Международный эндокринологический журнал Том 21, №2, 2025
Вернуться к номеру
Епігенетичний вплив довгих некодуючих РНК на розвиток інсулінорезистентності при метаболічно асоційованій жировій хворобі печінки (частина 1)
Авторы: O.E. Abaturov (1), V.S. Berezenko (2, 3), A.O. Nikulina (1)
(1) - Dnipro State Medical University, Dnipro, Ukraine
(2) - Bogomolets National Medical University, Kyiv, Ukraine
(3) - Ukrainian Center of Maternity and Childhood of NAMSU, Kyiv, Ukraine
Рубрики: Эндокринология
Разделы: Справочник специалиста
Версия для печати
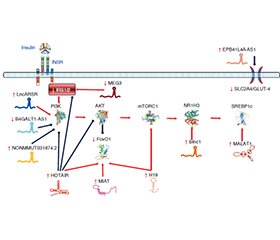
Інсулінорезистентність (ІР) метаболічного генезу є патологічним станом, в основі якого лежить зниження метаболічної відповіді інсулін-чутливих клітин на стимуляцію інсуліном. Вона часто супроводжує метаболічно асоційовану жирову хворобу печінки (МАЖХП) і є патогенетичною основою цукрового діабету (ЦД) 2-го типу. МАЖХП пов’язана з високим ризиком ЦД 2-го типу, її наявність збільшує ймовірність виникнення ЦД 2-го типу протягом наступних п’яти років життя хворого приблизно в два рази. У розвитку ІР безпосередню участь беруть довгі некодуючі РНК, визначення рівня експресії яких може суттєво підвищити ефективність діагностики й прогнозу захворювання. На сьогодні серед припущень, що пояснюють механізми виникнення ІР, домінують ліпоцентрична та глюкоцентрична гіпотези. В основі ліпоцентричної гіпотези лежить уявлення про те, що ІР є наслідком ліпотоксичної дії надлишкового внутрішньоклітинного вмісту вільних жирних кислот та їхніх похідних (діацилгліцерин, цераміди). Глюкоцентрична гіпотеза постулює, що розвиток ІР зумовлений рецидивуючими проявами гіперглікемії, які супроводжуються утворенням кінцевих продуктів глікування. Інсулінорезистентна тканина печінки характеризується підвищенням активності глюконеогенезу, виснаженням глікогенового депо та зниженням секреції тригліцеридів. Стеатоз печінки призводить до розвитку ІР, що асоціюється з посиленням активності глюконеогенезу. Селективна ІР печінки є первинною подією в системному порушенні інсулін-асоційованого сигнального шляху, викликаючи в подальшому ІР периферичних тканин. У розвитку печінкової інсулінорезистентності при МАЖХП беруть участь численні некодуючі РНК, як-от H19, MALAT1, MEG3, MIAT, SRA та інші. Довгі некодуючі РНК, рівень експресії яких підвищується в разі інсулінорезистентності печінки: Blnc1, EPB41L4A-AS1, H19, HCG18, HOTAIR, HOTTIP, LncARSR, MAYA, MALAT1, MIAT, NONMMUT031874.2. У той же час довгі некодуючі РНК, рівень експресії яких знижується при розвитку інсулінорезистентності печінки, представлені B4GALT1-AS1/LncSHGL, MEG3.
Insulin resistance (IR) of metabolic origin is a pathological condition, which is based on a decrease in the metabolic response of insulin-sensitive cells to insulin stimulation. It often accompanies metabolically associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) and is the pathogenetic basis of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). MAFLD is associated with a high risk of developing T2DM, its presence increases the likelihood of T2DM by approximately two times during the next five years of the patient’s life. Long non-coding RNAs are directly involved in the development of IR, the determination of the level of their expression can significantly increase the effectiveness of diagnosis and prognosis of the disease. Today, among the assumptions explaining the mechanisms of IR development, the lipocentric and glucocentric hypotheses dominate. The lipocentric hypothesis is based on the idea that IR is a consequence of the lipotoxic effect of excessive intracellular content of free fatty acids and their derivatives (diacylglycerol, ceramides). The glucocentric hypothesis postulates that the development of IR is due to recurrent manifestations of hyperglycemia, which are accompanied by the generation of advanced glycation end products. Insulin-resistant liver tissue is characterized by increased activity of gluconeogenesis, depletion of glycogen depot and decreased secretion of triglycerides. Hepatic steatosis leads to the development of IR, which is accompanied by increased activity of gluconeogenesis. Selective hepatic IR is the primary event in the systemic disruption of the insulin-associated signaling pathway, which subsequently leads to the development of IR of peripheral tissues. Numerous long non-coding RNAs, such as H19, MALAT1, MEG3, MIAT, SRA, and others, are involved in the development of hepatic insulin resistance in MAFLD. Long non-coding RNAs, the expression level of which increases in case of the development of hepatic insulin resistance, are Blnc1, EPB41L4A-AS1, H19, HCG18, HOTAIR, HOTTIP, LncARSR, MAYA, MALAT1, MIAT, NONMMUT031874.2. At the same time, long non-coding RNAs, the expression level of which decreases hepatic insulin resistance, are represented by B4GALT1-AS1/LncSHGL, MEG3.
діти; ожиріння; метаболічно асоційована жирова хвороба печінки; довгі некодуючі РНК; літературний огляд
children; obesity; metabolically associated fatty liver disease; long non-coding RNAs; literature review
Для ознакомления с полным содержанием статьи необходимо оформить подписку на журнал.
- Kumar S, Kelly AS. Review of Childhood Obesity: From Epi–demiology, Etiology, and Comorbidities to Clinical Assessment and Treatment. Mayo Clin Proc. 2017 Feb;92(2):251-265. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2016.09.017.
- Alipoor B, Nikouei S, Rezaeinejad F, et al. Long non-co–ding RNAs in metabolic disorders: pathogenetic relevance and potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets. J Endocrinol Invest. 2021 Oct;44(10):2015-2041. doi: 10.1007/s40618-021-01559-8.
- Abaturov A, Nikulina A. Predicting metabolically unhealthy obesity in children. Horm Res Paediatr. 2024;97(suppl 3):495. doi: 10.1159/000541189.
- Scapaticci S, D’Adamo E, Mohn A, et al. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Obese Youth With Insulin Resistance and Type 2 Diabetes. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Apr 6;12:639548. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.639548.
- Mastromauro C, Polidori N, Giannini C. Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease in obese youth with insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2022 Aug 1;34(4):414-422. doi: 10.1097/MOP.0000000000001138.
- Da Silva Rosa SC, Nayak N, Caymo AM, et al. Mechanisms of muscle insulin resistance and the cross-talk with liver and adipose tissue. Physiol Rep. 2020 Oct;8(19):e14607. doi: 10.14814/phy2.14607.
- Sakurai Y, Kubota N, Yamauchi T, et al. Role of Insulin Resistance in MAFLD. Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 16;22(8):4156. doi: 10.3390/ijms22084156.
- Marušić M, Paić M, Knobloch M, et al. NAFLD, Insulin Resistance, and Diabetes Mellitus Type 2. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021 Feb 17;2021:6613827. doi: 10.1155/2021/6613827.
- Tkach S, Pankiv V, Dorofeev A. Relationship between serum 25-hydroxyvitamine D and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. International Journal of Endocrinology (Ukraine). 2023;19(3):194-199. doi: 10.22141/2224-0721.19.3.2023.1271.
- Pearson T, Wattis JA, King JR, et al. The Effects of Insulin Resistance on Individual Tissues: An Application of a Mathe–matical Model of Metabolism in Humans. Bull Math Biol. 2016 Jun;78(6):1189-217. doi: 10.1007/s11538-016-0181-1.
- Mittra S, Bansal VS, Bhatnagar PK. From a glucocentric to a lipocentric approach towards metabolic syndrome. Drug Discov Today. 2008 Mar;13(5–6):211-8. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2008.01.006.
- Yazıcı D, Sezer H. Insulin Resistance, Obesity and Lipotoxi–city. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;960:277-304. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-48382-5_12.
- Opazo-Ríos L, Mas S, Marín-Royo G, et al. Lipotoxicity and Diabetic Nephropathy: Novel Mechanistic Insights and Therapeutic Opportunities. Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Apr 10;21(7):2632. doi: 10.3390/ijms21072632.
- James DE, Stöckli J, Birnbaum MJ. The aetiology and molecular landscape of insulin resistance. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021 Nov;22(11):751-771. doi: 10.1038/s41580-021-00390-6.
- Jeschke MG, Finnerty CC, Herndon DN, et al. Severe injury is associated with insulin resistance, endoplasmic reticulum stress response, and unfolded protein response. Ann Surg. 2012 Feb;255(2):370-8. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e31823e76e7.
- Lee SH, Park SY, Choi CS. Insulin Resistance: From Mechanisms to Therapeutic Strategies. Diabetes Metab J. 2022 Jan;46(1):15-37. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2021.0280.
- Ajoolabady A, Liu S, Klionsky DJ, et al. ER stress in obesity pathogenesis and management. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2022 Feb;43(2):97-109. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2021.11.011.
- Khalid M, Petroianu G, Adem A. Advanced Glycation End Products and Diabetes Mellitus: Mechanisms and Perspectives. Biomolecules. 2022 Apr 4;12(4):542. doi: 10.3390/biom12040542.
- Twarda-Clapa A, Olczak A, Białkowska AM, et al. Advanced Glycation End-Products (AGEs): Formation, Chemistry, Classification, Receptors, and Diseases Related to AGEs. Cells. 2022 Apr 12;11(8):1312. doi: 10.3390/cells11081312.
- Gill V, Kumar V, Singh K, et al. Advanced Glycation End Products (AGEs) May Be a Striking Link Between Modern Diet and Health. Biomolecules. 2019 Dec 17;9(12):888. doi: 10.3390/biom9120888.
- Portero-Otin M, de la Maza MP, Uribarri J. Dietary Advanced Glycation End Products: Their Role in the Insulin Resistance of Aging. Cells. 2023 Jun 21;12(13):1684. doi: 10.3390/cells12131684.
- Parwani K, Mandal P. Role of advanced glycation end products and insulin resistance in diabetic nephropathy. Arch Physiol Biochem. 2023 Feb;129(1):95-107. doi: 10.1080/13813455.2020.1797106.
- Choi E, Bai XC. The Activation Mechanism of the Insulin Receptor: A Structural Perspective. Annu Rev Biochem. 2023 Jun 20;92:247-272. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-052521-033250.
- Petersen MC, Shulman GI. Mechanisms of Insulin Action and Insulin Resistance. Physiol Rev. 2018 Oct 1;98(4):2133-2223. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00063.2017.
- Li M, Chi X, Wang Y, et al. Trends in insulin resistance: insights into mechanisms and therapeutic strategy. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022 Jul 6;7(1):216. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01073-0.
- Abaturov OE, Nikulina AO. Metabolically associated fatty liver disease in children. Dnipro: Lira; 2021. 724 p. (in Ukrainian).
- Boucher J, Kleinridders A, Kahn CR. Insulin receptor signaling in normal and insulin-resistant states. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2014 Jan 1;6(1):a009191. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a009191.
- Tanase DM, Gosav EM, Costea CF, et al. The Intricate Relationship between Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM), Insulin Resistance (IR), and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD). J Diabetes Res. 2020 Jul 31;2020:3920196. doi: 10.1155/2020/3920196.
- Li X, Hu S, Cai Y, et al. Revving the engine: PKB/AKT as a key regulator of cellular glucose metabolism. Front Physiol. 2024 Jan 8;14:1320964. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1320964.
- Petersen MC, Vatner DF, Shulman GI. Regulation of hepatic glucose metabolism in health and disease. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2017 Oct;13(10):572-587. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2017.80.
- Fu Y, Wang Z, Qin H. Examining the Pathogenesis of MAFLD and the Medicinal Properties of Natural Products from a Metabolic Perspective. Metabolites. 2024 Apr 12;14(4):218. doi: 10.3390/metabo14040218.
- Scoditti E, Sabatini S, Carli F, et al. Hepatic glucose metabolism in the steatotic liver. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 May;21(5):319-334. doi: 10.1038/s41575-023-00888-8.
- Ahmed B, Sultana R, Greene MW. Adipose tissue and insulin resistance in obese. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 May;137:111315. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111315.
- Pielok A, Marycz K. Non-Coding RNAs as Potential Novel Biomarkers for Early Diagnosis of Hepatic Insulin Resistance. Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 11;21(11):4182. doi: 10.3390/ijms21114182.
- Tello-Flores VA, Beltrán-Anaya FO, Ramírez-Vargas MA, et al. Role of Long Non-Coding RNAs and the Molecular Mechanisms Involved in Insulin Resistance. Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 6;22(14):7256. doi: 10.3390/ijms22147256.
- Yang W, Lyu Y, Xiang R, et al. Long Noncoding RNAs in the Pathogenesis of Insulin Resistance. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 16;23(24):16054. doi: 10.3390/ijms232416054.
- Zhao XY, Xiong X, Liu T, et al. Long noncoding RNA licen–sing of obesity-linked hepatic lipogenesis and NAFLD pathogenesis. Nat Commun. 2018 Jul 30;9(1):2986. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-05383-2.
- Lin M, Mao ZJ. lncRNA-mRNA competing endogenous RNA network in IR-hepG2 cells ameliorated by APBBR decreasing ROS levels: a systematic analysis. PeerJ. 2020 Feb 24;8:e8604. doi: 10.7717/peerj.8604.
- Liao W, Xu N, Zhang H, et al. Persistent high glucose induced EPB41L4A-AS1 inhibits glucose uptake via GCN5 mediating crotonylation and acetylation of histones and non-histones. Clin Transl Med. 2022 Feb;12(2):e699. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.699.
- Xia Y, Zhang Y, Wang H. Upregulated lncRNA HCG18 in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Its Regulatory Effect on Insulin Resistance. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2021 Dec 3;14:4747-4756. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S333431.
- Li M, Guo Y, Wang XJ, et al. HOTAIR participates in hepatic insulin resistance via regulating SIRT1. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018 Nov;22(22):7883-7890. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201811_16414.
- Cao Q, Zhang X, Xie F, et al. Long-noncoding RNA HOXA transcript at the distal tip ameliorates the insulin resistance and hepatic gluconeogenesis in mice with gestational diabetes mellitus via the microRNA-423-5p/wingless-type MMTV integration site family member 7A axis. Bioengineered. 2022 May;13(5):13224-13237. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2076982.
- Chi Y, Gong Z, Xin H, et al. Long noncoding RNA lncARSR promotes nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma by promoting YAP1 and activating the IRS2/AKT pathway. J Transl Med. 2020 Mar 13;18(1):126. doi: 10.1186/s12967-020-02225-y.
- Zhang ZM, Liu ZH, Nie Q, et al. Metformin improves high-fat diet-induced insulin resistance in mice by downregulating the expression of long noncoding RNA NONMMUT031874.2. Exp Ther Med. 2022 May;23(5):332. doi: 10.3892/etm.2022.11261.
- Wang J, Yang W, Chen Z, et al. Long Noncoding RNA lncSHGL Recruits hnRNPA1 to Suppress Hepatic Gluconeogenesis and Lipogenesis. Diabetes. 2018 Apr;67(4):581-593. doi: 10.2337/db17-0799.
- Zou D, Liu L, Zeng Y, et al. LncRNA MEG3 up-regulates SIRT6 by ubiquitinating EZH2 and alleviates nonalcoholic fatty li–ver disease. Cell Death Discov. 2022 Mar 7;8(1):103. doi: 10.1038/s41420-022-00889-7.
- Tkach S, Pankiv V, Krushinska Z. Features of type 2 diabetes combined with metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease under conditions of chronic stress. International Journal of Endocrinology (Ukraine). 2024;20(1):18-24. doi: 10.22141/2224-0721.20.1.2024.1353
- Alrefai AA, Khader HF, et al. Evaluation of the expression levels of lncRNAs H19 and MEG3 in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Mol Biol Rep. 2023 Jul;50(7):6075-6085. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-08569-0.
- Li Z, Zheng D, Zhang T, et al. The roles of nuclear receptors in cholesterol metabolism and reverse cholesterol transport in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatol Commun. 2023 Dec 15;8(1):e0343. doi: 10.1097/HC9.0000000000000343.
- Wu HY, Cheng Y, Jin LY, et al. Paternal obesity impairs hepatic gluconeogenesis of offspring by altering Igf2/H19 DNA methy–lation. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2021 Jun 1;529:111264. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2021.111264.
- Chen L, Li C, Peng Z, et al. miR-197 Expression in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells from Hepatitis B Virus-Infected Patients. Gut Liver. 2013 May;7(3):335-42. doi: 10.5009/gnl.2013.7.3.335.
- Akkaya-Ulum YZ, Akbaba TH, Tavukcuoglu Z, et al. Fami–lial Mediterranean fever-related miR-197-3p targets IL1R1 gene and modulates inflammation in monocytes and synovial fibroblasts. Sci Rep. 2021 Jan 12;11(1):685. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-80097-4.
- Niknam N, Nikooei S, Ghasemi H, et al. Circulating Levels of HOTAIR- lncRNA Are Associated with Disease Progression and Cli–nical Parameters in Type 2 Diabetes Patients. Rep Biochem Mol Biol. 2023 Oct;12(3):448-457. doi: 10.61186/rbmb.12.3.448.
- Zhou S, Tang X, Chen HZ. Sirtuins and Insulin Resistance. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018 Dec 6;9:748. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2018.00748.
- Perisset S, Potilinski MC, Gallo JE. Role of Lnc-RNAs in the Pathogenesis and Development of Diabetic Retinopathy. Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 11;24(18):13947. doi: 10.3390/ijms241813947.
- Geng C, Xue Y, Yang JH et al. SIRT1 Mediates Sestrin1-Induced Improvement in Hepatic Insulin Resistance. Biomed Environ Sci. 2022 Jan 20;35(1):79-83. doi: 10.3967/bes2022.011.
- Zhou L, Wang L, Hu X, et al. PTEN in propofol-induced insulin resistance in mouse primary hepatocytes. Exp Ther Med. 2018 Dec;16(6):4831-4835. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.6815.
- Shaker OG, Abdelaleem OO, Mahmoud RH, et al. Diagnostic and prognostic role of serum miR-20b, miR-17-3p, HOTAIR, and MALAT1 in diabetic retinopathy. IUBMB Life. 2019 Mar;71(3):310-320. doi: 10.1002/iub.1970.
- Khokhar M, Roy D, Modi A, et al. Perspectives on the role of PTEN in diabetic nephropathy: an update. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 2020 Nov;57(7):470-483. doi: 10.1080/10408363.2020.1746735.
- Li YZ, Di Cristofano A, Woo M. Metabolic Role of PTEN in Insulin Signaling and Resistance. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2020 Aug 3;10(8):a036137. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a036137.
- Kaur P, Kotru S, Singh S, et al. Role of miRNAs in the pathogenesis of T2DM, insulin secretion, insulin resistance, and β cell dysfunction: the story so far. J Physiol Biochem. 2020 Nov;76(4):485-502. doi: 10.1007/s13105-020-00760-2.
- Gu L, Ding X, Wang Y, et al. Spexin alleviates insulin resistance and inhibits hepatic gluconeogenesis via the FoxO1/PGC-1α pathway in high-fat-diet-induced rats and insulin resistant cells. Int J Biol Sci. 2019 Nov 1;15(13):2815-2829. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.31781.
- Wang W, Zhang F, Yan X, et al. Wnt7a regulates high autopha–gic and inflammatory response of epidermis in high-glucose environment. Burns. 2020 Feb;46(1):121-127. doi: 10.1016/j.burns.2019.07.025.
- Zhang M, Chi X, Qu N, et al. Long noncoding RNA lncARSR promotes hepatic lipogenesis via Akt/SREBP-1c pathway and contributes to the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018 Apr 30;499(1):66-70. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.03.127.
- Jeong SH, Kim HB, Kim MC, et al. Hippo-mediated suppression of IRS2/AKT signaling prevents hepatic steatosis and liver cancer. J Clin Invest. 2018 Mar 1;128(3):1010-1025. doi: 10.1172/JCI95802.
- Honma M, Sawada S, Ueno Y, et al. Selective insulin resistance with differential expressions of IRS-1 and IRS-2 in human NAFLD livers. Int J Obes (Lond). 2018 Sep;42(9):1544-1555. doi: 10.1038/s41366-018-0062-9.
- Yuan P, Qi X, Song A, et al. LncRNA MAYA promotes iron overload and hepatocyte senescence through inhibition of YAP in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Aug;25(15):7354-7366. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16764.
- Biswas S, Thomas AA, Chen S, et al. Chakrabarti S. MALAT1: An Epigenetic Regulator of Inflammation in Diabetic Retinopathy. Sci Rep. 2018 Apr 25;8(1):6526. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-24907-w.
- Klimczak S, Śliwińska A. Epigenetic regulation of inflammation in insulin resistance. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Feb 15;154(Pt C):185-192. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2022.09.004.
- Naveed A, Fortini E, Li R, et al. Long non-coding RNAs and nuclear body formation and function. In: Khalil A, ed. Molecular Biology of Long Non-Coding RNAs. Cham, Switzerland: Springer; 2019. 65-84.
- Yang C, Zhang Y, Yang B. MIAT, a potent CVD-promo–ting lncRNA. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Dec 18;79(1):43. doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-04046-8.
- Yan C, Li J, Feng S, et al. Long noncoding RNA Gomafu upregulates Foxo1 expression to promote hepatic insulin resistance by sponging miR-139-5p. Cell Death Dis. 2018 Feb 19;9(3):289. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-0321-7.
- Ghafouri-Fard S, Azimi T, Taheri M. Myocardial Infarction Associated Transcript (MIAT): Review of its impact in the tumorige–nesis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 Jan;133:111040. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.111040.
- Dooley J, Garcia-Perez JE, Sreenivasan J, et al. The micro–RNA-29 Family Dictates the Balance Between Homeostatic and Pathological Glucose Handling in Diabetes and Obesity. Diabetes. 2016 Jan;65(1):53-61. doi: 10.2337/db15-0770.
- Macvanin MT, Gluvic Z, Bajic V, et al. Novel insights regar–ding the role of noncoding RNAs in diabetes. World J Diabetes. 2023 Jul 15;14(7):958-976. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i7.958.
- Kurtz CL, Peck BC, Fannin EE, et al. MicroRNA-29 fine-tunes the expression of key FOXA2-activated lipid metabolism genes and is dysregulated in animal models of insulin resistance and diabetes. Diabetes. 2014 Sep;63(9):3141-8. doi: 10.2337/db13-1015.
- Qu Y, Xiao H, Xiao W, et al. Upregulation of MIAT Regulates LOXL2 Expression by Competitively Binding MiR-29c in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;48(3):1075-1087. doi: 10.1159/000491974.
- Dongiovanni P, Meroni M, Baselli GA, et al. Insulin resistance promotes Lysyl Oxidase Like 2 induction and fibrosis accumulation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin Sci (Lond). 2017 Jun 7;131(12):1301-1315. doi: 10.1042/CS20170175.
- Ying W, Tseng A, Chang RC, et al. miR-150 regulates obesity-associated insulin resistance by controlling B cell functions. Sci Rep. 2016 Feb 1;6:20176. doi: 10.1038/srep20176.
- Calderari S, Diawara MR, Garaud A, et al. Biological roles of microRNAs in the control of insulin secretion and action. Phy–siol Genomics. 2017 Jan 1;49(1):1-10. doi: 10.1152/physiolgeno–mics.00079.2016.
- Torisu T, Sato N, Yoshiga D, et al. The dual function of hepatic SOCS3 in insulin resistance in vivo. Genes Cells. 2007 Feb;12(2):143-54. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2443.2007.01044.x.
- Ahvaz S, Amini M, Yari A, et al. Downregulation of long noncoding RNA B4GALT1-AS1 is associated with breast cancer development. Sci Rep. 2024 Feb 7;14(1):3114. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-51124-x.
- Elseweidy MM, Ali AE, Hassanin SM, et al. Empagliflozin ameliorates liver fibrosis in NASH rat model via targeting hepatic NF-κB/SOX9/OPN signaling and osteocalcin level. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024 May;397(5):3449-3459. doi: 10.1007/s00210-023-02826-6.
- Li J, Gong L, Liu S, et al. Adipose HuR protects against diet–-induced obesity and insulin resistance. Nat Commun. 2019 May 30;10(1):2375. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-10348-0.
- Cheng X, Shihabudeen Haider Ali MS, Moran M, et al. Long non-coding RNA Meg3 deficiency impairs glucose homeostasis and insulin signaling by inducing cellular senescence of hepatic endothelium in obesity. Redox Biol. 2021 Apr;40:101863. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2021.101863.
- Chen DL, Shen DY, Han CK, et al. LncRNA MEG3 aggravates palmitate-induced insulin resistance by regulating miR-185-5p/Egr2 axis in hepatic cells. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019 Jun;23(12):5456-5467. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201906_18215.
- Zhu X, Wu YB, Zhou J, et al. Upregulation of lncRNA MEG3 promotes hepatic insulin resistance via increasing FoxO1 expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016 Jan 8;469(2):319-25. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.11.048.
- Abaturov OE, Nikulina AO. Posttranslational modifications of histones associated with the development of metabolically associa–ted fatty liver disease. Part 1. General provisions. Gastroenterology. 2024;58(3):210-221. doi: 10.22141/2308-2097.58.3.2024.626 (in Ukrainian).
- Zhu X, Li H, Wu Y, et al. CREB-upregulated lncRNA MEG3 promotes hepatic gluconeogenesis by regulating miR-302a-3p-CRTC2 axis. J Cell Biochem. 2019 Mar;120(3):4192-4202. doi: 10.1002/jcb.27706.
- Abaturov A, Nikulina A, Nikulin D. Single Nucleotide Va–riants of the PNPLA3 Gene are Important Genetic Modifiers for the Progression of Metabolically Unhealthy Obesity in Children. Meta–bolism — Clinical and Experimental. 2023;142(Suppl):155450. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2023.155450.