Международный эндокринологический журнал Том 17, №4, 2021
Вернуться к номеру
Неалкогольна жирова хвороба печінки: час для змін
Авторы: Єфіменко Т.І.(1), Микитюк М.Р.(1, 2)
(1) — ДУ «Інститут проблем ендокринної патології ім. В.Я. Данилевського НАМН України», м. Харків, Україна
(2) — Харківська медична академія післядипломної освіти, м. Харків, Україна
Рубрики: Эндокринология
Разделы: Справочник специалиста
Версия для печати
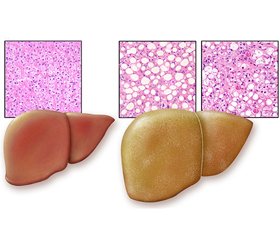
Огляд містить оновлену інформацію щодо епідеміології, етіології, патогенезу, діагностики, лікування і профілактики неалкогольної жирової хвороби печінки (НАЖХП). Ми провели пошук термінів, включаючи «НАЖХП», «неалкогольний стеатогепатит» (НАСГ), «метаболічний синдром» та «цукровий діабет 2-го типу» (ЦД 2-го типу) в літературних матеріалах, опублікованих за останні 5 років, із використанням баз даних Scopus, Web of Science, CyberLeninka, PubMed. Поняття НАЖХП включає дві морфологічні форми захворювання з різним прогнозом: неалкогольний жировий гепатоз і НАСГ. Тяжкість захворювання за НАСГ досить варіабельна, включаючи фіброз, цироз і гепатоцелюлярну карциному. НАЖХП — спектр жирових розладів печінки вірусної, автоімунної, індукованої наркотиками та генетичної етіології, що виникають не внаслідок зловживання алкоголем, — нещодавно була перейменована на метаболічну (дисфункціональну) асоційовану жирову хворобу печінки (МАЖХП). Середня поширеність НАЖХП становить приблизно 25 % серед дорослого населення у світі, а в деяких регіонах — понад 30 %. Збільшення поширеності даної патології відбувається паралельно глобальній епідемії ожиріння та ЦД 2-го типу у світі. Настав час досягти загального консенсусу в науковому товаристві щодо зміни номенклатури та переходу від негативного до позитивного визначення НАЖХП/НАСГ. Нова номенклатура вказує на позитивні детермінанти захворювання, а саме на тісний зв’язок із порушеннями обміну речовин замість того, щоб визначати його тим, чим він не є (тобто неалкогольною). Абревіатура МАЖХП точніше розкриває наявні знання про жирові захворювання печінки, пов’язані з метаболічною дисфункцією, і повинна замінити НАЖХП/НАСГ, оскільки це буде стимулювати зусилля дослідницького товариства щодо оновлення номенклатури та субфенотипу захворювання і пришвидшить поступальний шлях до нових методів лікування. Важливо, щоб лікарі первинної ланки, ендокринологи та інші спеціалісти були обізнані про масштаби та довгострокові наслідки НАЖХП. Рання ідентифікація хворих на НАСГ може сприяти поліпшенню результатів лікування, уникненню трансплантації печінки у хворих із декомпенсованим цирозом. На сьогодні не існує методів ефективного лікування НАЖХП, тому важливо дотримуватися мультидисциплінарного підходу, під яким розуміють застосування заходів, спрямованих на покращення прогнозу, зниження ризику смертності, пов’язаної з НАЖХП, розвитку цирозу або гепатоцелюлярної карциноми. Епідеміологічні дані вказують на тісний зв’язок між нездоровим способом життя і НАЖХП, тому корекція способу життя необхідна всім пацієнтам. У терапії НАЖХП використовують сенситайзери інсуліну, статини, інгібітор абсорбції холестерину езетиміб, гепатопротектори, антиоксиданти, інкретинові аналоги, інгібітори дипептидилпептидази 4, пентоксифілін, пробіотики, блокатори рецептора ангіотензинперетворюючого ферменту, ендоканабіноїдні антагоністи.
The review contains updated information on the epidemiology, etiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis, treatment and prevention of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). We searched for terms including NAFLD, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes mellitus in literature published over the past 5 years using the Scopus, Web of Science, CyberLeninka, PubMed databases. The concept of NAFLD includes two morphological forms of the disease with different prognosis: non-alcoholic fatty hepatosis and NASH. The severity of NASH is quite variable, including fibrosis, cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. NAFLD, a spectrum of fatty liver disorders of viral, autoimmune, drug-induced, and genetic origin, which are not caused by alcohol abuse, has recently been renamed as metabolic (dysfunction) associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD). The average prevalence of NAFLD is approximately 25 % among the adult population worldwide, and in some regions exceeds 30 %. An increase in the prevalence of this pathology is in parallel with the global epidemic of obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus in the world. It is time to reach a general consensus in the scientific community on changing the nomenclature and moving from a negative to a positive definition of NAFLD/NASH. The new nomenclature points to the “positive” determinants of the disease, namely the close relationship with metabolic disorders, instead of defining it as what it is not (ie. non-alcoholic). The MAFLD abbreviation more accurately discloses existing knowledge about fatty liver diseases associated with metabolic dysfunction and should replace NAFLD/NASH, as this will stimulate the research community’s efforts to update the disease nomenclature and subphenotype and accelerate the transition to new treatments. It is important that primary care physicians, endocrinologists, and other specialists are aware of the extent and long-term consequences of NAFLD. Early identification of patients with NASH can help improve treatment outcomes, avoid liver transplantation in patients with decompensated cirrhosis. There are currently no effective treatments for NAFLD, so it is important to follow a multidisciplinary approach, which means using measures to improve prognosis, reduce the risk of death associated with NAFLD, the development of cirrhosis or hepatocellular carcinoma. Epidemiological data suggest a close relationship between unhealthy lifestyles and NAFLD, so lifestyle adjustments are needed to all patients. Insulin sensitizers, statins, ezetimibe, a cholesterol absorption inhibitor, hepatoprotectors, antioxidants, incretin analogues, dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors, pentoxifylline, probiotics, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, and endocannabinoid antagonists are used in the treatment of NAFLD.
неалкогольна жирова хвороба печінки; метаболічно асоційована жирова хвороба печінки; огляд
non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; metabolic associated fatty liver disease; review
- European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL); European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD); European Association for the Study of Obesity (EASO). EASL-EASD-EASO Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Management of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Obes. Facts. 2016. 9(2). 65-90. doi: 10.1159/000443344. Epub. 2016, Apr 8. PMID: 27055256; PMCID: PMC5644799.
- Bedossa P. Pathology of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Liver Int. 2017 Jan. 37, Suppl 1. 85-89. doi: 10.1111/liv.13301. PMID: 28052629.
- Friedman S.L., Neuschwander-Tetri B.A., Rinella M., Sanyal A.J. Mechanisms of NAFLD development and therapeutic strategies. Nat. Med. 2018 Jul. 24(7). 908-922. doi: 10.1038/s41591-018-0104-9.
- Eslam M., Sanyal A.J., George J. International Consensus Panel. MAFLD: A Consensus-Driven Proposed Nomenclature for Metabolic Associated Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology. 2020. 158(7). 1999-2014. e1. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.11.312.
- Choi H.S.J., Brouwer W.P., Zanjir W.M.R., de Man R.A., Feld J.J., Hansen B.E., Janssen H.L.A., Patel K. Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Is Associated With Liver-Related Outcomes and All-Cause Mortality in Chronic Hepatitis B. Hepatology. 2020 Feb. 71(2). 539-548. doi: 10.1002/hep.30857.
- Brunt E.M., Ramrakhiani S., Cordes B.G., Neuschwander-Tetri B.A., Janney C.G., Bacon B.R., Di Bisceglie A.M. Concurrence of histologic features of steatohepatitis with other forms of chronic liver disease. Mod. Pathol. 2003 Jan. 16(1). 49-56. doi: 10.1097/01.MP.0000042420.21088.C7.
- Bellentani S., Tiribelli C. Is it time to change NAFLD and NASH nomenclature? Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017 Aug. 2(8). 547-548. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(17)30146-2. PMID: 28691681.
- Castera L., Friedrich-Rust M., Loomba R. Noninvasive Assessment of Liver Disease in Patients With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology. 2019. 156(5). 1264-1281.e4. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.12.036.
- Younossi Z., Tacke F., Arrese M., Chander Sharma B., Mostafa I., Bugianesi E., Wai-Sun Wong V. et al. Global Perspectives on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Hepatology. 2019 Jun. 69(6). 2672-2682. doi: 10.1002/hep.30251.
- Fiorucci S., Biagioli M., Distrutti E. Future trends in the treatment of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Pharmacol. Res. 2018. 134. 289-298. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2018.07.014.
- Pankiv V.I., Yuzvenko T.Yu., Pashkovska N.V., Pankiv I.V. Effect of vitamin D on insulin resistance and anthropometric parameters in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Clinical Endocrinology and Endocrine Surgery. 2019. 1(65). 53-58. doi: 10.30978/CEES-2019-1-53.
- Vernon G., Baranova A., Younossi Z.M. Systematic review: the epidemiology and natural history of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in adults. Aliment Pharmacol. Ther. 2011. 34(3). 274-285. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2011.04724.x.
- Younossi Z.M., Stepanova M., Negro F., Hallaji S., Younossi Y., Lam B., Srishord M. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in lean individuals in the United States. Medicine (Baltimore). 2012. 91(6). 319-327. doi: 10.1097/MD.0b013e3182779d49.
- Schwimmer J.B., Deutsch R., Kahen T., Lavine J.E., Stanley C., Behling C. Prevalence of fatty liver in children and adolescents. Pediatrics. 2006 Oct. 118(4). 1388-1393. doi: 10.1542/peds.2006-1212.
- Rinella M.E. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review. JAMA. 2015, Jun 9. 313(22). 2263-2273. doi: 10.1001/jama.2015.5370.
- Cotter T.G., Rinella M. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease 2020: The State of the Disease. Gastroenterology. 2020 May. 158(7). 1851-1864. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.01.052.
- Younossi Z.M., Golabi P., de Avila L., Paik J.M., Srishord M., Fukui N., Qiu Y. et al. The global epidemiology of NAFLD and NASH in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Hepatol. 2019 Oct. 71(4). 793-801. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.06.021.
- Ludwig J., Viggiano T.R., McGill D.B., Oh B.J. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: Mayo Clinic experiences with a hitherto unnamed disease. Mayo Clin. Proc. 1980. 55(7). 434-438. PMID: 7382552.
- Lazo M., Clark J.M. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and type 2 diabetes: a burgeoning problem with unclear solutions. Hepatobiliary Surg. Nutr. 2020. 9(4). 514-517. doi: 10.21037/hbsn.2019.11.28.
- Frerichs F.T. A Clinical Treatise on Diseases of the Liver. 1861. Vol. II. Р. 34. New Syden. Soc., London.
- Pankiv V. Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. The Effects of Metformin. International Journal of Endocrinology (Ukraine). 2013. 5. 55-63. doi: 10.22141/2224-0721.5.53.2013.84493.
- Ekstedt M., Franzén L.E., Mathiesen U.L., Thorelius L., Holmqvist M., Bodemar G., Kechagias S. Long-term follow-up of patients with NAFLD and elevated liver enzymes. Hepatology. 2006 Oct. 44(4). 865-873. doi: 10.1002/hep.21327.
- White D.L., Kanwal F., El-Serag H.B. Association between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and risk for hepatocellular cancer, based on systematic review. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012 Dec. 10(12). 1342-1359.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2012.10.001.
- Chalasani N., Younossi Z., Lavine J.E., Charlton M., Cusi K., Rinella M., Harrison S.A., et al. The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice guidance from the Ameri–can Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2018 Jan. 67(1). 328-357. doi: 10.1002/hep.29367.
- Ekstedt M., Hagström H., Nasr P., Fredrikson M., Stål P., Kechagias S., Hultcrantz R. Fibrosis stage is the strongest predictor for disease-specific mortality in NAFLD after up to 33 years of follow-up. Hepatology. 2015 May. 61(5). 1547-1554. doi: 10.1002/hep.27368.
- Angulo P., Kleiner D.E., Dam-Larsen S., Adams L.A., Bjornsson E.S., Charatcharoenwitthaya P., Mills P.R. et al. Liver Fibrosis, but No Other Histologic Features, Is Associated With Long-term Outcomes of Patients With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology. 2015 Aug. 149(2). 389-397.e10. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.04.043.
- Dulai P.S., Singh S., Patel J., Soni M., Prokop L.J., Younossi Z., Sebastiani G. et al. Increased risk of mortality by fibrosis stage in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Hepatology. 2017 May. 65(5). 1557-1565. doi: 10.1002/hep.29085.
- Singh S., Allen A.M., Wang Z., Prokop L.J., Murad M.H., Loomba R. Fibrosis progression in nonalcoholic fatty liver vs nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of paired-biopsy studies. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015 Apr. 13(4). 643-654.e1-9; quiz e39-40. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2014.04.014.
- Angulo P., Hui J.M., Marchesini G., Bugianesi E., George J., Farrell G.C., Enders F. et al. The NAFLD fibrosis score: a noninvasive system that identifies liver fibrosis in patients with NAFLD. Hepatology. 2007 Apr. 45(4). 846-854. doi: 10.1002/hep.21496.
- Sørensen H.T., Mellemkjaer L., Jepsen P., Thulstrup A.M., Baron J., Olsen J.H., Vilstrup H. Risk of cancer in patients hospitalized with fatty liver: a Danish cohort study. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2003 Apr. 36(4). 356-359. doi: 10.1097/00004836-200304000-00015.
- McPherson S., Hardy T., Henderson E., Burt A.D., Day C.P., Anstee Q.M. Evidence of NAFLD progression from steatosis to fibrosing-steatohepatitis using paired biopsies: implications for prognosis and clinical management. J. Hepatol. 2015 May. 62(5). 1148-1155. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2014.11.034.
- Starley B.Q., Calcagno C.J., Harrison S.A. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma: a weighty connection. Hepatology. 2010 May. 51(5). 1820-1832. doi: 10.1002/hep.23594. PMID: 20432259.
- Yasui K., Hashimoto E., Komorizono Y., Koike K., Arii S., Imai Y., Shima T. et al. Japan NASH Study Group, Ministry of Health, Labour, and Welfare of Japan. Characteristics of patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis who develop hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011 May. 9(5). 428-433; quiz e50. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2011.01.023.
- White D.L., Kanwal F., El-Serag H.B. Association between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and risk for hepatocellular cancer, based on systematic review. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012 Dec. 10(12). 1342-1359. e2. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2012.10.001.
- Milić S., Stimac D. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/steatohepatitis: epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinical presentation and treatment. Dig. Dis. 2012. 30(2). 158-162. doi: 10.1159/000336669.
- Chalasani N., Younossi Z., Lavine J.E., Diehl A.M., Brunt E.M., Cusi K., Charlton M., Sanyal A.J. The diagnosis and management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: practice Guideline by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, American College of Gastroenterology, and the American Gastroenterological Association. Hepatology. 2012 Jun. 55(6). 2005-2023. doi: 10.1002/hep.25762. PMID: 22488764.
- Porepa L., Ray J.G., Sanchez-Romeu P., Booth G.L. Newly diagnosed diabetes mellitus as a risk factor for serious liver disease. CMAJ. 2010, Aug 10. 182(11). 526-531. doi: 10.1503/cmaj.092144.
- Shulman G.I. Cellular mechanisms of insulin resistance. J. Clin. Invest. 2000 Jul. 106(2). 171-176. doi: 10.1172/JCI10583.
- Ciupińska-Kajor M., Hartleb M., Kajor M., Kukla M., Wyleżoł M., Lange D., Liszka L. Hepatic angiogenesis and fibrosis are common features in morbidly obese patients. Hepatol. Int. 2013 Mar. 7(1). 233-240. doi: 10.1007/s12072-011-9320-9.
- National Guideline Centre (UK). Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Assessment and Management. London: National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (UK). 2016 Jul. PMID: 27441333.
- World Gastroenterology Organization, Global Guidelines Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis June 2012 English. World Gastroenterology Organisation.
- Donnelly K.L., Smith C.I., Schwarzenberg S.J., Jessurun J., Boldt M.D., Parks E.J. Sources of fatty acids stored in liver and secreted via lipoproteins in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Clin. Invest. 2005 May. 115(5). 1343-1351. doi: 10.1172/JCI23621.
- Maurice J., Manousou P. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin. Med. (Lond). 2018. 18(3). 245-250. doi: 10.7861/clinmedicine.18-3-245.
- Jelenik T., Kaul K., Séquaris G., Flögel U., Phielix E., Kotzka J., Knebel B. et al. Mechanisms of Insulin Resistance in Primary and Secondary Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver. Diabetes. 2017. 66(8). 2241-2253. doi: 10.2337/db16-1147.
- Finck B.N. Targeting Metabolism, Insulin Resistance, and Diabetes to Treat Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Diabetes. 2018 Dec. 67(12). 2485-2493. doi: 10.2337/dbi18-0024.
- Kobyliak N.M., Abenavoli L., Pavlenko G.P., Komisarenko Yu.I. Gut microbiota composition changes associated with obesity: new lights from metagenomic analysis. International Journal of Endocrinology (Ukraine). 2020. 16(8). 78-85. doi: 10.22141/2224-0721.16.8.2020.222886.
- Greco D., Kotronen A., Westerbacka J., Puig O., Arkkila P., Kiviluoto T. et al. Gene expression in human NAFLD. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2008. 294(5). 1281-1287. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00074.2008.
- Fabbrini E., Magkos F., Mohammed B.S., Pietka T., Abumrad N.A., Patterson B.W., Okunade A., Klein S. Intrahepatic fat, not visceral fat, is linked with metabolic complications of obesity. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2009. 106(36). 15430-15435. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0904944106.
- Jou J., Choi S.S., Diehl A.M. Mechanisms of disease progression in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Semin. Liver Dis. 2008 Nov. 28(4). 370-379. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1091981.
- Jiang W., Wu N., Wang X., Chi Y., Zhang Y., Qiu X., Hu Y., Li J., Liu Y. Dysbiosis gut microbiota associated with inflammation and impaired mucosal immune function in intestine of humans with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Sci. Rep. 2015. 5. 8096. doi: 10.1038/srep08096.
- Anderson N., Borlak J. Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic targets in steatosis and steatohepatitis. Pharmacol. Rev. 2008 Sep. 60(3). 311-357. doi: 10.1124/pr.108.00001.
- Joshi-Barve S., Barve S.S., Amancherla K., Gobejishvili L., Hill D., Cave M., Hote P., McClain C.J. Palmitic acid induces production of proinflammatory cytokine interleukin-8 from hepatocytes. Hepatology. 2007 Sep. 46(3). 823-830. doi: 10.1002/hep.21752. PMID: 17680645.
- Ramadori G., Armbrust T. Cytokines in the liver. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2001 Jul. 13(7). 777-84. doi: 10.1097/00042737-200107000-00004. PMID: 11474306.
- Torisu T., Sato N., Yoshiga D., Kobayashi T., Yoshioka T., Mori H., Iida M., Yoshimura A. The dual function of hepatic SOCS3 in insulin resistance in vivo. Genes Cells. 2007 Feb. 12(2). 143-154. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2443.2007.01044.x. PMID: 17295835.
- Shao R.X., Zhang L., Peng L.F., Sun E., Chung W.J., Jang J.Y., Tsai W.L., Hyppolite G., Chung R.T. Suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 suppresses hepatitis C virus replication in an mTOR-dependent manner. J. Virol. 2010 Jun. 84(12). 6060-6069. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02484-09.
- Targher G., Lonardo A., Byrne C.D. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and chronic vascular complications of diabetes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018 Feb. 14(2). 99-114. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2017.173. Epub. 2017, Dec 29. PMID: 29286050.
- Tarantino G., Finelli C. What about non-alcoholic fatty liver disease as a new criterion to define metabolic syndrome? World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, Jun 14. 19(22). 3375-3384. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i22.3375.
- Attar B.M., Van Thiel D.H. Current concepts and management approaches in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Scientific World Journal. 2013. 2013. 481893. doi: 10.1155/2013/481893.
- Targher G., Bertolini L., Rodella S., Lippi G., Franchini M., Zoppini G., Muggeo M., Day C.P. NASH predicts plasma inflammatory biomarkers independently of visceral fat in men. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2008 Jun. 16(6). 1394-1399. doi: 10.1038/oby.2008.64.
- Milner K.L., van der Poorten D., Xu A., Bugianesi E., Kench J.G., Lam K.S., Chisholm D.J., George J. Adipocyte fatty acid binding protein levels relate to inflammation and fibrosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2009 Jun. 49(6). 1926-1934. doi: 10.1002/hep.22896. PMID: 19475694.
- Mofrad P., Contos M.J., Haque M., Sargeant C., Fisher R.A., Luketic V.A., Sterling R.K., Shiffman M.L., Stravitz R.T., Sanyal A.J. Clinical and histologic spectrum of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease associated with normal ALT values. Hepatology. 2003 Jun. 37(6). 1286-1292. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2003.50229. PMID: 12774006.
- Musso G., Gambino R., Cassader M. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease from pathogenesis to management: an update. Obes. Rev. 2010 Jun. 11(6). 430-445. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-789X.2009.00657.x.
- Milić S., Lulić D., Štimac D. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and obesity: biochemical, metabolic and clinical presentations. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, Jul 28. 20(28). 9330-9337. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i28.9330.
- Monsour H.P. Jr, Frenette C.T., Wyne K. Fatty liver: a link to cardiovascular disease — its natural history, pathogenesis, and treatment. Methodist Debakey Cardiovasc. J. 2012 Jul-Sep. 8(3). 21-25. doi: 10.14797/mdcj-8-3-21. PMID: 23227282; PMCID: PMC3487573.
- Abiru S., Migita K., Maeda Y., Daikoku M., Ito M., Ohata K., Nagaoka S. et al. Serum cytokine and soluble cytokine receptor levels in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Liver Int. 2006 Feb. 26(1). 39-45. doi: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2005.01191.x.
- Italian Association for the Study of the Liver (AISF) AISF position paper on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): updates and future directions. Dig. Liver Dis. 2017. 49. 471-483. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2017.01.147.
- Glen J., Floros L., Day C., Pryke R. Guideline Development Group. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): summary of NICE guidance. BMJ. 2016, Sep 7. 354. i4428. doi: 10.1136/bmj.i4428. PMID: 27605111.
- Chalasani N., Younossi Z., Lavine J.E., Charlton M., Cusi K., Rinella M., Harrison S.A. et al. The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2018 Jan. 67(1). 328-357. doi: 10.1002/hep.29367.
- Portillo-Sanchez P., Bril F., Maximos M., Lomonaco R., Biernacki D., Orsak B., Subbarayan S. et al. High Prevalence of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Normal Plasma Aminotransferase Levels. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015 Jun. 100(6). 2231-2238. doi: 10.1210/jc.2015-1966.
- National Guideline Centre (UK). Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Assessment and Management. London: National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (UK); 2016 Jul. PMID: 27441333.
- Kleiner D.E., Brunt E.M., Van Natta M., Behling C., Contos M.J., Cummings O.W., Ferrell L.D. et al. Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Clinical Research Network. Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2005 Jun. 41(6). 1313-1321. doi: 10.1002/hep.20701. PMID: 15915461.
- Bedossa P., Poitou C., Veyrie N., Bouillot J.L., Basdevant A., Paradis V., Tordjman J., Clement K. Histopathological algorithm and scoring system for evaluation of liver lesions in morbidly obese patients. Hepatology. 2012 Nov. 56(5). 1751-1759. doi: 10.1002/hep.25889.
- Kleiner D.E., Makhlouf H.R. Histology of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis in Adults and Children. Clin. Liver Dis. 2016 May. 20(2). 293-312. doi: 10.1016/j.cld.2015.10.011.
- Sandrin L., Fourquet B., Hasquenoph J.M., Yon S., Fournier C., Mal F., Christidis C. et al. Transient elastography: a new noninvasive method for assessment of hepatic fibrosis. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2003 Dec. 29(12). 1705-1713. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2003.07.001.
- Attar B.M., Van Thiel D.H. Current concepts and management approaches in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Scientific World Journal. 2013. 2013. 481893. doi: 10.1155/2013/481893.
- Castéra L., Foucher J., Bernard P.H., Carvalho F., Allaix D., Merrouche W., Couzigou P., de Lédinghen V. Pitfalls of liver stiffness measurement: a 5-year prospective study of 13,369 examinations. Hepatology. 2010 Mar. 51(3). 828-835. doi: 10.1002/hep.23425.
- Wong G.L., Wong V.W., Chim A.M., Yiu K.K., Chu S.H., Li M.K., Chan H.L. Factors associated with unreliable liver stiffness measurement and its failure with transient elastography in the Chinese population. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011 Feb. 26(2). 300-305. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2010.06510.x. PMID: 21261720.
- Bonder A., Tapper E.B., Afdhal N.H. Contemporary assessment of hepatic fibrosis. Clin. Liver Dis. 2015 Feb. 19(1). 123-134. doi: 10.1016/j.cld.2014.09.007.
- Szczepaniak L.S., Nurenberg P., Leonard D., Browning J.D., Reingold J.S., Grundy S., Hobbs H.H., Dobbins R.L. Magnetic resonance spectroscopy to measure hepatic triglyceride content: prevalence of hepatic steatosis in the general population. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005. 288. 462-468. doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00064.2004.
- Bonekamp S., Tang A., Mashhood A., Wolfson T., Changchien C., Middleton M.S., Clark L. et al. Spatial distribution of MRI-Determined hepatic proton density fat fraction in adults with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging. 2014 Jun. 39(6). 1525-1532. doi: 10.1002/jmri.24321.
- Caussy C., Reeder S.B., Sirlin C.B., Loomba R. Noninvasive, Quantitative Assessment of Liver Fat by MRI-PDFF as an Endpoint in NASH Trials. Hepatology. 2018 Aug. 68(2). 763-772. doi: 10.1002/hep.29797.
- Gu J., Liu S., Du S., Zhang Q., Xiao J., Dong Q., Xin Y. Diagnostic value of MRI-PDFF for hepatic steatosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a meta-analysis. Eur. Radiol. 2019 Jul. 29(7). 3564-3573. doi: 10.1007/s00330-019-06072-4.
- Bedogni G., Bellentani S., Miglioli L., Masutti F., Passalacqua M., Castiglione A., Tiribelli C. The Fatty Liver Index: a simple and accurate predictor of hepatic steatosis in the general population. BMC Gastroenterol. 2006, Nov 2. 6. 33. doi: 10.1186/1471-230X-6-33.
- Kotronen A., Peltonen M., Hakkarainen A., Sevastianova K., Bergholm R., Johansson L.M., Lundbom N. et al. Prediction of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and liver fat using metabolic and genetic factors. Gastroenterology. 2009 Sep. 137(3). 865-872. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2009.06.005.
- Lee J.H., Kim D., Kim H.J., Lee C.H., Yang J.I., Kim W., Kim Y.J. et al. Hepatic steatosis index: a simple screening tool reflecting nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Dig. Liver Dis. 2010 Jul. 42(7). 503-508. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2009.08.002.
- Amato M.C., Giordano C., Galia M., Criscimanna A., Vitabile S., Midiri M., Galluzzo A. AlkaMeSy Study Group. Visceral Adiposity Index: a reliable indicator of visceral fat function associated with cardiometabolic risk. Diabetes Care. 2010 Apr. 33(4). 920-922. doi: 10.2337/dc09-1825.
- Fedchuk L., Nascimbeni F., Pais R., Charlotte F., Housset C., Ratziu V. LIDO Study Group. Performance and limitations of steatosis biomarkers in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014 Nov. 40(10). 1209-1222. doi: 10.1111/apt.12963.
- Dixon J.B., Bhathal P.S., O’Brien P.E. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: predictors of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and liver fibrosis in the severely obese. Gastroenterology. 2001 Jul. 121(1). 91-100. doi: 10.1053/gast.2001.25540. PMID: 11438497.
- Byrne C.D., Patel J., Scorletti E., Targher G. Tests for diagnosing and monitoring non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in adults. BMJ. 2018, Jul 12. 362. k2734. doi: 10.1136/bmj.k2734. PMID: 30002017.
- Lichtinghagen R., Pietsch D., Bantel H., Manns M.P., Brand K., Bahr M.J. The Enhanced Liver Fibrosis (ELF) score: normal values, influence factors and proposed cut-off values. J. Hepatol. 2013 Aug. 59(2). 236-242. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.03.016.
- http://nafldscore.com
- Musso G., Gambino R., Cassader M., Pagano G. Meta-analysis: natural history of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and diagnostic accuracy of non-invasive tests for liver disease severity. Ann. Med. 2011 Dec. 43(8). 617-649. doi: 10.3109/07853890.2010.518623.
- Wieckowska A., McCullough A.J., Feldstein A.E. Noninvasive diagnosis and monitoring of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: present and future. Hepatology. 2007 Aug. 46(2). 582-589. doi: 10.1002/hep.21768. PMID: 17661414.
- Zelber-Sagi S., Ratziu V., Oren R. Nutrition and physical activity in NAFLD: an overview of the epidemiological evidence. World J. Gastroenterol. 2011, Aug 7. 17(29). 3377-3389. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i29.3377.
- Petersen K.F., Dufour S., Befroy D., Lehrke M., Hendler R.E., Shulman G.I. Reversal of nonalcoholic hepatic steatosis, hepatic insulin resistance, and hyperglycemia by moderate weight reduction in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2005 Mar. 54(3). 603-608. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.54.3.603.
- Vilar-Gomez E., Martinez-Perez Y., Calzadilla-Bertot L., Torres-Gonzalez A., Gra-Oramas B., Gonzalez-Fabian L., Friedman S.L. et al. Weight Loss Through Lifestyle Modification Significantly Reduces Features of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology. 2015 Aug. 149(2). 367-378. e5. quiz e14-5. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.04.005.
- Adams L.A., Sanderson S., Lindor K.D., Angulo P. The histological course of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a longitudinal study of 103 patients with sequential liver biopsies. J. Hepatol. 2005 Jan. 42(1). 132-138. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2004.09.012.
- Sanyal A.J., Friedman S.L., McCullough A.J., Dimick-Santos L. American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases; United States Food and Drug Administration. Challenges and opportunities in drug and biomarker development for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: findings and recommendations from an American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases-U.S. Food and Drug Administration Joint Workshop. Hepatology. 2015 Apr. 61(4). 1392-1405. doi: 10.1002/hep.27678.
- Singh S., Osna N.A., Kharbanda K.K. Treatment options for alcoholic and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A review. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, Sep 28. 23(36). 6549-6570. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i36.6549.
- Loomba R., Lutchman G., Kleiner D.E., Ricks M., Feld J.J., Borg B.B., Modi A., Nagabhyru P., Sumner A.E., Liang T.J., Hoofnagle J.H. Clinical trial: pilot study of metformin for the treatment of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2009 Jan. 29(2). 172-182. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2008.03869.x.
- Haukeland J.W., Konopski Z., Eggesbø H.B., von Volkmann H.L., Raschpichler G., Bjøro K., Haaland T., Løberg E.M., Birkeland K. Metformin in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a randomized, controlled trial. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2009. 44(7). 853-860. doi: 10.1080/00365520902845268.
- Yki-Järvinen H. Thiazolidinediones. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, Sep 9. 351(11). 1106-1118. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra041001.
- Bajaj M., Suraamornkul S., Piper P., Hardies L.J., Glass L., Cersosimo E., Pratipanawatr T. et al. Decreased plasma adiponectin concentrations are closely related to hepatic fat content and hepatic insulin resistance in pioglitazone-treated type 2 diabetic patients. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004. 89(1). 200-206. doi: 10.1210/jc.2003-031315.
- Agarwal B., Lamba B.M.S., Sharma N., Tanwar M. Prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in patients with prediabetes. International Journal of Endocrinology (Ukraine). 2021. 17(1). 35-40. doi: 10.22141/2224-0721.17.1.2021.226427.
- Ratziu V., Giral P., Jacqueminet S., Charlotte F., Hartemann-Heurtier A., Serfaty L., Podevin P. et al. LIDO Study Group. Rosiglitazone for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: one-year results of the randomized placebo-controlled Fatty Liver Improvement with Rosiglitazone Therapy (FLIRT) Trial. Gastroenterology. 2008 Jul. 135(1). 100-110. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.03.078.
- Sanyal A.J., Chalasani N., Kowdley K.V., McCullough A., Diehl A.M., Bass N.M., Neuschwander-Tetri B.A. et al. NASH CRN. Pioglitazone, vitamin E, or placebo for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, May 6. 362(18). 1675-1685. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0907929.
- Miller E.R. 3rd, Pastor-Barriuso R., Dalal D., Riemersma R.A., Appel L.J., Guallar E. Meta-analysis: high-dosage vitamin E supplementation may increase all-cause mortality. Ann. Intern. Med. 2005, Jan 4. 142(1). 37-46. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-142-1-200501040-00110.
- Tushuizen M.E., Bunck M.C., Pouwels P.J., van Waesberghe J.H., Diamant M., Heine R.J. Incretin mimetics as a novel therapeutic option for hepatic steatosis. Liver Int. 2006 Oct. 26(8). 1015-1057. doi: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2006.01315.x. PMID: 16953843.
- Balaban Y.H., Korkusuz P., Simsek H., Gokcan H., Gedikog–lu G., Pinar A., Hascelik G. et al. Dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DDP IV) in NASH patients. Ann. Hepatol. 2007 Oct-Dec. 6(4). 242-250. PMID: 18007554.
- Firneisz G., Varga T., Lengyel G., Fehér J., Ghyczy D., Wichmann B., Selmeci L., Tulassay Z., Rácz K., Somogyi A. Serum dipeptidyl peptidase-4 activity in insulin resistant patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a novel liver disease biomarker. PLoS One. 2010, Aug 18. 5(8). e12226. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012226.
- Baumeier C., Saussenthaler S., Kammel A., Jähnert M., Schlüter L., Hesse D., Canouil M. et al. Hepatic DPP4 DNA Methylation Associates With Fatty Liver. Diabetes. 2017 Jan. 66(1). 25-35. doi: 10.2337/db15-1716.
- Laurin J., Lindor K.D., Crippin J.S., Gossard A., Go–res G.J., Ludwig J., Rakela J., McGill D.B. Ursodeoxycholic acid or clofibrate in the treatment of non-alcohol-induced steatohepatitis: a pilot study. Hepatology. 1996 Jun. 23(6). 1464-1467. doi: 10.1002/hep.510230624. PMID: 8675165.
- Basaranoglu M., Acbay O., Sonsuz A. A controlled trial of gemfibrozil in the treatment of patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. J. Hepatol. 1999 Aug. 31(2). 384. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(99)80243-8. PMID: 10453959.
- Duman D.G., Ozdemir F., Birben E., Keskin O., Ekşioğlu-Demiralp E., Celikel C., Kalayci O., Kalayci C. Effects of pentoxi–fylline on TNF-alpha production by peripheral blood mononuclear cells in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2007 Oct. 52(10). 2520-2524. doi: 10.1007/s10620-006-9723-y.
- Van Wagner L.B., Koppe S.W., Brunt E.M., Gottstein J., Gardikiotes K., Green R.M., Rinella M.E. Pentoxifylline for the treatment of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: a randomized controlled trial. Ann. Hepatol. 2011 Jul-Sep. 10(3). 277-286. PMID: 21677329.
- Singh S., Khera R., Allen A.M., Murad M.H., Loomba R. Comparative effectiveness of pharmacological interventions for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Hepatology. 2015 Nov. 62(5). 1417-1432. doi: 10.1002/hep.27999.
- Shiffman M., Freilich B., Vuppalanchi R., Watt K., Burgess G., Morris M., Sheedy B., Schiff E. LP37: A placebo-controlled, multicenter, double-blind, randomised trial of emricasan in subjects with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and raised transaminases. J. Hepatol. 2015. 62. 282.
- Ratziu V., Harrison S.A., Francque S., Bedossa P., Lehert P., Serfaty L., Romero-Gomez M. et al. GOLDEN-505 Investigator Study Group. Elafibranor, an Agonist of the Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor-α and -δ, Induces Resolution of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Without Fibrosis Worsening. Gastroenterology. 2016 May. 150(5). 1147-1159. e5. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.01.038.
- Friedman S., Sanyal A., Goodman Z., Lefebvre E., Gottwald M., Fischer L., Ratziu V. Efficacy and safety study of cenicriviroc for the treatment of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in adult subjects with liver fibrosis: CENTAUR Phase 2b study design. Contemp. Clin. Trials. 2016 Mar. 47. 356-365. doi: 10.1016/j.cct.2016.02.012.
- Neuschwander-Tetri B.A., Loomba R., Sanyal A.J., Lavine J.E., Van Natta M.L., Abdelmalek M.F., Chalasani N. et al. NASH Clinical Research Network. Farnesoid X nuclear receptor ligand obeticholic acid for non-cirrhotic, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (FLINT): a multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2015, Mar 14. 385(9972). 956-965. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61933-4.
- Inagaki T. Research Perspectives on the Regulation and Physiological Functions of FGF21 and its Association with NAFLD. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2015, Sep 23. 6. 147. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2015.00147. PMID: 26441837; PMCID: PMC4585294.
- Safadi R., Konikoff F.M., Mahamid M., Zelber-Sagi S., Halpern M., Gilat T., Oren R. FLORA Group. The fatty acid-bile acid conjugate Aramchol reduces liver fat content in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014 Dec. 12(12). 2085-2091.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2014.04.038.
- https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01672866
- Colak Y., Ozturk O., Senates E., Tuncer I., Yorulmaz E., Adali G., Doganay L., Enc F.Y. SIRT1 as a potential therapeutic target for treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Med. Sci. Monit. 2011 May. 17(5). HY5-9. doi: 10.12659/msm.881749.
- Stephen S., Baranova A., Younossi Z.M. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and bariatric surgery. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012 Apr. 6(2). 163-171. doi: 10.1586/egh.11.97. PMID: 22375522.
- Charlton M., Kasparova P., Weston S., Lindor K., Maor-Kendler Y., Wiesner R.H., Rosen C.B., Batts K.P. Frequency of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis as a cause of advanced liver disease. Liver Transpl. 2001 Jul. 7(7). 608-614. doi: 10.1053/jlts.2001.25453.