м. Харків, Україна
Рубрики: Эндокринология
Разделы: Справочник специалиста
Версия для печати
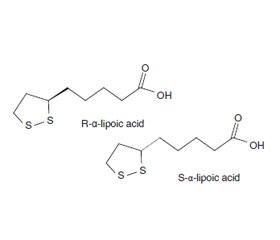
У роботі наведено аналіз сучасних літературних даних стосовно застосування R-енантіомеру α-ліпоєвої кислоти як гіпотензивного лікування у хворих з артеріальною гіпертензією та метаболічним синдромом. Проведено аналіз літератури щодо застосування вищезазначеного засобу як протизапального при запальних захворюваннях. Зараз дуже важливим аспектом досліджень є можливість застосування R-α-ліпоєвої кислоти як мікронутрієнту та терапевтичного засобу для лікування діабетичних полінейропатій та нейродегенеративних захворювань, в першу чергу хвороби Альцгеймера, порушень вуглеводного обміну та метаболічного синдрому. Ліпоєва кислота сьогодні стала важливим інгредієнтом у полівітамінних формулах, добавках проти старіння. R-α-ліпоєва кислота — це метаболічний антиоксидант, її молекула вміщує дитіоланове кільце в окисленій формі, яке має здатність до розщеплювання з утворенням дигідроліпоєвої кислоти. А через те, що α-ліпоєва кислота, фізіологічна форма тіоктової кислоти, є сильним антиоксидантом, який знімає симптоми діабетичної нейропатії, то в літературному огляді було проаналізовано дані різних авторів стосовно антиоксидантних ефектів R-енантіомеру α-ліпоєвої кислот і виявлено, що засіб проявляє дуже високі антиоксидантні ефекти, а його доза 300 мг біоеквівалентна 600 мг рацемічної α-ліпоєвої кислоти. Як подано в достатній кількості проаналізованих джерел, біологічна роль ліпоєвої кислоти досить різноманітна. Важливо визначити точний причинно-наслідковий зв’язок між ліпоєвою кислотою та її клітинними мішенями негайної дії. Ліпоєва кислота може чинити низку важливих та різноманітних фізіологічних дій на стимуляцію нейрогормональної функції і, таким чином, опосередковано впливати на множинні клітинні сигнальні шляхи в периферичних тканинах.
The paper presents an analysis of current literature data on the use of the R-enantiomer of α-lipoic acid as an antihypertensive treatment in patients with hypertension and metabolic syndrome. An analysis of the literature was carried out on its use as an antiinflammatory agent in inflammatory diseases. Currently, a very important aspect of researches is the possibility of using R-α-lipoic acid as a micronutrient and therapeutic agent for the treatment of diabetic polyneuropathy and neurodegenerative diseases, especially Alzheimer’s disease, carbohydrate metabolism disorders and metabolic syndrome. Lipoic acid has now become an important ingredient in multivitamin formulas, anti-aging supplements. R-α-lipoic acid is a metabolic antioxidant, its molecule contains a dithiolane ring in oxidized form, this ring has the ability to cleave with formation of dihydrolipoic acid. And since α-lipoic acid, a physiological form of thioctic acid, is a strong antioxidant that relieves the symptoms of diabetic neuropathy, the literature review analyzed data from various authors on the antioxidant effects of the R-enantiomer of α-lipoic acid and found that it had strong antioxidant effects, and its dose of 300 mg is bioequivalent to 600 mg of racemic α-lipoic acid. As presented in a sufficient number of analyzed sources, the biological role of lipoic acid is quite diverse. It is important to determine the exact causal relationship between lipoic acid and its immediate cellular targets. Lipoic acid can have a number of important and diverse physiological effects on the stimulation of neurohormonal function and, thus, indirectly affect multiple cellular signaling pathways in peripheral tissues.
R-енантіомер α-ліпоєвої кислоти; артеріальна гіпертензія; метаболічний синдром; огляд
α-lipoic acid R-enantiomer; arterial hypertension; metabolic syndrome; review
Вступ
Використання LA як кофактора
/75.jpg)
Біологічна доступність та безпека перорального застосування LA
Висновки
- Reed L.J., Debusk B.G., Gunsalus I.C., Hornberger C.S. Jr. Crystalline alpha-lipoic acid; a catalytic agent associated with pyruvate dehydrogenase. Science. 1951. 114(2952). 93-4. doi: 10.1126/science.114.2952.93.
- Zdzisińska B., Żurek A., Kandefer-Szerszeń M. Alpha-Ketoglutarate as a Molecule with Pleiotropic Activity: Well-Known and Novel Possibilities of Therapeutic Use. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. (Warsz). 2017. 65(1). 21-36. doi: 10.1007/s00005-016-0406-x.
- Liu S., He L., Yao K. The Antioxidative Function of Alpha-Ketoglutarate and Its Applications. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018. 2018. 3408467. doi: 10.1155/2018/3408467.
- Smith A.R., Shenvi S.V., Widlansky M., Suh J.H., Hagen T.M. Lipoic acid as a potential therapy for chronic diseases associated with oxidative stress. Curr. Med. Chem. 2004. 11(9). 1135-46. doi: 10.2174/0929867043365387.
- Scott B.C., Aruoma O.I., Evans P.J., O’Neill C., Van der Vliet A., Cross C.E., Tritschler H., Halliwell B. Lipoic and dihydrolipoic acids as antioxidants. A critical evaluation. Free Radic Res. 1994. 20(2). 119-33. doi: 10.3109/10715769409147509.
- Devasagayam T.P., Subramanian M., Pradhan D.S., Sies H. Prevention of singlet oxygen-induced DNA damage by lipoate. Chem. Biol. Interact. 1993. 86(1). 79-92. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(93)90113-d. PMID: 8431966.
- Liu J., Head E., Gharib A.M., Yuan W., Ingersoll R.T., Hagen T.M., Cotman C.W., Ames BN. Memory loss in old rats is associated with brain mitochondrial decay and RNA/DNA oxidation: partial reversal by feeding acetyl-L-carnitine and/or R-alpha-lipoic acid. Proc. Natl. Acad Sci USA. 2002. 99(4). 2356-61. doi: 10.1073/pnas.261709299.
- Suh J.H., Shenvi S.V., Dixon B.M., Liu H., Jaiswal A.K., Liu R.M., Hagen T.M. Decline in transcriptional activity of Nrf2 causes age-related loss of glutathione synthesis, which is reversible with lipoic acid. Proc. Natl. Acad Sci USA. 2004. 101(10). 3381-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0400282101.
- Lodge J.K., Traber M.G., Packer L. Thiol chelation of Cu2+ by dihydrolipoic acid prevents human low density lipoprotein peroxidation. Free Radic Biol. Med. 1998. 25(3). 287-97. doi: 10.1016/s0891-5849(98)00048-3.
- Anuradha B., Varalakshmi P. Protective role of DL-alpha-lipoic acid against mercury-induced neural lipid peroxidation. Pharmacol. Res. 1999. 39(1). 67-80. doi: 10.1006/phrs.1998.0408.
- Han D., Sen C.K., Roy S., Kobayashi M.S., Tritschler H.J., Packer L. Protection against glutamate-induced cytotoxicity in C6 glial cells by thiol antioxidants. Am. J. Physiol. 1997. 273(5). R1771-8. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1997.273.5.R1771.
- Koval S.M., Yushko K.O., Snihurska I.O., Starchenko T.G., Pankiv V.I., Lytvynova O.M., Mysnychenko O.V. Relations of angiotensin-(1-7) with hemodynamic and cardiac structural and functional parameters in patients with hypertension and type 2 diabetes. Arterial Hypertension (Poland). 2019. 23(3). 183-189. doi: 10.5603/AH.a2019.0012.
- Vanden Boom T.J., Reed K.E., Cronan J.E. Jr. Lipoic acid metabolism in Escherichia coli: isolation of null mutants defective in lipoic acid biosynthesis, molecular cloning and characterization of the E. coli lip locus, and identification of the lipoylated protein of the glycine cleavage system. J. Bacteriol. 1991. 173(20). 6411-20. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.20.6411-6420.1991.
- Akiba S., Matsugo S., Packer L., Konishi T. Assay of protein-bound lipoic acid in tissues by a new enzymatic method. Anal. Biochem. 1998. 258(2). 299-304. doi: 10.1006/abio.1998.2615.
- Packer L., Kraemer K., Rimbach G. Molecular aspects of lipoic acid in the prevention of diabetes complications. Nutrition. 2001. 17(10). 888-95. doi: 10.1016/s0899-9007(01)00658-x.
- Wollin S.D., Jones P.J. Alpha-lipoic acid and cardiovascular disease. J. Nutr. 2003. 133(11). 3327-30. doi: 10.1093/jn/133.11.3327.
- Takaishi N., Yoshida K., Satsu H., Shimizu M. Transepithelial transport of alpha-lipoic acid across human intestinal Caco-2 cell monolayers. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007. 55(13). 5253-9. doi: 10.1021/jf063624i. Epub 2007 May 31. PMID: 17536819.
- Balamurugan K., Vaziri N.D., Said H.M. Biotin uptake by human proximal tubular epithelial cells: cellular and molecular aspects. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 2005. 288(4). F823-31. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00375.2004.
- Prasad P.D., Wang H., Kekuda R., Fujita T., Fei Y.J., Devoe L.D., Leibach F.H., Ganapathy V. Cloning and functional expression of a cDNA encoding a mammalian sodium-dependent vitamin transporter mediating the uptake of pantothenate, biotin, and lipoate. J. Biol. Chem. 1998. 273(13). 7501-6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.13.7501.
- Teichert J., Kern J., Tritschler H.J., Ulrich H., Preiss R. Investigations on the pharmacokinetics of alpha-lipoic acid in healthy volunteers. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1998. 36(12). 625-8. PMID: 9876998.
- Carlson D.A., Smith A.R., Fischer S.J., Young K.L., Pac–ker L. The plasma pharmacokinetics of R-(+)-lipoic acid administered as sodium R-(+)-lipoate to healthy human subjects. Altern. Med. Rev. 2007. 12(4). 343-51. PMID: 18069903.
- Breithaupt-Grögler K., Niebch G., Schneider E., Erb K., Hermann R., Blume H.H., Schug B.S., Belz G.G. Dose-proportionality of oral thioctic acid-coincidence of assessments via pooled plasma and individual data. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 1999. 8(1). 57-65. doi: 10.1016/s0928-0987(98)00061-x.
- Harrison E.H., McCormick D.B. The metabolism of dl-(1,6-14C)lipoic acid in the rat. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1974. 160(2). 514-22. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90428-7. PMID: 4598618.
- Panigrahi M., Sadguna Y., Shivakumar B.R., Kolluri S.V., Roy S., Packer L., Ravindranath V. Alpha-lipoic acid protects against reperfusion injury following cerebral ischemia in rats. Brain Res. 1996. 717(1-2). 184-8. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(96)00009-1. PMID: 8738270.
- Arivazhagan P., Shila S., Kumaran S., Panneerselvam C. Effect of DL-alpha-lipoic acid on the status of lipid peroxidation and antioxidant enzymes in various brain regions of aged rats. Exp. Gerontol. 2002. 37(6). 803-11. doi: 10.1016/s0531-5565(02)00015-3. PMID: 12175480.
- Jones W., Li X., Qu Z.C., Perriott L., Whitesell R.R., May J.M. Uptake, recycling, and antioxidant actions of alpha-lipoic acid in endothelial cells. Free Radic Biol. Med. 2002. 33(1). 83-93. doi: 10.1016/s0891-5849(02)00862-6.
- Biewenga G.P., Haenen G.R., Bast A. The pharmacology of the antioxidant lipoic acid. Gen. Pharmacol. 1997. 29(3). 315-31. doi: 10.1016/s0306-3623(96)00474-0.
- Searls R.L., Sanadi D.R. Alpha-ketoglutaric dehydrogenase. 8. Isolation and some properties of a flavoprotein compnent. J. Biol. Chem. 1960. 235. 2485-91. PMID: 14444366.
- Suzuki Y.J., Tsuchiya M., Packer L. Antioxidant activities of dihydrolipoic acid and its structural homologues. Free Radic Res. Commun. 1993. 18(2). 115-22. doi: 10.3109/10715769309147348.
- Yuzvenko T., Tarasenko S., Marchenko O. New Opportunities for the Use of Alpha-Lipoic Acid: The Role of Enantiomers. International Journal Of Endocrinology (Ukraine). 2019. 15(6). 507-14. doi: 10.22141/2224-0721.15.6.2019.185414.
- Devasagayam T.P., Di Mascio P., Kaiser S., Sies H. Singlet oxygen induced single-strand breaks in plasmid pBR322 DNA: the enhancing effect of thiols. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1991 Mar 26. 1088(3). 409-12. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(91)90133-7. PMID: 2015303.
- Haenen G.R., Bast A. Scavenging of hypochlorous acid by lipoic acid. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1991. 42(11). 2244-6. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(91)90363-a. PMID: 1659823.
- Bast A., Haenen G.R. Lipoic acid: a multifunctional antioxidant. Biofactors. 2003. 17(1-4). 207-13. doi: 10.1002/biof.5520170120. PMID: 12897442.
- Ou P., Tritschler H.J., Wolff S.P. Thioctic (lipoic) acid: a therapeutic metal-chelating antioxidant? Biochem. Pharmacol. 1995. 50(1). 123-6. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(95)00116-h.
- Suh J.H., Moreau R., Heath S.H., Hagen T.M. Dietary supplementation with (R)-alpha-lipoic acid reverses the age-related accumulation of iron and depletion of antioxidants in the rat cerebral cortex. Redox. Rep. 2005. 10(1). 52-60. doi: 10.1179/135100005X21624.
- Bush A.I. Metal complexing agents as therapies for Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging. 2002. 23(6). 1031-8. doi: 10.1016/s0197-4580(02)00120-3. PMID: 12470799.
- Goralska M., Dackor R., Holley B., McGahan M.C. Alpha lipoic acid changes iron uptake and storage in lens epithelial cells. Exp. Eye Res. 2003. 76(2). 241-8. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4835(02)00307-x. PMID: 12565812.
- Schupke H., Hempel R., Peter G., Hermann R., Wessel K., Engel J., Kronbach T. New metabolic pathways of alpha-lipoic acid. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2001. 29(6). 855-62. PMID: 11353754.
- Lykkesfeldt J., Hagen T.M., Vinarsky V., Ames B.N. Age-associated decline in ascorbic acid concentration, recycling, and biosynthesis in rat hepatocytes-reversal with (R)-alpha-lipoic acid supplementation. FASEB J. 1998. 12(12). 1183-9. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.12.12.1183. PMID: 9737721.
- Michels A.J., Joisher N., Hagen T.M. Age-related decline of sodium-dependent ascorbic acid transport in isolated rat hepatocytes. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2003. 410(1). 112-20. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(02)00678-1. PMID: 12559983.
- Suh J.H., Shigeno E.T., Morrow J.D., Cox B., Rocha A.E., Frei B., Hagen T.M. Oxidative stress in the aging rat heart is reversed by dietary supplementation with (R)-(alpha)-lipoic acid. FASEB J. 2001. 15(3). 700-6. doi: 10.1096/fj.00-0176com. PMID: 11259388; PMCID: PMC4696539.
- Xu D.P., Wells W.W. Alpha-lipoic acid dependent regeneration of ascorbic acid from dehydroascorbic acid in rat liver mitochondria. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 1996. 28(1). 77-85. PMID: 8786242.
- Bast A., Haenen G.R. Interplay between lipoic acid and glutathione in the protection against microsomal lipid peroxidation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1988. 963(3). 558-61. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(88)90326-8. PMID: 3143421.
- Busse E., Zimmer G., Schopohl B., Kornhuber B. Influence of alpha-lipoic acid on intracellular glutathione in vitro and in vivo. Arzneimittelforschung. 1992. 42(6). 829-31. PMID: 1418040.
- Han D., Handelman G., Marcocci L., Sen C.K., Roy S., Kobuchi H., Tritschler H.J., Flohé L., Packer L. Lipoic acid increases de novo synthesis of cellular glutathione by improving cystine utilization. Biofactors. 1997. 6(3). 321-38. doi: 10.1002/biof.5520060303. PMID: 9288403.
- Suh J.H., Wang H., Liu R.M., Liu J., Hagen T.M. (R)-alpha-lipoic acid reverses the age-related loss in GSH redox status in post-mitotic tissues: evidence for increased cysteine requirement for GSH synthesis. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2004. 423(1). 126-35. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2003.12.020. PMID: 14871476; PMCID: PMC4696556.
- Kilic F., Handelman G.J., Traber K., Tsang K., Packer L., Trevithick J.R. Modelling cortical cataractogenesis XX. In vitro effect of alpha-lipoic acid on glutathione concentrations in lens in model diabetic cataractogenesis. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Int. 1998. 46(3). 585-95. doi: 10.1080/15216549800204112. PMID: 9818098.
- Wolz P., Krieglstein J. Neuroprotective effects of alpha-lipoic acid and its enantiomers demonstrated in rodent models of focal cerebral ischemia. Neuropharmacology. 1996. 35(3). 369-75. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(95)00172-7. PMID: 8783212.
- Biewenga G.P., Dorstijn M.A., Verhagen J.V., Haenen G.R., Bast A. Reduction of lipoic acid by lipoamide dehydrogenase. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1996. 51(3). 233-8. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(95)02124-8. PMID: 8573188.
- Hagen T.M., Vinarsky V., Wehr C.M., Ames B.N. (R)-alpha-lipoic acid reverses the age-associated increase in susceptibility of hepatocytes to tert-butylhydroperoxide both in vitro and in vivo. Antioxid Redox Signal. 200l. 2(3). 473-83. doi: 10.1089/15230860050192251. PMID: 11229361.
- Moini H., Tirosh O., Park Y.C., Cho K.J., Packer L. R-alpha-lipoic acid action on cell redox status, the insulin receptor, and glucose uptake in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2002. 397(2). 384-91. doi: 10.1006/abbi.2001.2680. PMID: 11795898.
- Dinkova-Kostova A.T., Holtzclaw W.D., Cole R.N., Itoh K., Wakabayashi N., Katoh Y., Yamamoto M., Talalay P. Direct evidence that sulfhydryl groups of Keap1 are the sensors regulating induction of phase 2 enzymes that protect against carcinogens and oxidants. Proc. Natl. Acad Sci USA. 2002. 99(18). 11908-13. doi: 10.1073/pnas.172398899.
- Zhang D.D., Lo S.C., Cross J.V., Templeton D.J., Hannink M. Keap1 is a redox-regulated substrate adaptor protein for a Cul3-dependent ubiquitin ligase complex. Mol. Cel.l Biol. 2004. 24(24). 10941-53. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.24.10941-10953.2004.
- Suzuki Y.J., Shi S.S., Day R.M., Blumberg J.B. Differential regulation of MAP kinase signaling by pro- and antioxidant biothiols. Ann. NY Acad Sci. 2000. 899. 159-67. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2000.tb06184.x.
- Shi S.S., Day R.M., Halpner A.D., Blumberg J.B., Suzuki Y.J. Homocysteine and alpha-lipoic acid regulate p44/42 MAP kinase phosphorylation in NIH/3T3 cells. Antioxid Redox Signal. 1999. 1(1). 123-8. doi: 10.1089/ars.1999.1.1-123.
- Konrad D., Somwar R., Sweeney G., Yaworsky K., Hayashi M., Ramlal T., Klip A. The antihyperglycemic drug alpha-lipoic acid stimulates glucose uptake via both GLUT4 translocation and GLUT4 activation: potential role of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in GLUT4 activation. Diabetes. 2001. 50(6). 1464-71. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.50.6.1464.
- Shay K.P., Hagen T.M. Age-associated impairment of Akt phosphorylation in primary rat hepatocytes is remediated by alpha-lipoic acid through PI3 kinase, PTEN, and PP2A. Biogerontology. 2009. 10(4). 443-56. doi: 10.1007/s10522-008-9187-x.
- Zhang W.J., Wei H., Hagen T., Frei B. Alpha-lipoic acid attenuates LPS-induced inflammatory responses by activating the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad Sci USA. 2007. 104(10). 4077-82. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0700305104.
- Smith A.R., Hagen T.M. Vascular endothelial dysfunction in aging: loss of Akt-dependent endothelial nitric oxide synthase phosphorylation and partial restoration by (R)-alpha-lipoic acid. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2003. 31(Pt 6). 1447-9. doi: 10.1042/bst0311447.
- Saengsirisuwan V., Perez F.R., Sloniger J.A., Maier T., Henriksen E.J. Interactions of exercise training and alpha-lipoic acid on insulin signaling in skeletal muscle of obese Zucker rats. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004. 287(3). E529-36. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00013.2004.
- Cho K.J., Moini H., Shon H.K., Chung A.S., Packer L. Alpha-lipoic acid decreases thiol reactivity of the insulin receptor and protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2003. 66(5). 849-58. doi: 10.1016/s0006-2952(03)00395-2.
- Foley T.D., Petro L.A., Stredny C.M., Coppa T.M. Oxidative inhibition of protein phosphatase 2A activity: role of catalytic subunit disulfides. Neurochem. Res. 2007. 32(11). 1957-64. doi: 10.1007/s11064-007-9394-x.
- Ross S.H., Lindsay Y., Safrany S.T., Lorenzo O., Villa F., Toth R., Clague M.J. et al. Differential redox regulation within the PTP superfamily. Cell. Signal. 2007. 19(7). 1521-30. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2007.01.026.
- Lee S.R., Yang K.S., Kwon J., Lee C., Jeong W., Rhee S.G. Reversible inactivation of the tumor suppressor PTEN by H2O2. J. Biol. Chem. 2002. 277(23). 20336-42. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111899200.
- Diesel B., Kulhanek-Heinze S., Höltje M., Brandt B., Höltje H.D., Vollmar A.M., Kiemer A.K. Alpha-lipoic acid as a directly binding activator of the insulin receptor: protection from hepatocyte apoptosis. Biochemistry. 2007. 46(8). 2146-55. doi: 10.1021/bi602547m.
- Jessen N., Goodyear L.J. Contraction signaling to glucose transport in skeletal muscle. J. Appl. Physiol. (1985). 2005. 99(1). 330-7. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00175.2005.
- Cartee G.D., Wojtaszewski J.F. Role of Akt substrate of 160 kDa in insulin-stimulated and contraction-stimulated glucose transport. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2007. 32(3). 557-66. doi: 10.1139/H07-026.
- Kim M.S., Park J.Y., Namkoong C., Jang P.G., Ryu J.W., Song H.S., Yun J.Y. et al. Anti-obesity effects of alpha-lipoic acid mediated by suppression of hypothalamic AMP-activated protein kinase. Nat. Med. 2004. 10(7). 727-33. doi: 10.1038/nm1061.
- Lee W.J., Lee I.K., Kim H.S., Kim Y.M., Koh E.H., Won J.C., Han S.M. et al. Alpha-lipoic acid prevents endothelial dysfunction in obese rats via activation of AMP-activated protein kinase. Arterioscler Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2005. 25(12). 2488-94. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.0000190667.33224.4c.
- Lee W.J., Song K.H., Koh E.H., Won J.C., Kim H.S., Park H.S., Kim M.S. et al. Alpha-lipoic acid increases insulin sensitivity by activating AMPK in skeletal muscle. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005. 332(3). 885-91. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.05.035.
- Paz K., Hemi R., LeRoith D., Karasik A., Elhanany E., Kanety H., Zick Y. A molecular basis for insulin resistance. Elevated serine/threonine phosphorylation of IRS-1 and IRS-2 inhibits their binding to the juxtamembrane region of the insulin receptor and impairs their ability to undergo insulin-induced tyrosine phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 1997. 272(47). 29911-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.47.29911.
- Jakobsen S.N., Hardie D.G., Morrice N., Tornqvist H.E. 5’-AMP-activated protein kinase phosphorylates IRS-1 on Ser-789 in mouse C2C12 myotubes in response to 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide riboside. J. Biol. Chem. 2001. 276(50). 46912-6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C100483200.
- Treebak J.T., Glund S., Deshmukh A., Klein D.K., Long Y.C., Jensen T.E., Jørgensen S.B. et al. AMPK-mediated AS160 phosphorylation in skeletal muscle is dependent on AMPK catalytic and regulatory subunits. Diabetes. 2006. 55(7). 2051-8. doi: 10.2337/db06-0175.
- Shen Q.W., Zhu M.J., Tong J., Ren J., Du M. Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase is involved in AMP-activated protein kinase activation by alpha-lipoic acid in C2C12 myotubes. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Physiol. 2007. 293(4). C1395-403. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00115.2007.
- Tsakiridis T., McDowell H.E., Walker T., Downes C.P., Hundal H.S., Vranic M., Klip A. Multiple roles of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in regulation of glucose transport, amino acid transport, and glucose transporters in L6 skeletal muscle cells. Endocrinology. 1995. 136(10). 4315-22. doi: 10.1210/endo.136.10.7664650.
- Yaworsky K., Somwar R., Ramlal T., Tritschler H.J., Klip A. Engagement of the insulin-sensitive pathway in the stimulation of glucose transport by alpha-lipoic acid in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Diabetologia. 2000. 43(3). 294-303. doi: 10.1007/s001250050047.
- Estrada D.E., Ewart H.S., Tsakiridis T., Volchuk A., Ramlal T., Tritschler H., Klip A. Stimulation of glucose uptake by the natural coenzyme alpha-lipoic acid/thioctic acid: participation of elements of the insulin signaling pathway. Diabetes. 1996. 45(12). 1798-804. doi: 10.2337/diab.45.12.1798.
- Henriksen E.J., Jacob S., Streeper R.S., Fogt D.L., Hokama J.Y., Tritschler H.J. Stimulation by alpha-lipoic acid of glucose transport activity in skeletal muscle of lean and obese Zucker rats. Life Sci. 1997. 61(8). 805-12. doi: 10.1016/s0024-3205(97)00562-6.
- Streeper R.S., Henriksen E.J., Jacob S., Hokama J.Y., Fogt D.L., Tritschler H.J. Differential effects of lipoic acid stereoisomers on glucose metabolism in insulin-resistant skeletal muscle. Am. J. Physiol. 1997. 273(1 Pt 1). E185-91. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1997.273.1.E185.
- Hughes V.A., Fiatarone M.A., Fielding R.A., Kahn B.B., Ferrara C.M., Shepherd P., Fisher E.C. et al. Exercise increases muscle GLUT-4 levels and insulin action in subjects with impaired glucose tolerance. Am. J. Physiol. 1993. 264(6 Pt 1). E855-62. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1993.264.6.E855.
- Jacob S., Streeper R.S., Fogt D.L., Hokama J.Y., Tritschler H.J., Dietze G.J., Henriksen E.J. The antioxidant alpha-lipoic acid enhances insulin-stimulated glucose metabolism in insulin-resistant rat skeletal muscle. Diabetes. 1996. 45(8). 1024-9. doi: 10.2337/diab.45.8.1024.
- Jacob S., Henriksen E.J., Schiemann A.L., Simon I., Clancy D.E., Tritschler H.J., Jung W.I. et al. Enhancement of glucose disposal in patients with type 2 diabetes by alpha-lipoic acid. Arzneimittelforschung. 1995. 45(8). 872-4. PMID: 7575750.
- Konrad T., Vicini P., Kusterer K., Höflich A., Assadkhani A., Böhles H.J., Sewell A. et al. alpha-Lipoic acid treatment decreases serum lactate and pyruvate concentrations and improves glucose effectiveness in lean and obese patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 1999. 22(2). 280-7. doi: 10.2337/diacare.22.2.280.
- Ziegler D., Nowak H., Kempler P., Vargha P., Low P.A. Treatment of symptomatic diabetic polyneuropathy with the antioxidant alpha-lipoic acid: a meta-analysis. Diabet. Med. 2004. 21(2). 114-21. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.2004.01109.x.
- Reljanovic M., Reichel G., Rett K., Lobisch M., Schuette K., Möller W., Tritschler H.J., Mehnert H. Treatment of diabetic polyneuropathy with the antioxidant thioctic acid (alpha-lipoic acid): a two year multicenter randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial (ALADIN II). Alpha Lipoic Acid in Diabetic Neuropathy. Free Radic Res. 1999. 31(3). 171-9. doi: 10.1080/10715769900300721.
- Ziegler D., Hanefeld M., Ruhnau K.J., Hasche H., Lobisch M., Schütte K., Kerum G., Malessa R. Treatment of symptomatic diabetic polyneuropathy with the antioxidant alpha-lipoic acid: a 7-month multicenter randomized controlled trial (ALADIN III Study). ALADIN III Study Group. Alpha-Lipoic Acid in Diabetic Neuropathy. Diabetes Care. 1999. 22(8). 1296-301. doi: 10.2337/diacare.22.8.1296.
- Ruhnau K.J., Meissner H.P., Finn J.R., Reljanovic M., Lobisch M., Schütte K., Nehrdich D. et al. Effects of 3-week oral treatment with the antioxidant thioctic acid (alpha-lipoic acid) in symptomatic diabetic polyneuropathy. Diabet. Med. 1999. 16(12). 1040-3. doi: 10.1046/j.1464-5491.1999.00190.x.
- Ametov A.S., Barinov A., Dyck P.J., Hermann R., Kozlova N., Litchy W.J., Low P.A. et al.; SYDNEY Trial Study Group. The sensory symptoms of diabetic polyneuropathy are improved with alpha-lipoic acid: the SYDNEY trial. Diabetes Care. 2003. 26(3). 770-6. doi: 10.2337/diacare.26.3.770.
- Ziegler D., Ametov A., Barinov A., Dyck P.J., Gurieva I., Low P.A., Munzel U. et al. Oral treatment with alpha-lipoic acid improves symptomatic diabetic polyneuropathy: the SYDNEY 2 trial. Diabetes Care. 2006. 29(11). 2365-70. doi: 10.2337/dc06-1216.
- Heitzer T., Finckh B., Albers S., Krohn K., Kohlschütter A., Meinertz T. Beneficial effects of alpha-lipoic acid and ascorbic acid on endothelium-dependent, nitric oxide-mediated vasodilation in diabetic patients: relation to parameters of oxidative stress. Free Radic Biol. Med. 2001. 31(1). 53-61. doi: 10.1016/s0891-5849(01)00551-2.
- Sena C.M., Nunes E., Louro T., Proença T., Fernandes R., Boarder M.R., Seiça R.M. Effects of alpha-lipoic acid on endothelial function in aged diabetic and high-fat fed rats. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008. 153(5). 894-906. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707474.
- Montagnani M., Ravichandran L.V., Chen H., Esposito D.L., Quon M.J. Insulin receptor substrate-1 and phosphoinositide-dependent kinase-1 are required for insulin-stimulated production of nitric oxide in endothelial cells. Mol. Endocrinol. 2002. 16(8). 1931-42. doi: 10.1210/me.2002-0074.
- Federici M., Menghini R., Mauriello A., Hribal M.L., Ferrelli F., Lauro D., Sbraccia P. et al. Insulin-dependent activation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase is impaired by O-linked glycosylation modification of signaling proteins in human coronary endothelial cells. Circulation. 2002. 106(4). 466-72. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.0000023043.02648.51.
- Hagen T.M., Moreau R., Suh J.H., Visioli F. Mitochondrial decay in the aging rat heart: evidence for improvement by dietary supplementation with acetyl-L-carnitine and/or lipoic acid. Ann. NY Acad Sci. 2002. 959. 491-507. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2002.tb02119.x.
- Petersen Shay K., Moreau R.F., Smith E.J., Hagen T.M. Is alpha-lipoic acid a scavenger of reactive oxygen species in vivo? Evidence for its initiation of stress signaling pathways that promote endogenous antioxidant capacity. IUBMB Life. 2008. 60(6). 362-7. doi: 10.1002/iub.40.
- Sola S., Mir M.Q., Cheema F.A., Khan-Merchant N., Menon R.G., Parthasarathy S, Khan BV. Irbesartan and lipoic acid improve endothelial function and reduce markers of inflammation in the metabolic syndrome: results of the Irbesartan and Lipoic Acid in Endothelial Dysfunction (ISLAND) study. Circulation. 2005. 111(3). 343-8. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000153272.48711.B9.
- Vasdev S., Gill V., Longerich L., Parai S., Gadag V. Salt-induced hypertension in WKY rats: prevention by alpha-lipoic acid supplementation. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2003. 254(1-2). 319-26. doi: 10.1023/a:1027354005498.
- Pankiv V. Efficacy of Using Alpha-Lipoic Acid in Diabetic Neuropathy. International Journal of Endocrinology (Ukraine). 2015. 5. doi: 10.22141/2224-0721.2.66.2015.75440.
- Vasdev S., Ford C.A., Parai S., Longerich L., Gadag V. Dietary alpha-lipoic acid supplementation lowers blood pressure in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J. Hypertens. 2000. 18(5). 567-73. doi: 10.1097/00004872-200018050-00009.
- Vasdev S., Gill V., Parai S., Gadag V. Dietary lipoic acid supplementation attenuates hypertension in Dahl salt sensitive rats. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2005. 275(1-2). 135-41. doi: 10.1007/s11010-005-1095-7.
- Louhelainen M., Merasto S., Finckenberg P., Lapatto R., Cheng Z.J., Mervaala E.M. Lipoic acid supplementation prevents cyclosporine-induced hypertension and nephrotoxicity in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J. Hypertens. 2006. 24(5). 947-56. doi: 10.1097/01.hjh.0000222766.37971.9f.
- El Midaoui A., de Champlain J. Prevention of hypertension, insulin resistance, and oxidative stress by alpha-lipoic acid. Hypertension. 2002. 39(2). 303-7. doi: 10.1161/hy0202.104345.
- Midaoui A.E., Elimadi A., Wu L., Haddad P.S., de Champlain J. Lipoic acid prevents hypertension, hyperglycemia, and the increase in heart mitochondrial superoxide production. Am. J. Hypertens. 2003. 16(3). 173-9. doi: 10.1016/s0895-7061(02)03253-3.
- Takaoka M., Kobayashi Y., Yuba M., Ohkita M., Matsumura Y. Effects of alpha-lipoic acid on deoxycorticosterone acetate-salt-induced hypertension in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2001. 424(2). 121-9. doi: 10.1016/s0014-2999(01)01120-7.
- McMackin C.J., Widlansky M.E., Hamburg N.M., Huang A.L., Weller S., Holbrook M. et al. Effect of combined treatment with alpha-Lipoic acid and acetyl-L-carnitine on vascular function and blood pressure in patients with coronary artery disease. J. Clin. Hypertens (Greenwich). 2007. 9(4). 249-55. doi: 10.1111/j.1524-6175.2007.06052.x.
- Packer L., Witt E.H., Tritschler H.J. alpha-Lipoic acid as a biological antioxidant. Free Radic Biol. Med. 1995. 19(2). 227-50. doi: 10.1016/0891-5849(95)00017-r.
- Kunt T., Forst T., Wilhelm A., Tritschler H., Pfuetzner A., Harzer O., Engelbach M. et al. Alpha-lipoic acid reduces expression of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 and endothelial adhesion of human monocytes after stimulation with advanced glycation end products. Clin. Sci (Lond). 1999. 96(1). 75-82. PMID: 9857109.
- Kim H.S., Kim H.J., Park K.G., Kim Y.N., Kwon T.K., Park J.Y., Lee K.U. et al. Alpha-lipoic acid inhibits matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression by inhibiting NF-kappaB transcriptional activity. Exp. Mol. Med. 2007. 39(1). 106-13. doi: 10.1038/emm.2007.12.
- Chaudhary P., Marracci G.H., Bourdette D.N. Lipoic acid inhibits expression of ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 by CNS endothelial cells and T cell migration into the spinal cord in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2006. 175(1-2). 87-96. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2006.03.007.
- Lee E.Y., Lee C.K., Lee K.U., Park J.Y., Cho K.J., Cho Y.S., Lee H.R. et al. Alpha-lipoic acid suppresses the development of collagen-induced arthritis and protects against bone destruction in mice. Rheumatol. Int. 2007. 27(3). 225-33. doi: 10.1007/s00296-006-0193-5. E
- Morini M., Roccatagliata L., Dell’Eva R., Pedemonte E., Furlan R., Minghelli S., Giunti D. et al. Alpha-lipoic acid is effective in prevention and treatment of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2004. 148(1-2). 146-53. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2003.11.021.
- Marracci G.H., Marquardt W.E., Strehlow A., McKeon G.P., Gross J., Buck D.C., Kozell L.B., Bourdette D.N. Lipoic acid downmodulates CD4 from human T lymphocytes by dissociation of p56(Lck). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006. 344(3). 963-71. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.03.172.
- Schillace R.V., Pisenti N., Pattamanuch N., Galligan S., Marracci G.H., Bourdette D.N., Carr D.W. Lipoic acid stimulates cAMP production in T lymphocytes and NK cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007. 354(1). 259-64. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.12.195.
- Zhang W.J., Frei B. Alpha-lipoic acid inhibits TNF-alpha-induced NF-kappaB activation and adhesion molecule expression in human aortic endothelial cells. FASEB J. 2001. 15(13). 2423-32. doi: 10.1096/fj.01-0260com.
- Ikeda U., Ito T., Shimada K. Interleukin-6 and acute coronary syndrome. Clin. Cardiol. 2001. 24(11). 701-4. doi: 10.1002/clc.4960241103.

/76.jpg)
/79.jpg)