Международный эндокринологический журнал Том 21, №5, 2025
Вернуться к номеру
Дослідження клінічного ефекту дапагліфлозину на метаболічні показники у хворих на цукровий діабет 2-го типу із різними фенотипами ожиріння
Авторы: Прибила О.В., Зінич О.В., Кушнарьова Н.М., Ковальчук А.В., Шишкань-Шишова К.О.
ДУ «Інститут ендокринології та обміну речовин імені В.П. Комісаренка НАМН України», м. Київ, Україна
Рубрики: Эндокринология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
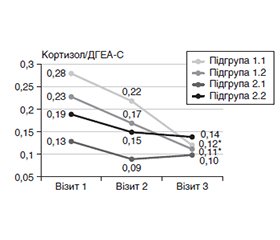
Актуальність. Актуальною проблемою сучасної ендокринології є вивчення молекулярних механізмів метаболічних розладів при цукровому діабеті 2-го типу (ЦД2). Сьогодні в терапії ЦД2 застосовуються препарати групи інгібіторів натрійзалежного котранспортера глюкози 2 (іНЗКТГ2), які сприяють зменшенню ступеня ожиріння, проявляють кардіовазопротекторні властивості. Мета: оцінити ефекти терапії дапагліфлозином у пацієнтів з ЦД2 на морфометаболічні показники пацієнтів залежно від фенотипу ожиріння. Матеріали та методи. Обстежено 165 хворих на ЦД2 (71 жінка та 94 чоловіки) віком 32–82 роки, рівень глікованого гемоглобіну (HbA1c) в яких становив ≥ 6,5 %. Пацієнтам призначали дапагліфлозин у дозі 10 мг/добу, спостереження тривало 12 місяців. Фенотип пацієнтів визначали за ступенем загального ожиріння (без ожиріння ІМТ < 30 кг/м2, з ожирінням ІМТ ≥ 30 кг/м2). Методом біоелектричного імпедансу визначали показники композиції тіла: загальний вміст жиру в організмі (%), рівень вісцерального жиру (ВЖ) від 1 до 59 од. Визначали рівень HbA1c (%), інсуліну, відношення дегідроепіандростерону сульфат (ДГЕА-С)/кортизол; розраховували ступінь інсулінорезистентності (HOMA-IR), індекс вісцерального ожиріння (ІВО). Результати. Виділено групи пацієнтів: перша — без ожиріння (ІМТ < 30 кг/м2; n = 72); друга — з ожирінням (ІМТ ≥ 30 кг/м2; n = 93). У межах кожної групи виділили підгрупи з нормальним (< 12 од.) або підвищеним рівнем ВЖ (≥ 12 од.). Через 12 місяців терапії дапагліфлозином у всіх групах пацієнтів зафіксовано вірогідне зниження рівня глікемії, тенденцію або вірогідне зниження рівня HbA1c, зменшення відсоткового вмісту жиру та зниження ІВО, що відповідає поліпшенню функціонального стану жирової тканини. У хворих із загальним та/або вісцеральним ожирінням виявлено зниження індексу маси тіла, відсотка загального та вісцерального жиру на тлі поліпшення характеристик ліпідного та вуглеводного обмінів. У підгрупі 2.2 вірогідно знизився рівень інсулінемії, при цьому в усіх підгрупах пацієнтів (крім 1.1) знизився показник HOMA-IR. Між групами пацієнтів із фенотипом без ожиріння та з ожирінням незалежно від рівня ВЖ виявлено суттєву різницю у клінічному ефекті довготривалої терапії іНЗКТГ2 щодо рівнів кортизолу і ДГЕА-С. Значний або середній клінічний ефект щодо зміни відношення кортизол/ДГЕА-С виявлено у підгрупах 1.1 (0,86) та 1.2 (0,95), що засвідчує ефективність терапії дапагліфлозином. Висновки. Отримані результати підтверджують доцільність застосування терапії іНЗКТГ2 та її ефективність щодо оптимізації морфометаболічних характеристик у пацієнтів з ЦД2 з різними фенотипами, особливо у пацієнтів з фенотипом без ожиріння.
Background. The study of molecular mechanisms of metabolic disorders in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is an actual problem of modern endocrinology. Today, sodium-dependent glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors (SGLT2i) are used in the therapy of T2DM, which contribute to a decrease in the degree of obesity and exhibit cardiovasoprotective properties. The aim of the study was to evaluate the effects of dapagliflozin therapy in T2DM patients on the morpho-metabolic parameters depending on the obesity phenotype. Materials and methods. One hundred and sixty-five patients with T2DM (71 women and 94 men) aged 32–82 years were examined, their glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) level was ≥ 6.5 %. Patients were prescribed dapagliflozin (10 mg/day) and were monitored for 12 months. The phenotype of patients determined by the degree of general obesity (non-obese: body mass index < 30 kg/m2, obese: body mass index ≥ 30 kg/m2). Body composition indices were determined by the bioelectrical impedance method: total body fat content (%), visceral fat level (VF, from 1 to 59 units). HbA1c (%), insulin, dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEA-S)/cortisol ratio were determined; the degree of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR), visceral obesity index (VAI) were calculated. Results. The following groups of patients created: first — non-obese (n = 72); second — obese (n = 93). Within each group, subgroups with normal (< 12 units) or increased VF level (≥ 12 units) were identified. After 12 months of dapagliflozin therapy, all groups of patients reported a significant decrease in glycemia; a trend or significant decrease in HbA1c; a decrease in the percentage of fat content and a decrease in VAI, which corresponds to an improvement in the functional state of adipose tissue. In patients with general and/or visceral obesity, a decrease in body mass index, percentage of total and visceral fat was detected together with an improvement in the characteristics of lipid and carbohydrate metabolism. In subgroup 2.2, the level of insulinemia significantly decreased, while in all subgroups of patients (except 1.1), the HOMA-IR index decreased. Between the groups of patients with a non-obese and obese phenotype, a significant difference in the clinical effect of long-term SGLT2i therapy on cortisol and DHEA-s levels were found, regardless of the level of VF. A significant or moderate clinical effect was found on the change in the DHEA-s/cortisol ratio in subgroups 1.1 (0.86) and 1.2 (0.95), which indicates the effectiveness of dapagliflozin therapy. Conclusions. The results obtained confirm the feasibility of using SGLT2i therapy and its effectiveness in optimizing morpho-metabolic characteristics in type 2 diabetes patients with different phenotypes, especially in those with a non-obese phenotype.
цукровий діабет 2-го типу; ожиріння; фенотип; композиція тіла; інсулін; кортизол; дегідроепіандростерону сульфат; фармакотерапія; дапагліфлозин
type 2 diabetes mellitus; obesity; phenotype; body composition; insulin; cortisol; dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate; pharmacotherapy; dapagliflozin
Для ознакомления с полным содержанием статьи необходимо оформить подписку на журнал.
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 9. Pharmacologic Approaches to Glycemic Treatment: Standards of Care in Diabetes-2025. Diabetes Care. 2025 Jan 1;48(1 Suppl 1):S181-S206. doi: 10.2337/dc25-S009. PMID: 39651989; PMCID: PMC11635045.
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. Summary of Revisions: Standards of Care in Diabetes-2025. Diabetes Care. 2025 Jan 1;48(1 Suppl 1):S6-S13. doi: 10.2337/dc25-SREV. PMID: 39651984; PMCID: PMC11635056.
- Cuttone A, Cannavò V, Abdullah RMS, et al. Expanding the Use of SGLT2 Inhibitors in T2D Patients Across Clinical Settings. Cells. 2025 May 2;14(9):668. doi: 10.3390/cells14090668. PMID: 40358192; PMCID: PMC12071329.
- Morieri ML, Raz I, Consoli A, et al; DARWIN-FUP network l. Short-term effectiveness of dapagliflozin versus DPP-4 inhibitors in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes: a multicentre retrospective study. J Endocrinol Invest. 2023 Jul;46(7):1429-1439. doi: 10.1007/s40618-022-02002-2.
- Palmer SC, Tendal B, Mustafa RA, et al. Sodium-glucose cotransporter protein-2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists for type 2 diabetes: systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. BMJ. 2021 Jan 13;372:m4573.
- Chung S, Kim GH. Urate Transporters in the Kidney: What Clinicians Need to Know. Electrolyte Blood Press. 2021 Jun;19(1):1-9.
- Abdul-Ghani MA, Norton L, DeFronzo RA. Renal sodium-glucose cotransporter inhibition in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2015 Dec 1;309(11):F889-900.
- Serhiyenkо V, Chemerys O, Pankiv V, Serhiyenko A. Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder, Metabolic Syndrome, Diabetic Distress, and Vitamin B1/Benfotiamine. International neurological journal. 2025;21(1):96-107. doi: 10.22141/2224-0713.21.1.2025.1157.
- Cherney D, Dekkers C, Barbour S, et al.; DIAMOND investigators. Effects of the SGLT2 inhibitor dapagliflozin on proteinuria in non-diabetic patients with chronic kidney disease (DIAMOND): a randomised, double-blind, crossover trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020 Jul;8(7):582-593. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30162-5.
- Ni L, Yuan C, Chen G, Zhang C, Wu X. SGLT2i: beyond the glucose-lowering effect. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2020 Jun 26;19(1):98. doi: 10.1186/s12933-020-01071-y.
- Patel DK, Strong J. The Pleiotropic Effects of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors: Beyond the Glycemic Benefit. Diabetes Ther. 2019 Oct;10(5):1771-1792. doi: 10.1007/s13300-019-00686-z.
- Vergara A, Jacobs-Cachá C, Soler MJ. Sodium-glucose cotransporter inhibitors: beyond glycaemic control. Clin Kidney J. 2019 Mar 6;12(3):322-325. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfz019.
- Pratama KG, Tandarto K, Hengky A. Weight loss effect of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors in patients with obesity without diabetes: a systematic review. Acta Endocrinol (Buchar). 2022 Apr–Jun;18(2):216-224. doi: 10.4183/aeb.2022.216.
- Usman M, Khan M, Siddiqui H, et al. SGLT2 Inhibitors in Patients with Overweight or Obesity: Systematic Review and Meta-Analyses. Abstract 14060. Circulation. 2022;146:A14060.
- Consensus Development Conference on Insulin Resistance. 5-6 November 1997. American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care. 1998 Feb;21(2):310-4. doi: 10.2337/diacare.21.2.310.
- Amato MC, Giordano C, Galia M, Criscimanna A. Visceral Adiposity Index. A reliable indicator of visceral fat function associa–ted with cardiometabolic risk. Diab. Care. 2010;33(4):920-922. doi: 10.2337/dc09-1825.
- Wildman RP, Muntner P, Reynolds K, et al. The obese without cardiometabolic risk factor clustering and the normal weight with cardiometabolic risk factor clustering: prevalence and correlates of 2 phenotypes among the US population (NHANES 1999-2004). Arch Intern Med. 2008 Aug 11;168(15):1617-24.
- Damman K, Beusekamp JC, Boorsma EM, et al. Rando–mized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre pilot study on the effects of empagliflozin on clinical outcomes in patients with acute decompensated heart failure (EMPA-RESPONSE-AHF). Eur J Heart Fail. 2020;22:713-722.
- Latva-Rasku A, Honka MJ, Kullberg J, et al. The SGLT2 inhi–bitor dapagliflozin reduces liver fat but does not affect tissue insulin sensitivity: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study with 8-week treatment in type 2 diabetes patients. Diabetes Care. 2019;42:931-937.
- Packer M, Anker SD, Butler J, et al. Cardiovascular and renal outcomes with empagliflozin in heart failure. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:1413-1424.
- Yaribeygi H, Sathyapalan T, Maleki M, Jamialahmadi T, Sahebkar A. Molecular mechanisms by which SGLT2 inhibitors can induce insulin sensitivity in diabetic milieu: A mechanistic review. Life Sci. 2020 Jan 1;240:117090.